7-7 雪花ID求解(含个人理解)
雪花ID(Snowflake ID)
本人大一新生,遇到下题无法完全正确理解,提供个人想法希望各位帮忙
具体题目如下


以及题目提供的样例
个人思路如下:
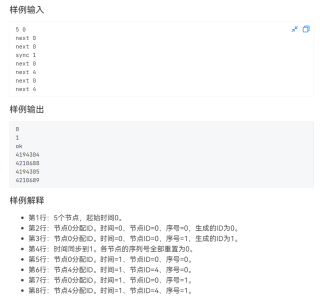
首先是题目所说的雪花ID具体形式大概为下(个人理解,有错误望指正)
而题目中提到>>首行是节点数量N(范围[0, 1024))
其中 1024 = 2 的10次方
说明 13 到 22号位置应该是 生成ID的序列号的节点
其次 通过 <<最低12-bit是节点生成ID的序列号。从0开始。于是每个节点每毫秒允许生成4096个ID。>>
可以知道 4096 = 2 的12次方
也就是说0 到 12 位是生成ID的序列号的节点
那么综上可以知道
但是,当时间为1的时候 节点0为 4194304
当时间为0的时候 节点0为 0
这俩者id差别只有时间位置不同
而 4194304 = 2 的 22 次方
再根据 节点4 = 2^22 + 2^14 + 0 = 4210688
那么最末12位应该是 0为下标 到 11
12 位作为 节点位置开始
这样 时间位置应该从 22 号开始
又因为 当时间为1的时候节点0和节点4相差为 2 的 14 次方
而4转换成2进制为100
0 为 000
正好 1在14位
因此 id 应该 等于 时间位置数+节点位置数+序号
以下是我个人代码
#include运行结果如下:
当然最后提交答案是错误的,这里请问有没有人能帮我解决这个问题,当然也可能是我题目理解有问题hh
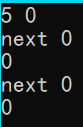
我不是很明白你的代码,p这个数组恒等于0,我不明白它有什么用。而且我复制你的代码,执行结果和你的不一样(如下图),将36行到40行的条件语句删掉,并改为“id+=p[N]++;”后就和样例一样了。
我的理解和你的一样。不过这道题应该用位运算(&、|),用乘方和乘除效率低。
我的代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void resettime(long long int *node, long long int time) { //将节点时间戳设为指定值,序列号设为0
*node&=0x3ff000;//指定节点保留13~22位(节点编号),其余位设置为0
*node|=time<<22;//将时间左移22位放到指定节点的时间戳
}
int main() {
char str[20];
int N, i;
long long int T;
scanf("%d%lld", &N, &T);
long long int a[N];
//初始化节点,将节点编号左移12位,赋值,再将初始时间左移22位
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
a[i]=i<<12;
a[i]|=T<<22;
}
while (scanf("%s", str) == 1) {
if (!strcmp(str, "sync")) {
scanf("%lld",&T);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
resettime(a+i,T);
}
printf("ok\n");
} else if(!strcmp(str,"next")){
scanf("%d",&i);
printf("%lld\n",a[i]++);
}
}
return 0;
}
执行结果:
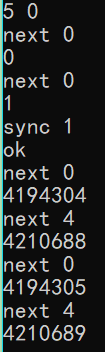
先根据题目要求写的:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdint>
#include <vector>
// 定义雪花 ID 的结构
struct SnowflakeID {
// 使用 int64_t 类型表示雪花 ID
int64_t id;
// 构造函数,用于初始化
SnowflakeID(int64_t id) : id(id) {}
};
// Snowflake ID 生成器类
class Snowflake {
public:// 构造函数,用于初始化
Snowflake(int node_id, int64_t epoch) : node_id_(node_id), epoch_(epoch), sequence_(0) {}
// 返回下一个 Snowflake ID
SnowflakeID next() {
// 获取当前时间
int64_t now = get_current_time();// 获取生成下一个 Snowflake ID 所需的时间
int64_t next_timestamp = now;
if (now <= last_timestamp_) {
sequence_ = (sequence_ + 1) % kMaxSequence;
if (sequence_ == 0) {
next_timestamp = get_next_timestamp(last_timestamp_);
}
} else {
sequence_ = 0;
}
last_timestamp_ = next_timestamp;
// 根据时间、节点 ID 和序列号生成雪花 ID
int64_t id = (next_timestamp - epoch_) << kTimestampLeftShift;
id |= node_id_ << kNodeIdShift;
id |= sequence_;
return SnowflakeID(id);}
// 同步时间
void sync(int64_t timestamp) {
epoch_ = timestamp;
sequence_ = 0;
}
private:
// 返回下一个有效时间戳
int64_t get_next_timestamp(int64_t last_timestamp) {
int64_t timestamp = get_current_time();
while (timestamp <= last_timestamp) {
timestamp = get_current_time();
}
return timestamp;
}
// 返回当前时间戳
int64_t get_current_time() {
// 使用 C++11 的 std::chrono 来获取当前时间
return std::chrono::duration_caststd::chrono::milliseconds(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count();
}
// 节点 ID
int node_id_;
// 起始时间
int64_t epoch_;
// 上一次生成 Snowflake ID 的时间
int64_t last_timestamp_;
// 序列号
int sequence_;
// 常量
// 时间戳左移位数
const int kTimestampLeftShift = 22;
// 节点 ID 左移位数
const int kNodeIdShift = 12;// 序列号最大值
const int kMaxSequence = (1 << 12) - 1;
};
// 生成雪花 ID 的生成器
std::vector<Snowflake> snowflakes;
int main() {
// 读入节点数量和起始时间
int n;
int64_t t;
std::cin >> n >> t;
// 初始化雪花 ID 生成器
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
snowflakes.emplace_back(i, t);
}// 读入指令
while (true) {
std::string command;
std::cin >> command;
if (command == "sync") {
// 同步时间
int64_t t;
std::cin >> t;
for (auto& s : snowflakes) {
s.sync(t);
}
std::cout << "ok" << std::endl;
} else if (command == "next") {
// 生成下一个 Snowflake ID
int m;
std::cin >> m;
std::cout << snowflakes[m].next().id << std::endl;
} else {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}