python GUI的窗口启动滞后
这个代码想用监听到的剪贴板数据,输入到输入框中
现在运行起来,必须复制一个数据,才能启动窗口,怎么能让窗口在运行时就启动
import pyperclip
import time
import os
import tkinter as tk
# 创建一个窗口对象
window = tk.Tk()
# 设置一下窗口标题
window.title("My Window")
# 设置窗口的大小
window.geometry("400x"
"400")
# 设置一个输入框对象
e = tk.Entry(window)
# 安置在窗口;pack主要帮你放置在上方下方左方右方这个几个位置
e.pack()
# 定义inert_point函数,可以从箭头指向的位置进行插入
class Shuju():
def Dayin(self):
while True:
# jianting().main()
t = jianting().main()
return (t)
def clipboard_get():
"""获取剪贴板数据"""
data = pyperclip.paste()
return data
class jianting():
def main(self):
"""后台脚本:每隔0.2秒,读取剪切板文本,检查有无指定字符或字符串,如果有则执行替换"""
# recent_txt 存放最近一次剪切板文本,初始化值只多执行一次paste函数读取和替换
recent_txt = clipboard_get()
while True:
# txt 存放当前剪切板文本
txt = clipboard_get()
# 剪切板内容和上一次对比如有变动,再进行内容判断,判断后如果发现有指定字符在其中的话,再执行替换
if txt != recent_txt:
# print(f'txt:{txt}')
recent_txt = txt # 没查到要替换的子串,返回None
return recent_txt
# 检测间隔(延迟0.2秒)
time.sleep(0.2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
shuju = Shuju()
t = shuju.Dayin()
global path
path = t # 将Shuju类中获取的数据赋值给path变量
e.insert("end", path)
# 刷新显示
window.mainloop()
e.pack之后马上e.insert一个空字符或者空格是不是就可以了
不知道你这个问题是否已经解决, 如果还没有解决的话:- 你可以参考下这个问题的回答, 看看是否对你有帮助, 链接: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7418406
- 我还给你找了一篇非常好的博客,你可以看看是否有帮助,链接:Python:GUI 中如何设置分割线、设计一个计时器
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: 保证你几分钟都能学会的python界面GUI可视化教程,逼格有手就能玩可视化中的 正确登录执行登录就执行功能 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或者直接跳转源博客中阅读:
为了便于有手就会,我们采用比较暴力简单的手段学习。如果我们要在这个py文件,可以执行另一个py文件怎么办?来个简单的例子:
比如说我这个文件为2.py,我想在这个文件里执行1.py,就如下代码即可:import os str = ('python 1.py') p = os.system(str) if p == 0: print('可执行') else: print('不可执行')那么我们同样道理,正确登录才能执行我们的的某个功能代码,我们就把上面那段代码加到原来的登录代码就能正确执行4.py:
# coding=gbk """ 作者:川川 公众号:玩转大数据 @时间 : 2022/2/10 12:33 群:428335755 输入正确账号和密码方可执行函数 """ from gooey import Gooey, GooeyParser import os @Gooey( richtext_controls=True, # 打开终端对颜色支持 program_name="疲劳驾驶检测", # 程序名称 encoding="utf-8", # 设置编码格式,打包的时候遇到问题 progress_regex=r"^progress: (\d+)%$" # 正则,用于模式化运行时进度信息 ) def start(): parser = GooeyParser(description="————川川菜鸟制作") parser.add_argument('username', widget="TextField") parser.add_argument('password', widget="TextField") args = parser.parse_args() return args if __name__ == '__main__': args = start() user = args.username password = args.password if user == '川川' and password == '123456': print('正确,可以开始使用') str = ('python 2.py') p = os.system(str) if p == 0: print('可执行') else: print('不可执行') # 检测是哪里不对 if user != '川川': print('用户名错误') if password != '123456': print('密码错误') else: print('账号或者密码不正确,请确保为本人在使用,请重新输入账号密码')假设4.py为任意一个正确的代码如下:
#HappyBirthday import turtle import time def move(angle,length): turtle.penup() turtle.seth(angle) turtle.fd(length) #prepare turtle.setup(1000,400,100,100) turtle.penup() turtle.fd(-350) turtle.seth(90) turtle.fd(50) turtle.pendown() turtle.pensize(10) turtle.pencolor("green") turtle.seth(0) turtle.hideturtle() turtle.speed(5) #呀 turtle.fd(100) #生 turtle.pencolor("green") turtle.circle(50,90) turtle.circle(50,-30) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(100) turtle.fd(-50) turtle.left(90) turtle.fd(30) turtle.fd(-60) turtle.left(90) turtle.fd(50) turtle.fd(-100) turtle.fd(50) turtle.left(90) turtle.fd(50) turtle.right(90) turtle.fd(60) turtle.fd(-120) #日 turtle.penup() turtle.fd(-30) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(90) turtle.fd(100) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(70) turtle.seth(-90) turtle.fd(50) turtle.seth(180) turtle.fd(70) turtle.seth(-90) turtle.fd(50) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(70) turtle.seth(90) turtle.fd(50) #移动 move(0,30) #快 turtle.pensize(8) turtle.circle(30,15) turtle.pendown() turtle.circle(30,60) turtle.penup() turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(13) turtle.seth(90) turtle.pendown() turtle.fd(40) turtle.fd(-50) turtle.penup() turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(13) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(-180) turtle.circle(20,-90) turtle.circle(20,90) turtle.penup() turtle.fd(13) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(-90) turtle.fd(60) move(0,40) move(90,80) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(30) turtle.seth(90) turtle.fd(30) turtle.fd(-30) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(20) turtle.seth(-90) turtle.fd(35) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(10) turtle.fd(-30) turtle.seth(90) turtle.fd(35) turtle.fd(-35) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(-25) move(-90,50) move(180,25) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(0) turtle.penup() turtle.circle(50,20) turtle.pendown() turtle.circle(50,70) turtle.seth(-90) turtle.circle(50,60) #移动 move(0,50) move(90,45) #乐 turtle.pensize(10) turtle.pendown() turtle.fd(40) turtle.seth(0) turtle.circle(50,60) turtle.circle(50,-25) move(-90,15) turtle.pendown() turtle.fd(30) turtle.seth(0) turtle.fd(-25) turtle.fd(65) turtle.fd(-40) turtle.seth(-90) turtle.fd(60) turtle.seth(135) turtle.fd(20) move(135,10) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(-135) turtle.fd(20) move(0,70) turtle.pendown() turtle.seth(135) turtle.fd(20)登录:
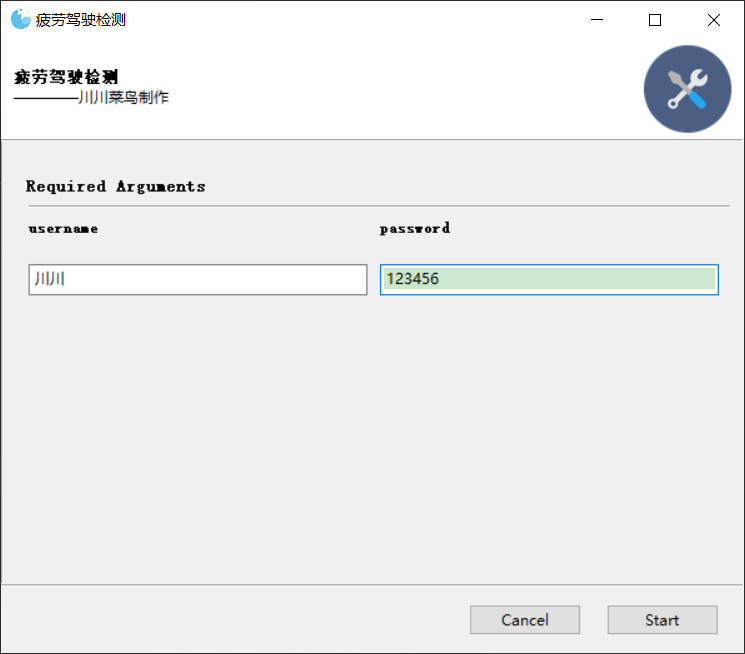
点击start执行: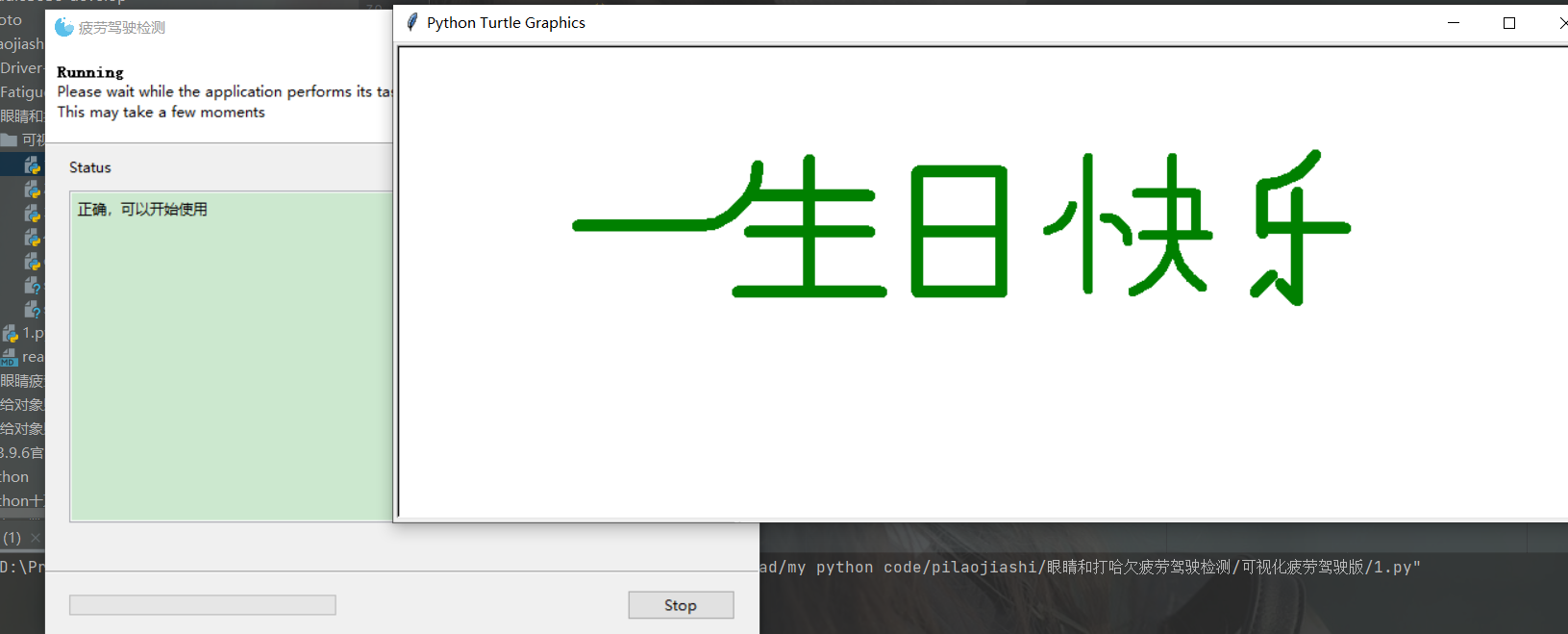
最后送上官方文档:https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey - 您还可以看一下 李兴华老师的Python实战编程课程中的 GUI编程入门小节, 巩固相关知识点
- 以下回答来自chatgpt:
# 首先,要确保代码在运行时立即启动窗口,可以在创建show_rank对象时使用root.deiconify()方法来显示窗口。 # 创建show_rank对象,并显示窗口 root = Tk() app = show_rank(root) root.deiconify() # 接下来,要确保窗口能够监听剪贴板的数据变化,可以使用Tkinter的after()方法周期性地检测剪贴板的变化。 # 首先,我们需要使用Tkinter的clipboard_get()方法获取剪贴板中的数据。然后,我们将这个过程包装成一个函数,并使用after()方法定期调用。 from tkinter import * import tkinter as tk import time def clipboard_monitor(): global clipboard_data # 检测剪贴板的变化 new_clipboard_data = root.clipboard_get() # 如果剪贴板的数据发生变化 if new_clipboard_data != clipboard_data: clipboard_data = new_clipboard_data # 将新的剪贴板数据输入到输入框中 app.input_box.delete('1.0', 'end') # 清空输入框 app.input_box.insert('1.0', clipboard_data) # 插入新的数据 # 继续周期性地检测剪贴板的变化 root.after(1000, clipboard_monitor) # 创建一个变量来存储剪贴板的数据 clipboard_data = root.clipboard_get() # 开始周期性地检测剪贴板的变化 root.after(1000, clipboard_monitor) # 最后,运行Tkinter的mainloop()方法来启动窗口的事件循环。 root.mainloop()上述代码中包含了
clipboard_monitor()函数,该函数可以周期性地检测剪贴板的变化,并将新的剪贴板数据输入到输入框中。clipboard_monitor()函数会在窗口启动后立即启动,并且会在每次剪贴板数据变化时被调用。请注意,这一步涉及到Tkinter的内部机制,因此需要将上述代码与你所给的代码进行适当的整合和修改。另外,可能还需要进一步的代码调整和优化才能完全实现你所描述的需求。
如果你有任何问题或需要进一步的帮助,请随时告诉我。
如果你已经解决了该问题, 非常希望你能够分享一下解决方案, 写成博客, 将相关链接放在评论区, 以帮助更多的人 ^-^