在计算机控制台输出模拟过程。
思考题:
构造一个扔骰子模型。小明和小王每人都掷骰子3次,每次都扔3个骰子,每次都比较大小,骰子点数和较大的一方赢。如果骰子点数相同则为平局,如果一方投出3个一点或者3个六点,则立即取得胜利。整个游戏五局三胜。请在计算机控制台输出模拟过程。

import random
v =[0,0]
while 5 not in v:
s = [random.randint(1,6) for _ in range(6)]
print('A点数::',*s[:3])
print('B点数::',*s[3:])
if sum(s[:3]) in [3,18]:
v[0] += 1
print('A胜')
continue
if sum(s[3:]) in [3,18]:
v[1] += 1
print('B胜')
continue
if sum(s[:3]) > sum(s[3:]):
v[0] += 1
print('A胜')
elif sum(s[:3]) < sum(s[3:]):
v[1] += 1
print('B胜')
else:
print('平局')
print('最终','A胜' if v[0] > v[1] else 'B胜',sep=':')
- 帮你找了个相似的问题, 你可以看下: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/645035
- 你也可以参考下这篇文章:用户画像(四):基于用户搜索数据可以做什么,采取哪些方案呢
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: <<从零入门机器学习>>之线性回归-房价预测问题中的 2.1 以面积为输入量,建立单因子模型,评估模型表现,可视化线性回归预测结果 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
2.1.1 将usa_housing_price.csv文件通过pandas的read_csv(path)方法读取到内存中来,然后通过head()方法查看文件的部分内容特征,如下代码和图所示:
注意read_csv方法当中的path是存放usa_housing_price.csv文件的本地路径,每个人存放的路径都不同,可以自定义。
import pandas as pd import numpy as np data = pd.read_csv('D:/Google/picture/usa_housing_price.csv') data.head()data.head()方法显示出的内容和我们表格的表头内容格式一致,只不过其只显示源文件内容的一部分
2.1.2 引入matplotlib包将每个影响因子和Price结合起来绘制关系图(其中Price作为y轴、其余影响因子分别作为x轴):
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) fig1 = plt.subplot(231) #两行三列第一幅图(两行三列:x走两个单元格,y走三个单元格),下同 plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Avg. Area Income'],data.loc[:,'Price']) #plt.scatter(x,y) 花点图 (下同) plt.title('Price VS Income') fig2 = plt.subplot(232) plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Avg. Area House Age'],data.loc[:,'Price']) plt.title('Price VS Age') fig3 = plt.subplot(233) plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Avg. Area Number of Rooms'],data.loc[:,'Price']) plt.title('Price VS Rooms') fig4 = plt.subplot(234) plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Area Population'],data.loc[:,'Price']) plt.title('Price VS Population') fig5 = plt.subplot(235) plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'size'],data.loc[:,'Price']) #plt.scatter(x,y) plt.title('Price VS size') plt.show()
2.1.3 将面积因子size作为x、对应的房屋价格Price作为y,调用 sklearn包的相关方法训练线性回归模型。接下来,再以size作为输入变量,预测Price的值,并以MSE和R2_score的值来评估单因子模型:
定义x、y,训练出线性回归模型,而且以size作为x,通过已训练出的模型,预测y的值并打印输出出来:
#define x and y x = data.loc[:,'size'] y = data.loc[:,'Price'] x = np.array(x).reshape(-1,1) #需要将x转换成一维的数组 #set up the linear regression model from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression LR1 = LinearRegression() LR1.fit(x,y) y_predict_1 = LR1.predict(x) print(y_predict_1)y_predict的值:

通过预测出来的y_predict的值来评估线性回归模型的表现,其中主要是通过MSE以及R2_score来作为判别的标准(MSE的值越小越好,R2_score的值越接近1越好):#evaluate the model from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error,r2_score mean_squared_error_1 = mean_squared_error(y,y_predict_1) #MSE r2_score_1 = r2_score(y,y_predict_1) print(mean_squared_error_1,r2_score_1)MSE和R2_score的值:
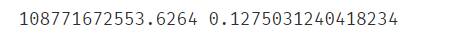
将源数据的size作为x、Price作为y画出散点图,预测出来的y_predict_1作为y画出直线图(斜率k越接近1越好):fig6 = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) plt.scatter(x,y) #画点图 plt.plot(x,y_predict_1,'r') #画直线图 r->代表红色 plt.show()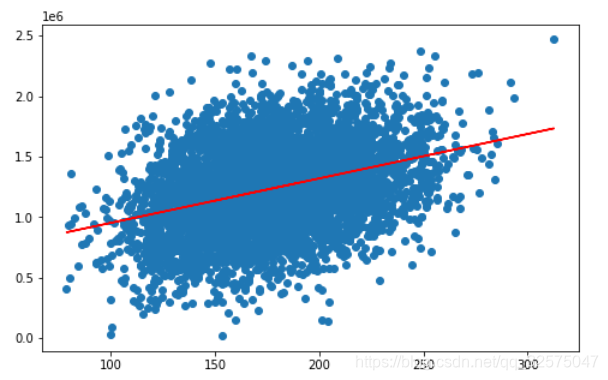
- 您还可以看一下 张先凤老师的《计算机体系结构—网络篇3、4》之IP分类与组成、网络标识、子网掩码、私网组建等课程中的 子网掩码2小节, 巩固相关知识点
- 以下回答由chatgpt基于相关博客总结生成:
我可以使用Python中的随机数生成函数来模拟扔骰子的过程,并使用print语句输出其结果。以下是实现代码:
# 导入random库 import random # 定义小明和小王 player1 = '小明' player2 = '小王' # 定义比赛规则 num_rounds = 5 # 五局三胜 num_wins = 3 # 胜利条件 num_dice = 3 # 每次掷骰子次数 num_sides = 6 # 每个骰子的面数 winning_scores = {3: 'three of a kind', 18: 'big six', 21: 'big one'} # 获胜条件 # 定义比赛函数 def play_game(player1, player2): # 初始化局数和胜利数 round_num = 1 player1_wins = 0 player2_wins = 0 print('Starting game between {} and {}...'.format(player1, player2)) # 进入循环,直到有一方获胜 while player1_wins < num_wins and player2_wins < num_wins: # 输出当前局数 print('Round {}...'.format(round_num)) # 初始化每个玩家的得分 player1_score = 0 player2_score = 0 # 玩家轮流掷骰子 for i in range(num_dice): # 小明掷骰子 dice_rolls = [random.randint(1, num_sides) for _ in range(3)] print('{} rolls a {}...'.format(player1, dice_rolls)) # 小王掷骰子 dice_rolls = [random.randint(1, num_sides) for _ in range(3)] print('{} rolls a {}...'.format(player2, dice_rolls)) # 比对每个玩家的得分 player1_score += sum(sorted(dice_rolls)[1:]) # 筛子取两个最大值相加 player2_score += sum(sorted(dice_rolls)[1:]) print('Round {} scores: {} - {}'.format(round_num, player1_score, player2_score)) # 判断获胜者 if player1_score == player2_score: print('Round {} is a tie.'.format(round_num)) elif player1_score in winning_scores: print('{} wins round {} with a {}!'.format(player1, round_num, winning_scores[player1_score])) player1_wins += 1 elif player2_score in winning_scores: print('{} wins round {} with a {}!'.format(player2, round_num, winning_scores[player2_score])) player2_wins += 1 else: print('Round {} is a tie.'.format(round_num)) # 输出当前比分 print('Current score: {} - {}'.format(player1_wins, player2_wins)) # 增加局数 round_num += 1 # 输出获胜者 if player1_wins > player2_wins: print('{} wins the game!'.format(player1)) else: print('{} wins the game!'.format(player2)) # 开始比赛 play_game(player1, player2)此程序将对控制台进行输出以显示每一轮比赛的结果。每个玩家的每个回合将由随机数生成函数生成,以模拟投掷骰子的过程。