用CNN卷积神经网络识别手写数字(MNIS 厂数据集)
本人刚入门。对于这类问题没有解决的思路,希望能求得专业人士的解答。
- 这篇博客: mnist手写数字体识别CNN训练测试完美复现,以及自己手写数字进行测试中的 1、mnist数据集介绍 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
这个数据集是来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)。训练集 (training set) 由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成, 其中 50% 是高中学生, 50% 来自人口普查局 (the Census Bureau) 的工作人员. 测试集(test set) 也是同样比例的手写数字数据。
为什么要找这么多人来写呢?就是要增强学习结果的泛化能力,避免最后只认识某几个人的手写体。
import pylab print('训练数据:',data.train.images) print('训练集尺寸:',data.train.images.shape) print('训练集标签尺寸:',data.train.labels.shape) print('测试集尺寸:',data.test.images.shape) print('测试集标签尺寸:',data.test.labels.shape) ''' 回归: 训练数据: [[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] ... [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]] 训练集尺寸: (55000, 784) 训练集标签尺寸: (55000, 10) 测试集尺寸: (10000, 784) 测试集标签尺寸: (10000, 10) '''可以看到,在这个数据集中,训练集一共有55000个图片,存放在一个矩阵数组中,每一行是一个图片。测试机一共有10000个图片。他们对应的标签就是one_hot编码,例如数字0的标签是1000000000,数字1的标签是0100000000,以此类推。
打印几张mnist中的图片来看一下:
import pylab import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data DATA_DIR = 'MNIST_data' data = input_data.read_data_sets(DATA_DIR, one_hot=True) pylab.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(10): im = data.train.images[i] im = im.reshape((28,28)) pylab.imshow(im) pylab.show() im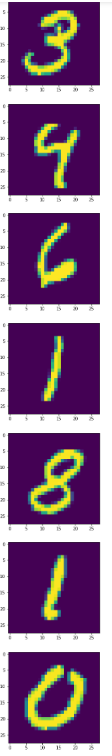
这个数字。。。有的连我自己都不认识。每一个图片是这样保存的,都是一个28*28的数组。
- 以下回答由chatgpt基于相关博客总结生成:
首先,感谢您对CNN卷积神经网络的学习和使用,下面是我对该问题的解答和建议:
数据集 首先需要下载MNIST数据集,可以使用TensorFlow提供的API进行下载,也可以到官网进行下载。下载完毕后可以采用TensorFlow提供的读取程序对数据集进行读取操作。
模型设计 CNN模型的设计主要包括卷积层、池化层、全连接层和输出层。这里建议使用TensorFlow框架,可以参考TensorFlow官网提供的样例进行操作。
模型训练 对于模型训练,可以采用TensorFlow提供的优化器进行梯度下降的计算。同时也需要对训练集和测试集进行分离,可以采用随机打乱的方式进行。
模型评估 在模型评估方面,可以采用测试集对训练好的模型进行评估和检验,主要包括准确率、精确率和召回率等指标,可以使用confusion_matrix函数进行计算。
代码实现 对于代码实现方面,在TensorFlow框架下可以采用以下代码进行实现:
# 导入相关包 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data # 读取MNIST数据集 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) # 设计卷积神经网络模型 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) x_reshape = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x_reshape, filters=32, kernel_size=[5, 5], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu) pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=pool1, filters=64, kernel_size=[5, 5], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu) pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv2, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) dense = tf.layers.dense(inputs=pool2_flat, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu) dropout = tf.layers.dropout(inputs=dense, rate=0.4) y_pred = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dropout, units=10) # 定义损失函数 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = y_pred, labels = y_true)) # 定义优化器进行梯度下降计算 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cross_entropy) # 评估模型准确率 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pred, 1), tf.argmax(y_true, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) # 训练模型并测试模型准确率 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for i in range(2000): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict = {x: batch_xs, y_true: batch_ys}) if i % 100 == 0: acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = {x: batch_xs, y_true: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.0}) print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, acc)) # 对模型进行测试 test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = {x: mnist.test.images, y_true: mnist.test.labels}) print("test accuracy %g" % test_acc)希望对您有所帮助,如有任何疑问可随时在评论区提出,感谢您的阅读。
我有一篇博客是针对非官方手写数据集进行识别的,数据集是自制的,并不是官方自带的那个,你可以参考一下,谢谢支持!
博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52417436/article/details/128208842