Microsoft visual c++清屏函数
菜单执行完一功能后,为简洁清晰,使用函数对其上一过程实现清屏
简单版:
system("cls");
专业版(参考其中的对应函数):
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void ConPrint(char *CharBuffer, int len);
void ConPrintAt(int x, int y, char *CharBuffer, int len);
void gotoXY(int x, int y);
void ClearConsole(void);
void ClearConsoleToColors(int ForgC, int BackC);
void SetColorAndBackground(int ForgC, int BackC);
void SetColor(int ForgC);
void HideTheCursor(void);
void ShowTheCursor(void);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
HideTheCursor();
ClearConsoleToColors(15, 1);
ClearConsole();
gotoXY(1, 1);
SetColor(14);
printf("This is a test...\n");
Sleep(5000);
ShowTheCursor();
SetColorAndBackground(15, 12);
ConPrint("This is also a test...\n", 23);
SetColorAndBackground(1, 7);
ConPrintAt(22, 15, "This is also a test...\n", 23);
gotoXY(0, 24);
SetColorAndBackground(7, 1);
return 0;
}
//This will clear the console while setting the forground and
//background colors.
void ClearConsoleToColors(int ForgC, int BackC)
{
WORD wColor = ((BackC & 0x0F) << 4) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
//Get the handle to the current output buffer...
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
//This is used to reset the carat/cursor to the top left.
COORD coord = {0, 0};
//A return value... indicating how many chars were written
//not used but we need to capture this since it will be
//written anyway (passing NULL causes an access violation).
DWORD count;
//This is a structure containing all of the console info
// it is used here to find the size of the console.
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//Here we will set the current color
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//This fills the buffer with a given character (in this case 32=space).
FillConsoleOutputCharacter(hStdOut, (TCHAR) 32, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
FillConsoleOutputAttribute(hStdOut, csbi.wAttributes, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
//This will set our cursor position for the next print statement.
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hStdOut, coord);
}
}
//This will clear the console.
void ClearConsole()
{
//Get the handle to the current output buffer...
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
//This is used to reset the carat/cursor to the top left.
COORD coord = {0, 0};
//A return value... indicating how many chars were written
// not used but we need to capture this since it will be
// written anyway (passing NULL causes an access violation).
DWORD count;
//This is a structure containing all of the console info
// it is used here to find the size of the console.
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//Here we will set the current color
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//This fills the buffer with a given character (in this case 32=space).
FillConsoleOutputCharacter(hStdOut, (TCHAR) 32, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
FillConsoleOutputAttribute(hStdOut, csbi.wAttributes, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
//This will set our cursor position for the next print statement.
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hStdOut, coord);
}
}
//This will set the position of the cursor
void gotoXY(int x, int y)
{
//Initialize the coordinates
COORD coord = {x, y};
//Set the position
SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord);
}
//This will set the forground color for printing in a console window.
void SetColor(int ForgC)
{
WORD wColor;
//We will need this handle to get the current background attribute
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//We use csbi for the wAttributes word.
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//Mask out all but the background attribute, and add in the forgournd color
wColor = (csbi.wAttributes & 0xF0) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
}
}
//This will set the forground and background color for printing in a console window.
void SetColorAndBackground(int ForgC, int BackC)
{
WORD wColor = ((BackC & 0x0F) << 4) + (ForgC & 0x0F);;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), wColor);
}
//Direct console output
void ConPrint(char *CharBuffer, int len)
{
DWORD count;
WriteConsole(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), CharBuffer, len, &count, NULL);
}
//Direct Console output at a particular coordinate.
void ConPrintAt(int x, int y, char *CharBuffer, int len)
{
DWORD count;
COORD coord = {x, y};
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hStdOut, coord);
WriteConsole(hStdOut, CharBuffer, len, &count, NULL);
}
//Hides the console cursor
void HideTheCursor()
{
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO cciCursor;
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
if(GetConsoleCursorInfo(hStdOut, &cciCursor))
{
cciCursor.bVisible = FALSE;
SetConsoleCursorInfo(hStdOut, &cciCursor);
}
}
//Shows the console cursor
void ShowTheCursor()
{
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO cciCursor;
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
if(GetConsoleCursorInfo(hStdOut, &cciCursor))
{
cciCursor.bVisible = TRUE;
SetConsoleCursorInfo(hStdOut, &cciCursor);
}
}
- 这个问题的回答你可以参考下: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/715158
- 这篇博客也不错, 你可以看下visual c++条件断点设置
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: 在Visual C++ 6.0中创建工程项目(多文件工程)中的 方法步骤: 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或者直接跳转源博客中阅读:
点击打开工具Visual c++ 6.0,初始界面如下:
(若出现未响应问题,用管理员方式运行打开)
首先创建一个工作空间,也可以直接创建工程,如果你没有先创建工作区,而是一打开VC++ 6.0便创建工程项目,那么你在创建一个项目的同时,也会创建一个工作区,工作区会有相应的工作区文件,其后缀名为dsw,此时,工作区文件的名称为所创建项目的名称。但为了区分开工作区和工程项目,即让工作区和工程项目有自己的名称,建议先创建工作区,再创建工程项目。创建工作区,需指明名称与位置,如下图,创建了一个名为workspace的工作区步骤为:File----工作区------命名(我的是workSpace)----选路径(任选,不推荐在C盘)-----确定
创建结果为:如图可知工作区中有0个工程,即还没有工程项目
接下来创建工程:
左击选中工作区,再右击,使出现浮动菜单,点击第一项添加新工程到工作空间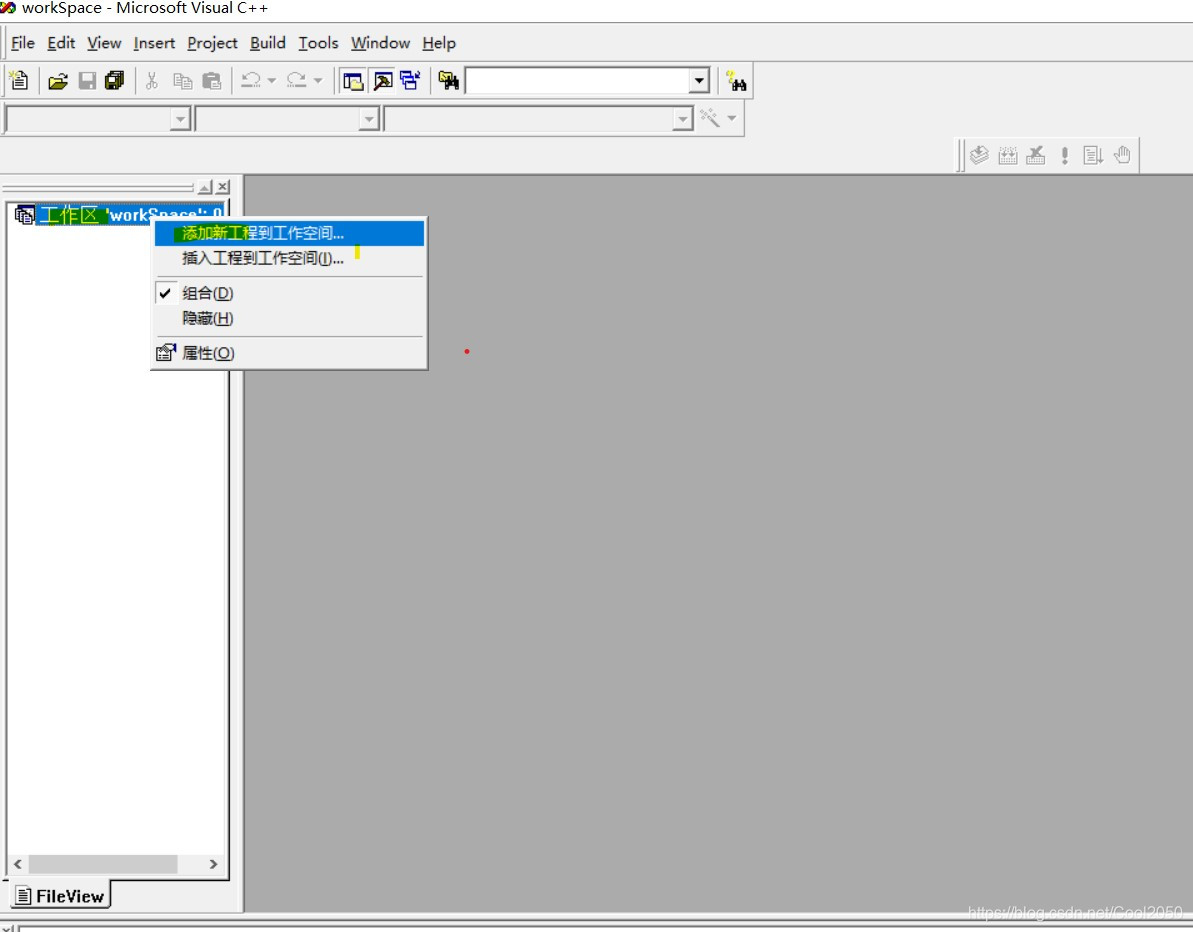 在出现的窗口中,选择工程类型,如果是控制台程序,选择”Win32 Console Application”,如果是可视化的窗口程序,选择”MFC AppWizard[exe]”,如果是制作动态链接库文件,选择“Win32 Dynamic-Link Library”,一般情况下,选择“Win32 Console Application”,即创建一个控制台程序,然后填写工程名称和工程的存储位置,和选择“添加到当前工作空间”(已默认选择)。点击“确定”,进入下一步
在出现的窗口中,选择工程类型,如果是控制台程序,选择”Win32 Console Application”,如果是可视化的窗口程序,选择”MFC AppWizard[exe]”,如果是制作动态链接库文件,选择“Win32 Dynamic-Link Library”,一般情况下,选择“Win32 Console Application”,即创建一个控制台程序,然后填写工程名称和工程的存储位置,和选择“添加到当前工作空间”(已默认选择)。点击“确定”,进入下一步
步骤:选定工程----Win32 Console Application-----命名-----位置–添加到当前工作空间—确定然后在弹出的窗口中选择“一个空工程”,然后点击”完成”
弹出的界面会显示新建工程的基本信息,在确认无误后,点击”确定”
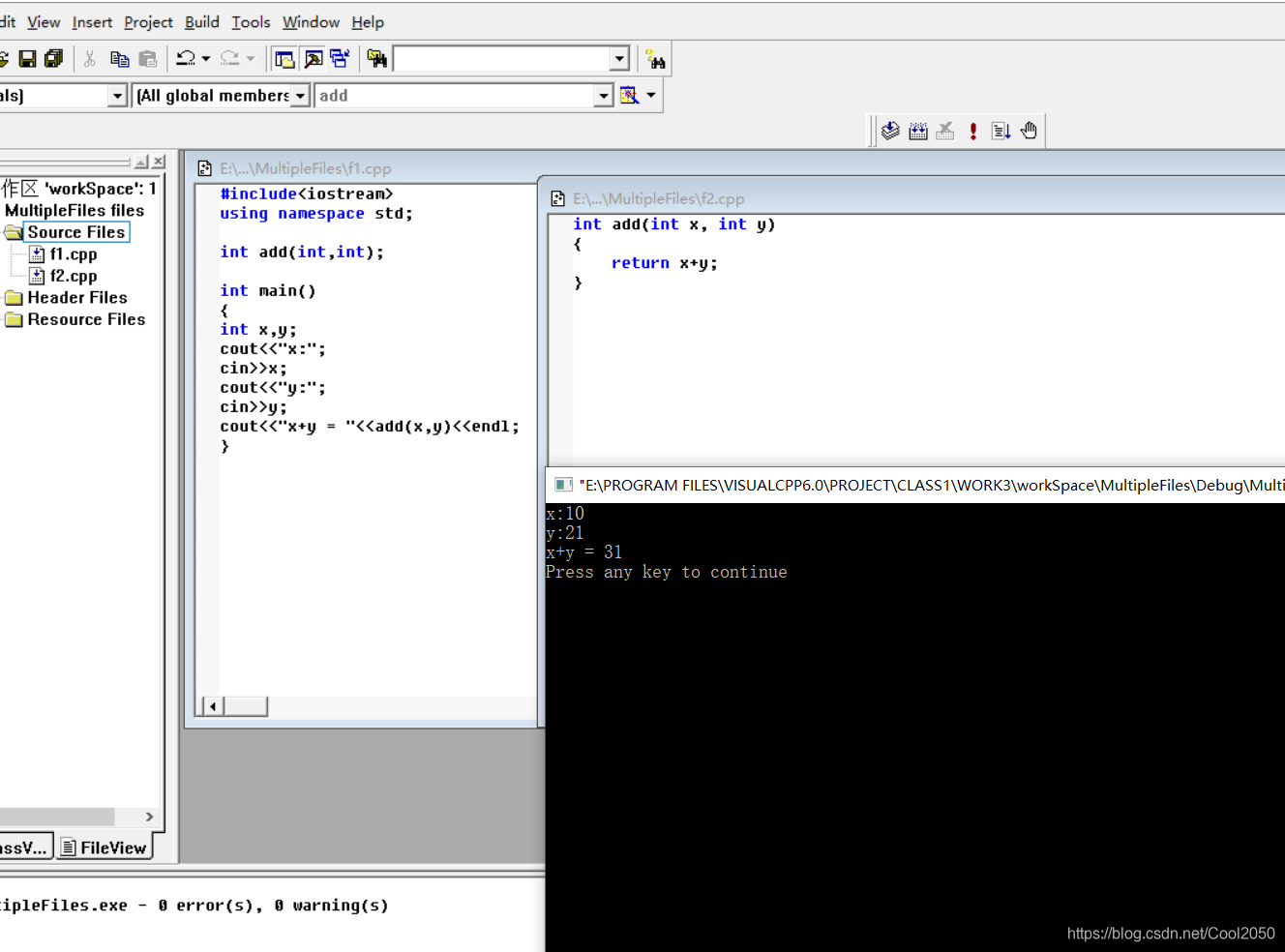
下图为创建一个工程项目“MultipleFiles”后的界面,由图可知,工作区“Workspace”中有一个工程,其工程名为“MultipleFiles”,图中显示的是工程项目“MultipleFiles”中“FileView”(文件视图)的信息
按照上述同样的方法可以再建工程文件在里面,可以自己尝试
现在就可以添加文件了,看项目里面可以增加source File 、Header File、Rsource File,添加方式都都差不多,我直接添加两个source File演示:
File-----新建-----文件------C++ source file------添加到项目中----文件名(不带后缀)------确认
如图:接着我们就可以在添加的文件里面编写程序啦!
再按照上述方式添加一个文件,同样写上程序
接着就可以保存编译运行啦!!!
- 您还可以看一下 刘安战老师的C语言程序设计(全程实践)课程中的 Visual C++下C程序编译和链接过程小节, 巩固相关知识点
- 以下回答来自chatgpt:
要实现清屏功能,可以使用Windows Console中的API函数:system("cls"),该函数可清空控制台中的所有内容。
具体实现步骤如下:
在头文件中包含Windows Console相关的API函数所需的头文件,例如Windows.h。
在需要进行清屏操作的地方调用system("cls")函数即可。
示例代码如下:
#include <Windows.h> int main() { // 进行一些菜单操作 // ... // 清屏 system("cls"); return 0; }
如果你已经解决了该问题, 非常希望你能够分享一下解决方案, 写成博客, 将相关链接放在评论区, 以帮助更多的人 ^-^