用React或js来循环给盒子添加点击事件
要求大盒子宽800高900,大盒子中有每行80个小盒子共20列,,小盒子每个宽8.5高44.5,visibility是visible,自带边框所有盒子添加点击事件,点击任意小盒子后,从当前盒子向后数16个小盒子合并成一个中盒子背景色变成绿色,这个中盒子宽度变成121共占用16个小盒子位置,其余15个小盒子visibility变成hidden隐藏掉,再次点击这个的绿色中盒子还原为刚才的16个小盒子
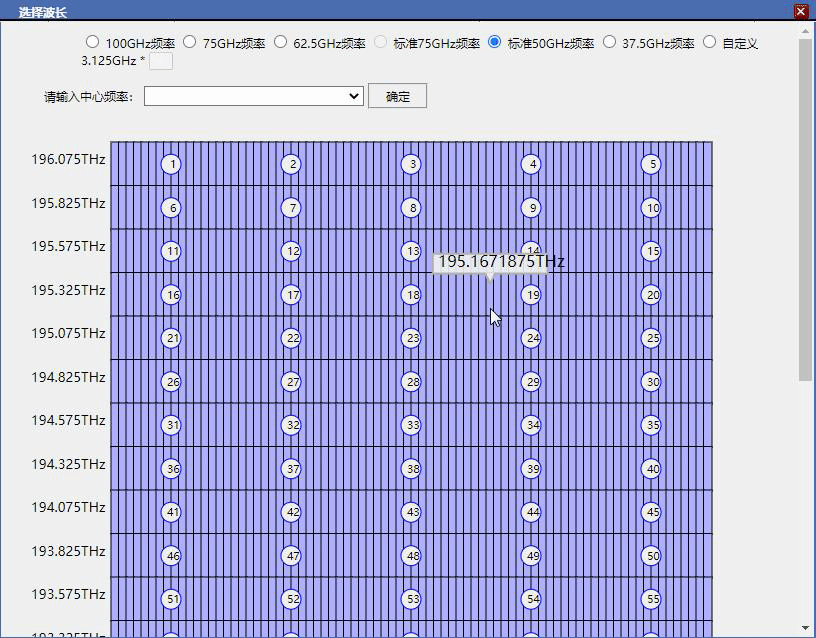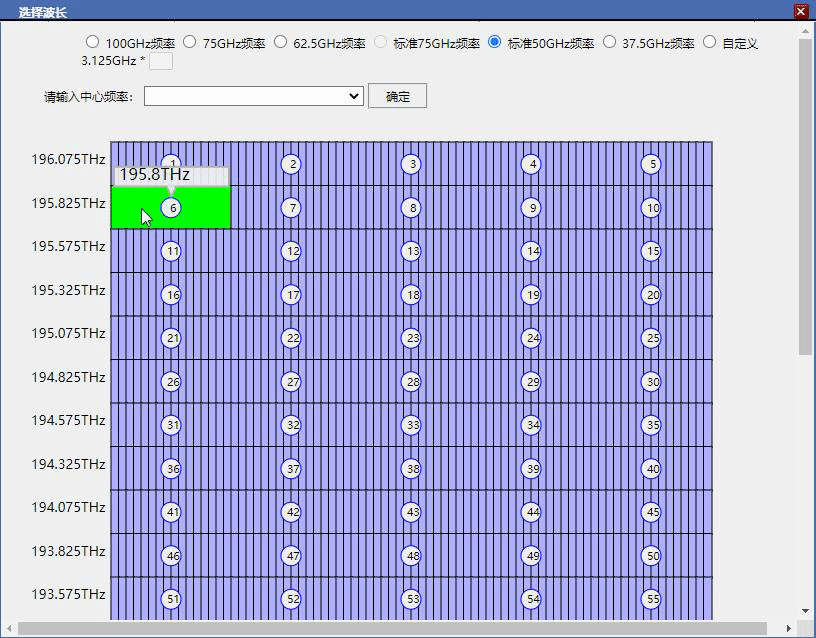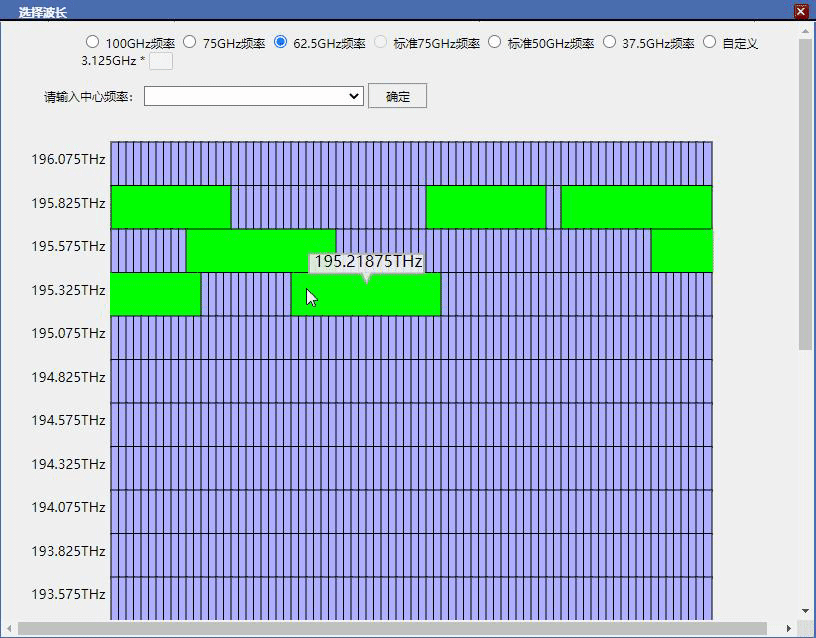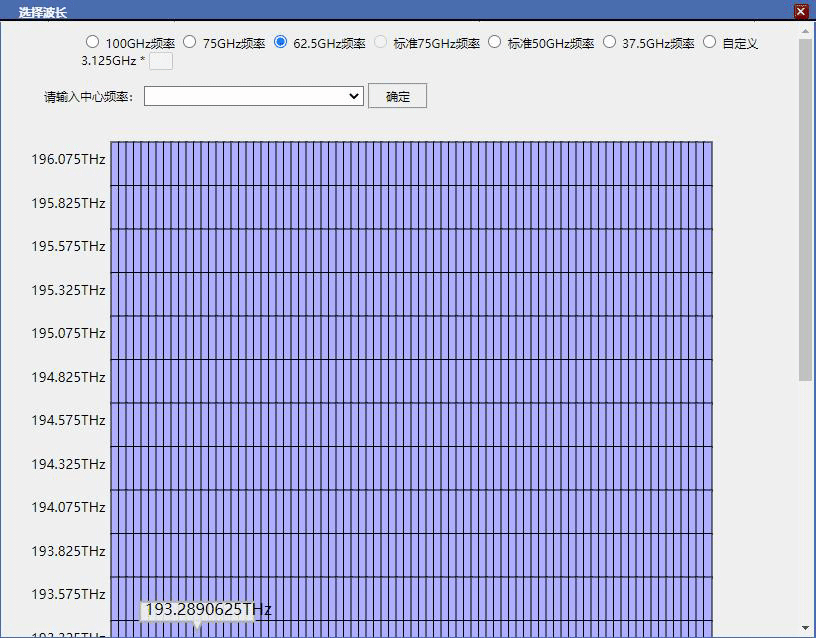


看下是不是这样就符合你的要求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
#container {
padding: 20px;
}
.main {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 800px;
height: 900px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.box {
width: 8px;
height: 44.5px;
}
.box-bg1 {
border: 1px solid #aaa;
}
.box-bg2 {
background-color: green;
border: 1px solid green;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div class="main">
<template v-for="l in list">
<template v-if="l.type == 1">
<div class="box box-bg1" @click="clc(l.no)">
<span></span>
</div>
</template>
<template v-if="l.type == 2">
<div class="box box-bg2" @click="unclc(l.start)">
</div>
</template>
</template>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="./vue-2.6.14.min.js"></script>
<script>
let vue = new Vue({
el: "#container",
data() {
return {
list: []
}
},
created() {
this.init();
},
methods: {
init() {
for (let i = 0; i < 1600; i++) {
temp = []
temp['no'] = i
temp['type'] = 1
temp['start'] = i
this.list.push(temp)
}
},
clc(number) {
for (let i = 0; i < 1600; i++) {
if ((this.list[i]['start'] <= number + 16 && this.list[i]['start'] > number)
&& this.list[i]['type'] == 2) {
alert("不允许")
return
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < 1600; i++) {
if (i >= number && i < number + 16) {
this.list[i]['type'] = 2
this.list[i]['start'] = number
}
}
this.$forceUpdate();
},
unclc(number) {
for (let i = 0; i < 1600; i++) {
if (this.list[i]['start'] == number) {
this.list[i]['type'] = 1
this.list[i]['start'] = i
}
}
this.$forceUpdate();
}
},
});
</script>
</html>
参考代码设计思路:使用了React的useState钩子来维护盒子状态,包括盒子数组boxes。在渲染盒子时,使用map函数遍历每一行的小盒子,将它们渲染成可见的div元素。每个小盒子的样式包括边框、高度、宽度和可见性。同时,每个小盒子也自带点击事件,点击后调用handleClick函数来处理合并和中盒子的还原。在handleClick函数中,首先获取当前小盒子的位置以及左右相邻的两个中盒子(如果存在的话),然后将左右两个中盒子合并成一个中盒子,并将中间的16个小盒子隐藏掉。最后,更新boxes状态以更新页面上的盒子。
import React, { useState } from "react";
function Boxes() {
const [boxes, setBoxes] = useState([[]]);
const handleClick = (index) => {
const { boxes: [left, ...middle], [left + middle.length - 1]: right } = boxes;
const mergedBoxes = left.concat(middle.reduce((acc, box, i) => {
if (i % 2 === 0) return [...acc, right[0]];
else return [...acc, box];
}, []), right);
setBoxes([...boxes[0], ...mergedBoxes]);
};
return (
<div style={{ height: "900px", width: "800px" }}>
{boxes.map((row, rowIndex) => (
<div
style={{
display: "flex",
flexDirection: "row",
height: "44.5px",
margin: "1px",
width: "8.5px",
}}
>
{row.map((box, boxIndex) => (
<div
key={`box-${rowIndex}-${boxIndex}`}
style={{
border: "1px solid black",
cursor: "pointer",
height: "44.5px",
width: "8.5px",
visibility: "visible",
}}
onClick={() => handleClick(boxIndex)}
/>
))}
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}
你这个问题逻辑有点奇怪啊 , 当我点击的时候 , 当前点击的小盒子向后数16个 合并成一个中盒子 , 如果 我点击的这个小盒子 向后数 不到16个小盒子 ,比如只有5个 怎么办呢 ? 而且一楼的代码有问题 你运行下看看就知道了
源码如下,在React中创建小盒子的组件:
function SmallBox(props) {
return (
<div className="small-box" style={{ width: '8.5px', height: '44.5px' }} onClick={props.onClick}></div>
);
}
接着,创建大盒子组件,使用循环将小盒子组件渲染出来:
class BigBox extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
boxes: new Array(1600).fill('visible')
}
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick(i) {
const boxes = this.state.boxes.slice();
const index = i % 80;
const start = index;
const end = index + 16;
for (let j = start; j < end; j++) {
boxes[i - index + j] = 'hidden';
}
const middleBoxIndex = i + 15;
boxes[middleBoxIndex] = 'green';
this.setState({ boxes: boxes });
document.getElementById(`box-${middleBoxIndex}`).addEventListener('click', () => {
boxes[middleBoxIndex] = 'visible';
for (let j = start; j < end; j++) {
boxes[i - index + j] = 'visible';
}
this.setState({ boxes: boxes });
});
}
renderSmallBox(i) {
return (
<SmallBox
onClick={() => this.handleClick(i)}
/>
);
}
render() {
const rows = [];
for (let r = 0; r < 20; r++) {
const boxes = [];
for (let c = 0; c < 80; c++) {
const i = r * 80 + c;
boxes.push(
<div
className="box"
id={`box-${i}`}
key={i}
style={{ ...boxStyle, visibility: this.state.boxes[i] }}
>
{this.renderSmallBox(i)}
</div>
);
}
rows.push(<div className="row" key={r} style={rowStyle}>{boxes}</div>);
}
return (
<div className="big-box" style={bigBoxStyle}>
{rows}
</div>
);
}
}
const bigBoxStyle = {
width: '800px',
height: '900px',
display: 'flex',
flexWrap: 'wrap',
border: '1px solid black'
}
const rowStyle = {
display: 'flex'
}
const boxStyle = {
boxSizing: 'border-box',
border: '1px solid black',
width: '10px',
height: '50px',
display: 'flex',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center'
}
在组件的构造函数中,初始化大小为1600(20 * 80)的数组,其中每个元素值都是'visible',表示小盒子的可见性。在渲染小盒子组件时,将盒子的可见性根据数组的值设置。每次点击小盒子,都会修改状态中的数组,然后重新渲染大盒子,从而让发生变化的小盒子重新绘制。同时,还要在点击时给对应的盒子添加事件监听,以便对中盒子的操作。当中盒子被点击时,同样需要修改数组,然后重新渲染大盒子,从而让原先隐藏的小盒子再次显示出来。
可以参考下
function Tetris(pos, type, dir) {
this.turn = function () {
var flag = 1;
switch (this.types_name[this.type]) {
case "SQUARE":
return true;
case "LINE":
flag = this.tetris[1].y-this.centor.y?1:-1;
break;
case "SWAGERLY":
case "RSWAGERLY":
flag = this.tetris[2].y-this.centor.y?1:-1;
break;
case "LBLOCK":
case "RLBLOCK":
case "TBLOCK":
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (var i = 1; i < this.tetris.length; i++) {
var diff = {"x":this.tetris[i].x-this.centor.x, "y":this.tetris[i].y-this.centor.y};
this.tetris[i].x = this.centor.x + flag*diff.y;
this.tetris[i].y = this.centor.y - flag*diff.x;
}
return true;
}
this.turnback = function () {
if (this.types_name[this.type] == "SQUARE")
return true;
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++)
this.turn();
}
this.leftSlice = function () {
this.pos.x--;
}
this.rightSlice = function () {
this.pos.x++;
}
this.drop = function () {
this.pos.y++;
}
this.rise = function() {
this.pos.y--;
}
this.body = function () {
var body = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.tetris.length; i++) {
if (this.tetris[i].y+this.pos.y >= 0)
body.push({"x":this.tetris[i].x+this.pos.x, "y":this.tetris[i].y+this.pos.y});
}
return body;
}
this.__init__ = function () {
var arr = this.types_body[this.type];
this.tetris = [];
this.centor = {"x":arr[0]%4-this.origin%4, "y":parseInt(arr[0]/4)-parseInt(this.origin/4)};
for (var i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
this.tetris[i] = {"x":arr[i]%4-this.origin%4, "y":parseInt(arr[i]/4)-parseInt(this.origin/4)};
}
}
this.types_name = ["LBLOCK", "RLBLOCK", "TBLOCK", "SWAGERLY", "RSWAGERLY", "LINE", "SQUARE"];
this.types_body = [
[5, 1, 2, 9], //LLL
[6, 1, 2,10],
[5, 1, 4, 6], //T
[5, 2, 6, 9], //555
[5, 1, 6,10],
[5, 4, 6, 7], //I
[5, 0, 1, 4],
]
this.origin = 5;
this.type = type%7;
this.pos = pos;
this.__init__();
for (i = 0; i < dir%4; i++)
this.turn();
return this;
}
在 React 中,可以使用嵌套的 div 元素来表示大盒子和小盒子。对于大盒子,可以使用一个 div 元素,并设置宽度和高度;对于小盒子,可以使用一个 div 元素,并设置宽度、高度、visibility 和边框。在小盒子上添加 onClick 属性来绑定点击事件,当用户点击小盒子时,React 会自动调用 handleClick 函数。在 handleClick 函数中,可以使用状态来记录当前选中的盒子,然后根据选中的盒子计算出中盒子的位置和大小,并更新状态,从而实现盒子的合并和隐藏。下面是一个示例代码:
jsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function BigBox() {
const [selectedBox, setSelectedBox] = useState(null);
function handleClick(index) {
if (selectedBox === index) {
setSelectedBox(null);
} else {
setSelectedBox(index);
}
}
function renderBox(index) {
const isSelected = selectedBox === index;
const isHidden = selectedBox !== null && (index < selectedBox || index >= selectedBox + 16);
const backgroundColor = isSelected ? 'green' : 'white';
const width = isSelected ? 121 : 8.5;
const height = isSelected ? 44.5 : 44.5;
const visibility = isHidden ? 'hidden' : 'visible';
return (
<div
key={index}
onClick={() => handleClick(index)}
style={{
width: `${width}px`,
height: `${height}px`,
backgroundColor,
border: '1px solid black',
visibility,
display: 'inline-block',
}}
/>
);
}
const boxes = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 80; j++) {
const index = i * 80 + j;
boxes.push(renderBox(index));
}
boxes.push(<br key={`br-${i}`} />);
}
return (
<div style={{ width: '800px', height: '900px' }}>
{boxes}
</div>
);
}
export default BigBox;
在上面的代码中,我们使用 useState 钩子来定义 selectedBox 状态,表示当前选中的盒子的索引。在 handleClick 函数中,我们根据 selectedBox 的值来判断当前点击的盒子是选中的还是取消选中的,然后更新 selectedBox 状态。在 renderBox 函数中,我们根据 selectedBox 和当前盒子的索引来计算盒子的样式,包括背景色、宽度、高度、visibility 等。最后,我们使用两个循环来生成所有的小盒子,并将它们放在一个大盒子中,以实现页面的渲染。
你要的是这个效果?

在React项目中,可以把上面的代码拆分成三部分,分别为HTML部分、CSS部分和JavaScript部分。然后可以将这些代码放到对应的React组件中。
HTML部分可以拆分成JSX,例如:
<div className="container">
{[...Array(1600)].map((_, i) => (
<div className="box" key={i}></div>
))}
</div>
CSS部分可以放在对应的CSS文件中,例如:
.container {
width: 800px;
height: 900px;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.box {
width: 8.5px;
height: 44.5px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin: -1px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: width 0.3s, background-color 0.3s;
display: block;
}
.box.hidden {
display: none;
}
.box.middle {
background-color: #8bc34a;
width: 136px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
transition: width 0.3s, background-color 0.3s;
}
JavaScript部分可以放在对应的React组件的JSX标签内的
React代码点击盒子
import React, { useState } from "react";
function Box() {
const [boxes, setBoxes] = useState(["box1", "box2", "box3"]);
const handleClick = (index) => {
console.log(`Clicked on ${boxes[index]}`);
};
return (
<div>
{boxes.map((box, index) => (
<div key={index} onClick={() => handleClick(index)}>
{box}
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}
export default Box;