多线程生产者消费者模型中,多个生产者与一个消费者,生产超过限定容量。
在编辑多线程的生产者-消费者模型的过程中,发现执行结果不符合理想结果,超出了限制。
1、问题:超过仓库容量,生产者继续生产。
2、代码:
public class producerAndConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list= new LinkedList();
MessageQueue queue = new MessageQueue(list,3);//仓库队列,容量设置为3
//创建并启动3个生产的线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
int obj = 0;
int j=0; //控制次数
while(j<10){
j++;
queue.producer(obj);
obj++;
}
},"producer"+i).start();
}
//创建并启动消费的线程
new Thread(()->{
int j=0; //控制次数
while(j<10){
j++;
queue.consumer();
}
},"consumer").start();
}
/**
* 生产消费队列
*/
static class MessageQueue{
private LinkedList list;
private int capacity; //容量
//生产
public void producer(Integer obj){
synchronized (this.list){
if(list.size()==capacity){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已满-------------->停止生产!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
list.add(obj);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产:"+obj+",size:"+list.size()+"--仓库:"+list);
list.notifyAll();
}
}
//消费方法
public Integer consumer(){
synchronized (this.list){
if(list.isEmpty()){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已空-------------->停止消费!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Integer obj = list.remove();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费:"+obj+",size:"+list.size()+"--仓库:"+list);
list.notifyAll();
return obj;
}
}
//构造方法
public MessageQueue(LinkedList list,int capacity ){
this.list = list;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
}
}
3、执行结果:
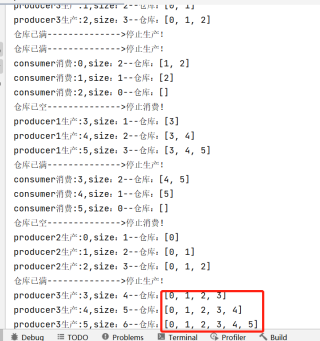
用我这份试试
public class ProducerAndConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list= new LinkedList<Integer>();
MessageQueue queue = new MessageQueue(list,3);//仓库队列,容量设置为3
//创建并启动3个生产的线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
int obj = 0;
int j=0; //控制次数
while(j<10){
j++;
queue.producer(obj);
obj++;
}
},"producer"+i).start();
}
//创建并启动消费的线程
new Thread(()->{
int j=0; //控制次数
while(j<10){
j++;
queue.consumer();
}
},"consumer").start();
}
/**
* 生产消费队列
*/
static class MessageQueue{
private volatile LinkedList<Integer> list;
private int capacity; //容量
//生产
public void producer(Integer obj){
synchronized (this.list){
while (list.size()>=capacity){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已满-------------->停止生产!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
list.add(obj);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产:"+obj+",size:"+list.size()+"--仓库:"+list);
list.notifyAll();
}
}
//消费方法
public Integer consumer(){
synchronized (this.list){
while (list.isEmpty()){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已空-------------->停止消费!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Integer obj = list.remove();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费:"+obj+",size:"+list.size()+"--仓库:"+list);
list.notifyAll();
return obj;
}
}
//构造方法
public MessageQueue(LinkedList<Integer> list,int capacity){
this.list = list;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
}
}
回答不易,求求您采纳点赞哦 感激不尽
在该多线程的生产者-消费者模型中,仓库的容量为3,但是当仓库已满时,生产者继续生产导致问题。这是因为生产者在获取锁之后,仅仅判断仓库是否已满,而没有再次判断是否已经被其他生产者生产过,因此可能会导致超过容量的情况。
为了解决这个问题,可以在生产者添加一个循环判断,如果仓库已满,就继续等待,并在获取到锁之后再次判断仓库是否已经被其他生产者生产过,如果已经被生产过,就释放锁并继续等待。具体的代码如下:
public void producer(Integer obj) {
synchronized (this.list) {
while (list.size() == capacity) {
try {
System.out.println("仓库已满-------------->停止生产!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (list.size() < capacity) {
list.add(obj);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产:" + obj + ",size:" + list.size() + "--仓库:" + list);
list.notifyAll();
}
}
}
通过这个修改,当仓库已满时,生产者就会等待,直到仓库中有商品被消费者消费掉之后,才会继续生产。同时,在获取锁之后,生产者还会再次判断仓库是否已经被其他生产者生产过,以避免超过仓库容量的情况。
在你的代码中,当仓库已满时,生产者线程调用了 wait() 方法来等待,但是没有进行唤醒。因此当仓库已满时,后续的生产者线程将一直等待,不会唤醒其他线程进行消费,导致程序出现了问题。
为了解决这个问题,你需要在生产者生产完毕后,使用 notify() 或 notifyAll() 方法来唤醒等待的线程。例如,你可以在 producer() 方法中,在添加完对象到队列后,加上 list.notifyAll();,如下所示:
//生产
public void producer(Integer obj){
synchronized (this.list){
if(list.size()==capacity){
try {
System.out.println("仓库已满-------------->停止生产!");
list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
list.add(obj);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产:"+obj+",size:"+list.size()+"--仓库:"+list);
list.notifyAll(); // 唤醒所有等待线程
}
}
同样地,在消费者的 consumer() 方法中,你需要在取出对象后,也加上 list.notifyAll(); 来唤醒等待的线程。
这样修改之后,你的代码就能够正常工作了。
- 这篇文章:多个生产者一个消费者的单线程处理队列 也许有你想要的答案,你可以看看