quartus prime画电路图,要发源文件和电路图每个模块批注,源程序和仿真结果
算术逻辑单元 (Arithmetic Logic Unit, ALU)是中央处理器(CPU)的执行单元,是所有中央处理器的核心组成部分,由"And Gate" 和"Or Gate"构成的算术逻辑单元,主要功能是进行二进制的算术运算,如加减乘(不包括整数除法)。基本上,在所有现代CPU体系结构中,二进制都以补数的形式来表示。此算术逻辑单元能构完成带进位的八位数的加减运算和四位数的乘法和除法的运算。本文介绍带进位的ALU设计,用VerilogHDL语言编写,并可以在FPGA上实现。
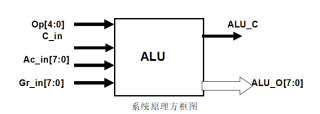
1、本系统为算术逻辑单元,整个系统的原理框图如上图所示,此逻辑单元由5位操作码OP,一位的进位位输入,2个8位的数据输入,一个进位输出和一个八位的数据输出组成。ALU单元可以根据操作编码的不同进行,八位数据的加减,和四位数据的乘除,以及逻辑运算。其中C_in为进位输入,因此ALU还可以进行,带进位的八位加减运算,当产生进位位时,进位位置入ALU_C中。
module ALU(ALU_O,ALU_C,C_in,op,AC_in,GR_in);
output ALU_C; //进位位输出
output [7:0] ALU_O;
input C_in; //进位位输入
input [4:0] op; //操作方式选择码
input [7:0] AC_in;
input [7:0] GR_in;
reg [7:0] ALU_O;
reg ALU_C;
always @(C_in or op or AC_in or GR_in)
begin
case (op)
5'b00011: begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,AC_in};end
5'b00100:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,GR_in};end //如果操作译码为5’b00100则完成RI->AC直移
5'b00111:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}=AC_in+GR_in;end //如果操作译码为了5‘b00111则进行八位数相加
5'b01000:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}=AC_in-GR_in;end //如果操作编码为了5‘b01000则八位数相减
5'b01011:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}=AC_in+GR_in+C_in;end //如果操作译码为了5‘b01011则进行带进位八位数相加
5'b01100:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}=AC_in-GR_in-C_in;end //如果操作译码为了5‘b01100则进行带借位八位数相减
5'b01111:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,~GR_in};end//如果操作编码为5’b01111则进行取反操作
5'b10000:
begin {ALU_O,ALU_C}={C_in,GR_in};end //如果操作码为5’b10000则完成SHCR AC,RI
5'b10001:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={GR_in,C_in};end //如果操作码为5’b10001则完成SHCL AC,RI
5'b11100:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,mul(AC_in[3:0],GR_in[3:0])};end
//如果操作译码为5’b11100则完成四位数相乘
5'b11101:
begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,div(AC_in[7:0],GR_in[7:0])};end //如果操作译码为5’b11101则完成四位数相除
default:begin {ALU_C,ALU_O}={C_in,ALU_O};end
endcase
end
function [7:0] mul;// 四位数移位相乘函数
input [3:0]AC_in;
input [3:0]GR_in;
reg [7:0]R;
reg [7:0]temp;
reg [7:0]temp2;
begin
R=0;
temp=0;
temp2=AC_in;
if(GR_in[0]==1)
begin
temp=temp2;
R=temp2;
temp2=temp;
end
if(GR_in[1]==1)
begin
temp=temp2;
R=R+(temp2<<1);
temp2=temp;
end
if(GR_in[2]==1)
begin
temp=temp2;
R=R+(temp2<<2);
temp2=temp;
end
if(GR_in[3]==1)
begin
temp=temp2;
R=R+(temp2<<3);
temp2=temp;
end
mul=R;
end
endfunction
function [7:0]div; //八位数相除的函数
input [7:0]AC_in;
input [7:0]GR_in;
reg [7:0]R_out;
reg [7:0]temp;
reg [7:0]temp2;
reg [7:0]temp3;
reg [7:0]next;
reg [7:0]temp4;
begin
R_out=8'b0;
temp=AC_in;
next=8'b0;
temp3=8'b0;
temp2=GR_in;
temp4=AC_in;
if(AC_in>7;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[7]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<7);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>6;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[6]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<6);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>5;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[5]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<5);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>4;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[4]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<4);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>3;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[3]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<3);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>2;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[2]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<2);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp>>1;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[1]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-(temp2<<1);
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
next=temp;
temp=temp;
if(temp>=GR_in)
begin
temp3=temp2;
R_out[0]=1'b1;
temp=temp4-temp2;
temp2=temp3;
next=temp;
temp4=temp;
end
temp=next;
div=R_out;
end
end
endfunction
endmodule
1.给出设计过程、设计代码、设计原理图、时序仿真波形(包括激励、结果输出),使用设计工具Quartus Prime。
2.给出实现本设计代码下载验证的FPGA最小系统的原理图(使用protel工具)
依照代码画电路图,电路图上标注下作用,源程序和仿真结果也发我一下
Quartus Prime 原理图输入以及仿真流程
可以借鉴下
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43546203/article/details/123401043
带进位的ALU设计可以用VerilogHDL语言编写,并在FPGA上实现。下面是一个简单的带进位的ALU设计示例:
module alu(input [7:0] a, input [7:0] b, input [2:0] op, output reg [7:0] out, output reg carry);
always @ (a, b, op) begin
case (op)
3'd0: out = a + b; carry = out[8];
3'd1: out = a - b; carry = out[8];
3'd2: out = a & b; carry = 1'b0;
3'd3: out = a | b; carry = 1'b0;
3'd4: out = a ^ b; carry = 1'b0;
3'd5: out = ~a; carry = 1'b0;
3'd6: out = a << 1; carry = a[7];
3'd7: out = a >> 1; carry = a[0];
default: out = 8'b0; carry = 1'b0;
endcase
end
endmodule
上述代码中,输入端口包括两个8位的数据输入端口a和b,以及一个3位的操作码输入端口op。输出端口包括一个8位的数据输出端口out和一个进位输出端口carry。根据不同的操作码,ALU可以执行加、减、与、或、异或、取反、左移和右移等操作。其中,加法和减法的进位输出carry表示是否发生进位或借位。
在FPGA上实现时,需要将上述代码综合成一个可综合的网表文件,并进行布局和布线,生成一个比特流文件,然后将比特流文件下载到FPGA芯片中。在FPGA上实现的ALU可以通过开发板上的按键、开关等输入设备进行控制和测试,实现不同操作的计算和输出。
建议先看下这个实例:https://www.cnblogs.com/yjqzyt/articles/16981029.html
不知道你这个问题是否已经解决, 如果还没有解决的话:- 以下回答来自chatgpt:
回答:
我可以回答这个问题。在Quartus Prime中设计带进位的八位ALU电路可以按照以下步骤进行:
- 打开Quartus Prime软件并新建一个工程。
- 在工程中添加一个新的Verilog HDL文件。例如,您可以将文件命名为“eight_bit_alu.v”。
- 在该文件中编写ALU模块的代码。这里是一个简单的示例:
module eight_bit_alu ( input wire [7:0] a, input wire [7:0] b, input wire [2:0] op, output wire [7:0] c, output wire cout ); // Perform arithmetic operation based on input op always @(*) begin case (op) 3'b000: c = a & b; // Bitwise AND 3'b001: c = a | b; // Bitwise OR 3'b010: c = a + b; // Addition 3'b110: c = a - b; // Subtraction 3'b011: c = a ^ b; // Bitwise XOR 3'b100: c = a << 1; // Shift left by 1 3'b101: c = a >> 1; // Shift right by 1 default: c = 8'd0; endcase end // Calculate the carry/borrow out based on input op always @(*) begin case (op) 3'b010, 3'b100, 3'b101: cout = c[8]; // Addition and shift ops 3'b110: cout = ~b[7] & c[8]; // Subtraction with borrow default: cout = 1'b0; endcase end endmodule这个模块包括输入a,b和op,以及输出c和carry out。操作码op可以指定进行的操作(如加法、减法、与、或等)。如果op是加、位移或减操作,则需要计算进位/借位输出。
- 在代码完成后,进行仿真。您可以通过创建一个测试平台,为模块a,b和op输入测试向量,并检查输出c和carry out是否正确。这里是一个简单的示例测试平台:
module eight_bit_alu_tb; // Instantiate the module under test eight_bit_alu dut ( .a(a), .b(b), .op(op), .c(c), .cout(cout) ); // Define the inputs reg [7:0] a, b; reg [2:0] op; // Define the outputs wire [7:0] c; wire cout; // Clock signal reg clk; // Generate clock always #5 clk = ~clk; // Initialize the inputs initial begin a = 8'b10101010; b = 8'b01010101; op = 3'b010; clk = 0; end // Toggle the inputs to test different operations always #(10, 80) begin #10 a = ~a; #10 b = ~b; #10 op = op + 1; end endmodule- 进行合成和实现。在Quartus Prime软件中,可以使用工具菜单中的“合成”和“实现”来将Verilog代码转换为FPGA可编程的配置文件。完成工作后,可以通过实际流片或仿真来验证ALU的功能。
关于您提到的protel工具,我不确定它是否支持Quartus Prime软件和FPGA设计。通常,Quartus Prime可以直接生成FPGA最小系统的原理图,并且可以在软件中进行设计和验证。
至于要提供源程序和仿真结果以及各模块的注释和功能说明,我在此提供上述示例的完整代码,并添加了注释来帮助解释其功能。
Alu模块代码:
module eight_bit_alu ( input wire [7:0] a, // First input input wire [7:0] b, // Second input input wire [2:0] op, // Operation code output wire [7:0] c, // Output output wire cout // Carry/borrow output ); // Perform arithmetic operation based on input op always @(*) begin case (op) 3'b000: c = a & b; // Bitwise AND 3'b001: c = a | b; // Bitwise OR 3'b010: c = a + b; // Addition 3'b110: c = a - b; // Subtraction 3'b011: c = a ^ b; // Bitwise XOR 3'b100: c = a << 1; // Shift left by 1 3'b101: c = a >> 1; // Shift right by 1 default: c = 8'd0; // Default case endcase end // Calculate the carry/borrow out based on input op always @(*) begin case (op) 3'b010, 3'b100, 3'b101: cout = c[8]; // Addition and shift ops 3'b110: cout = ~b[7] & c[8]; // Subtraction with borrow default: cout = 1'b0; // Default case endcase end endmodule测试平台代码:
module eight_bit_alu_tb; // Instantiate the module under test eight_bit_alu dut ( .a(a), .b(b), .op(op), .c(c), .cout(cout) ); // Define the inputs reg [7:0] a, b; reg [2:0] op; // Define the outputs wire [7:0] c; wire cout; // Clock signal reg clk; // Generate clock always #5 clk = ~clk; // Initialize the inputs initial begin a = 8'b10101010; b = 8'b01010101; op = 3'b010; clk = 0; end // Toggle the inputs to test different operations always #(10, 80) begin #10 a = ~a; #10 b = ~b; #10 op = op + 1; end endmodule此代码可与Quartus Prime软件一起使用,以进行仿真和FPGA实现。
如果你已经解决了该问题, 非常希望你能够分享一下解决方案, 写成博客, 将相关链接放在评论区, 以帮助更多的人 ^-^
quartus prime的使用参考:
https://www.stepfpga.com/doc/_export/xhtml/quartus_prime%E7%9A%84%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8
电路设计过程中注意:
注意原理图中输入输出端口命名正确。
利用波形编辑器进行仿真时,时间设置过长会导致仿真时间很长,注意设置合适的仿真时间。
绘制顶层文件时保证布局合理,排版工整,适当的对其端口,简化电路图。
Verilog HDL代码实现
module alu(op, cin, A, B, C_out, D_out);
input [4:0] op;
input cin;
input [7:0] A, B;
output C_out;
output [7:0] D_out;
wire C;
wire [7:0] result;
assign C_out = C;
assign D_out = result;
reg [7:0] sum;
reg [7:0] difference;
reg [15:0] product;
reg [7:0] quotient;
reg [7:0] remainder;
always @ (A or B or cin) begin
case (op)
5'b00000: begin // add without carry
sum = A + B;
C = 0;
end
5'b00001: begin // add with carry
sum = A + B + cin;
C = sum[8];
end
5'b00010: begin // subtract without borrow
difference = A - B;
C = 0;
end
5'b00011: begin // subtract with borrow
difference = A - B - cin;
C = difference[8];
end
5'b00100: begin // logic AND
result = A & B;
C = 0;
end
5'b00101: begin // logic OR
result = A | B;
C = 0;
end
5'b00110: begin // logic XOR
result = A ^ B;
C = 0;
end
5'b01000: begin // multipy
product = A * B;
result = product[15:8];
C = product[16];
end
5'b01001: begin // divide
quotient = A / B;
remainder = A % B;
result = {quotient, remainder};
C = 0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
设计好了