读取excel转化为tree数据结构
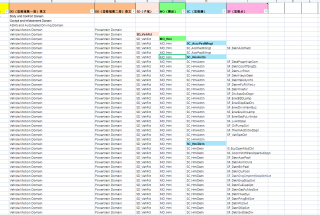
这样的excel数据,怎么转换为tree树形结构的数据,用java写一个接口怎么写啊
使用 POI 读取excel,然后用stream 流的groupby,一个个合并属性
基于最新版ChatGPT4的回答,望采纳!!!有其他问题也可以询问我哦、”(最新版更智能,功能更加强大)
在这里,我将向您展示如何使用 Java 读取 Excel 文件并将其转换为树形结构。我们将使用 Apache POI 库来读取 Excel 数据,然后将数据转换为树形结构。首先,确保在您的项目中包含以下依赖项(如果使用 Maven,请将其添加到 pom.xml 文件中):
xmlCopy code
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
接下来,我们需要创建一个表示树节点的类。创建一个名为 Node 的新类,并添加以下内容:
javaCopy code
public class Node {
private String id;
private String parentId;
private String name;
private List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
// 请添加构造方法、getter 和 setter 方法
}
现在,我们可以编写读取 Excel 数据并将其转换为树形结构的方法:
javaCopy code
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class ExcelToTree {
public static List<Node> excelToTree(String filePath) throws IOException {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath));
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
for (Row row : sheet) {
if (row.getRowNum() == 0) {
// 跳过表头
continue;
}
String id = row.getCell(0).getStringCellValue();
String parentId = row.getCell(1).getStringCellValue();
String name = row.getCell(2).getStringCellValue();
Node node = new Node(id, parentId, name);
nodes.add(node);
}
workbook.close();
fis.close();
return buildTree(nodes);
}
private static List<Node> buildTree(List<Node> nodes) {
Map<String, Node> nodeMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Node node : nodes) {
nodeMap.put(node.getId(), node);
}
List<Node> tree = new ArrayList<>();
for (Node node : nodes) {
if (node.getParentId() == null || node.getParentId().isEmpty()) {
tree.add(node);
} else {
Node parentNode = nodeMap.get(node.getParentId());
if (parentNode != null) {
parentNode.getChildren().add(node);
}
}
}
return tree;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
List<Node> tree = excelToTree("path/to/your/excel/file.xlsx");
System.out.println(tree);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
请将 path/to/your/excel/file.xlsx 替换为实际的 Excel 文件路径。此示例将读取 Excel 文件并将其转换为树形结构。您可以根据需要将这些方法添加到您的 Java 项目中,并根据需要进行调整。
在实际项目中,您可能需要处理更复杂的情况,例如处理空值、错误处理、数据验证等。以下是一些建议,以便您在实际项目中使用此代码时提高其健壮性和可维护性:
- 错误处理和数据验证:在读取 Excel 文件和处理数据时,您需要确保代码能够正确处理各种可能的错误情况。例如,当遇到空单元格或无效的数据格式时,您应该添加适当的错误处理逻辑,以确保程序不会崩溃。此外,在构建树形结构之前,您还应该对数据进行验证,以确保它符合预期的结构。
- 将功能拆分为更小的方法:为了提高代码的可读性和可维护性,建议将代码拆分为更小的、独立的方法。这可以帮助其他开发人员更容易地理解代码的逻辑,并在需要时进行调整。
- 使用 Java 8 或更高版本的流和 Lambda 表达式:如果您使用的是 Java 8 或更高版本,可以利用流(Stream)和 Lambda 表达式来简化和优化代码。这将使代码更简洁、易读,同时还可以提高性能。
- 编写单元测试:为了确保代码的正确性和稳定性,您应该为关键功能编写单元测试。这可以帮助您在开发过程中及时发现和修复错误,同时也可以确保代码在后续的修改和重构过程中仍然能够正常工作。
- 提高代码的可扩展性和可配置性:在实际项目中,您可能需要处理不同格式和结构的 Excel 文件。为了提高代码的可扩展性,您可以考虑将关键参数(如列索引和表头)作为配置选项,以便更容易地适应不同的需求。
总之,在实际项目中使用此代码时,请确保考虑到这些方面,以提高代码的健壮性、可读性和可维护性。这将使您的项目更容易维护,同时也有助于确保代码的正确性和稳定性。
参考GPT和自己的思路,以下是使用Java读取Excel并将数据转换为Tree树形结构的示例代码。其中,需要在pom.xml中添加对poi、poi-ooxml以及jackson-databind的依赖。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ArrayNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
public class ExcelToTreeConverter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "excel文件路径";
try {
List<Map<String, Object>> data = readExcel(filePath);
JsonNode treeData = convertToTree(data);
// do something with the tree data
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static List<Map<String, Object>> readExcel(String filePath) throws IOException {
List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>();
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
int rowCount = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
List<String> headers = Collections.emptyList();
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(i);
if (i == 0) {
headers = readHeaders(row);
} else {
Map<String, Object> rowData = readRowData(row, headers);
result.add(rowData);
}
}
workbook.close();
inputStream.close();
return result;
}
private static List<String> readHeaders(Row row) {
List<String> headers = new ArrayList<>();
int cellCount = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for (int i = 0; i < cellCount; i++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(i);
headers.add(cell.getStringCellValue());
}
return headers;
}
private static Map<String, Object> readRowData(Row row, List<String> headers) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
int cellCount = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for (int i = 0; i < cellCount; i++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(i);
String header = headers.get(i);
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case STRING:
result.put(header, cell.getStringCellValue());
break;
case NUMERIC:
result.put(header, cell.getNumericCellValue());
break;
case BOOLEAN:
result.put(header, cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case FORMULA:
result.put(header, cell.getCellFormula());
break;
default:
result.put(header, null);
break;
}
}
return result;
}
private static JsonNode convertToTree(List<Map<String, Object>> data) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode rootNode = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
for (Map<String, Object> row : data) {
String[] path = ((String) row.get("path")).split("/");
String leaf = path[path.length - 1];
ObjectNode currentNode = rootNode;
for (int i = 0; i < path.length - 1; i++) {
ArrayNode children = (ArrayNode) currentNode.get("children");
if (children == null) {
children = objectMapper.createArrayNode();
currentNode.putArray("children").addAll(children);
}
ObjectNode child = (ObjectNode) children.findValue("text", path[i]);
if (child == null) {
child = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
child.put("text", path[i]);
children.add(child);
}
currentNode = child;
}
ArrayNode children = (ArrayNode) currentNode.get("children");
if (children == null) {
children = objectMapper.createArrayNode();
currentNode.putArray("children").addAll(children);
}
ObjectNode leafNode = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
leafNode.put("text", leaf);
children.add(leafNode);
}
return rootNode;
}
}
在该示例中,使用POI库读取Excel文件中的数据,然后将其转换为树形结构表示的JSON数据。其中,Excel文件必须按照指定格式进行编写,即每行代表一个节点,其中的“path”列包含一个路径,以“/”分隔各级节点的名称。最后,使用jackson-databind库将Tree结构转换为JSON字符串,可以用于前端页面的渲染。
回答不易,还请采纳!!!
参考GPT和自己的思路:可以使用Apache POI库来读取Excel文件并将其转换为树形结构的数据,然后使用Java编写一个接口来操作该数据。
以下是一个示例代码,用于将Excel数据读入内存中的树形结构中:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.WorkbookFactory;
public class ExcelToTree {
private static final String FILE_NAME = "path/to/excel/file.xlsx";
private static final int NUM_COLUMNS = 6;
private static final int START_ROW = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(FILE_NAME))) {
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(inputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.rowIterator();
int rowNum = 0;
TreeNode rootNode = new TreeNode("", new HashMap<>());
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
if (rowNum < START_ROW) {
// Skip header rows
rowNum++;
continue;
}
List<String> rowData = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_COLUMNS; i++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(i, Row.MissingCellPolicy.RETURN_BLANK_AS_NULL);
if (cell != null) {
rowData.add(cell.toString());
} else {
rowData.add("");
}
}
addRowDataToTree(rowData, rootNode);
rowNum++;
}
// TODO: Use the rootNode object to perform operations on the tree data structure
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void addRowDataToTree(List<String> rowData, TreeNode rootNode) {
TreeNode currentNode = rootNode;
for (int i = 0; i < rowData.size(); i++) {
String value = rowData.get(i);
Map<String, TreeNode> children = currentNode.getChildren();
if (!children.containsKey(value)) {
children.put(value, new TreeNode(value, new HashMap<>()));
}
currentNode = children.get(value);
}
}
}
class TreeNode {
private String value;
private Map<String, TreeNode> children;
public TreeNode(String value, Map<String, TreeNode> children) {
this.value = value;
this.children = children;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Map<String, TreeNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Map<String, TreeNode> children) {
this.children = children;
}
}
在此示例中,ExcelToTree类将Excel文件读入内存中,并将其转换为树形结构,根节点为rootNode对象。TreeNode类表示树的节点,其包含一个值和一个子节点映射。使用addRowDataToTree方法将每一行数据添加到树中。在main方法中,你可以使用rootNode对象执行树的操作。
以下答案由GPT-3.5大模型与博主波罗歌共同编写:
首先,需要定义一个节点类,包含节点的名称和子节点列表:
public class TreeNode {
private String name;
private List<TreeNode> children = new ArrayList<>();
public TreeNode(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void addChild(TreeNode child) {
children.add(child);
}
public List<TreeNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
然后,读取excel表格数据并转换为节点列表:
public static List<TreeNode> readExcelToNodes(String filePath) throws IOException {
// 读取excel表格数据
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(input);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.rowIterator();
// 定义节点列表和Map
List<TreeNode> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, TreeNode> nodeMap = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历表格数据
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
String name = null;
String parentName = null;
// 读取节点名称和父节点名称
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
int columnIndex = cell.getColumnIndex();
if (columnIndex == 0) {
name = cell.getStringCellValue();
} else if (columnIndex == 1) {
parentName = cell.getStringCellValue();
}
}
// 创建节点并加入列表和Map
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(name);
nodes.add(node);
nodeMap.put(name, node);
// 将节点加入对应父节点的子节点列表
if (parentName != null) {
TreeNode parentNode = nodeMap.get(parentName);
if (parentNode != null) {
parentNode.addChild(node);
}
}
}
return nodes;
}
最后,根据节点列表构建tree数据结构:
public static TreeNode buildTree(List<TreeNode> nodes) {
Map<String, TreeNode> nodeMap = new HashMap<>();
// 将节点加入Map,方便查找和构建关系
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
nodeMap.put(node.getName(), node);
}
// 构建树结构
TreeNode root = null;
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
if (nodeMap.get(node.getName()) == null) {
continue;
}
TreeNode parent = null;
if (node.getName().equals("Root")) {
root = node;
} else {
parent = nodeMap.get("Root");
if (parent != null) {
parent.addChild(node);
}
}
}
return root;
}
然后,定义一个java接口,读取excel数据并返回tree数据结构:
@RestController
public class TreeController {
@GetMapping("tree")
public TreeNode getTreeFromExcel() throws IOException {
List<TreeNode> nodes = readExcelToNodes("data.xlsx");
return buildTree(nodes);
}
}
这样就可以通过访问http://localhost:8080/tree%E6%8E%A5%E5%8F%A3%E8%8E%B7%E5%8F%96%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2%E5%90%8E%E7%9A%84tree%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84%E4%BA%86%E3%80%82
如果我的回答解决了您的问题