想问下红圈的部分是不是有问题呀?
以下函数用于将定时任务结构体timer插入到链表中,list成员表示链表结点,该链表是双向循环链表,container_of是获取成员所在结构体的首地址,list_is_empty()判断链表是否为空,如果为空则返回1,否则返回0,list_add_to_behind函数将新节点插入到当前结点的next位置(后插)
想问下红圈的部分是不是有问题呀?
第一个问题是,我理解是链表结点应该是按照expire_jiffies值从小到大排列,但是这里插入却将结点插入到了后面,造成了前大后小的情况;
第二个问题是,感觉如果timer_list_head链表中所有结点的expire_jiffies值都比timer的小,那是不是while就进入了无限循环?因为双向循环链表的结尾指向了头结点
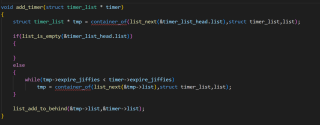
void add_timer(struct timer_list * timer)
{
struct timer_list * tmp = container_of(list_next(&timer_list_head.list),struct timer_list,list);
if(list_is_empty(&timer_list_head.list))
{
}
else
{
while(tmp->expire_jiffies < timer->expire_jiffies)
tmp = container_of(list_next(&tmp->list),struct timer_list,list);
}
list_add_to_behind(&tmp->list,&timer->list);
}
相关函数结构体定义如下:
struct timer_list
{
struct List list;
unsigned long expire_jiffies; //期望执行时间(延迟)
void (* func)(void * data); //处理方法
void *data; //参数
};
#define container_of(ptr,type,member) \
({ \
typeof(((type *)0)->member) * p = (ptr); \
(type *)((unsigned long)p - (unsigned long)&(((type *)0)->member)); \
})
inline struct List * list_next(struct List * entry)
{
if(entry->next != NULL)
return entry->next;
else
return NULL;
}
inline long list_is_empty(struct List * entry)
{
if(entry == entry->next && entry->prev == entry)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
inline void list_add_to_behind(struct List * entry,struct List * new) ////add to entry behind
{
new->next = entry->next;
new->prev = entry;
new->next->prev = new;
entry->next = new;
}
关于你提到的两个问题,我来分别解答一下:
- 关于插入顺序的问题
你说的比较对,链表结点应该按照 expire_jiffies 的值从小到大排列。但是在 add_timer 函数中,却是将新节点插入到了当前结点的后面。这样会导致如果插入的新节点的 expire_jiffies 值大于当前链表中所有节点的 expire_jiffies 值,那么它会被插入到链表的最后,而不是最前面。造成的结果就是链表结点不是按照 expire_jiffies 值从小到大排列的。
为了解决这个问题,需要在 while 循环中加入一个判断条件,让它在找到第一个 expire_jiffies 值大于等于新节点的 expire_jiffies 值时就停止循环。然后将新节点插入到当前节点的前面即可。
修改后的 add_timer 函数代码如下:
scss
void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer) { struct timer_list *tmp = container_of(list_next(&timer_list_head.list), struct timer_list, list); if (list_is_empty(&timer_list_head.list)) { list_add_to_behind(&timer_list_head.list, &timer->list); } else { while (tmp->expire_jiffies < timer->expire_jiffies) { tmp = container_of(list_next(&tmp->list), struct timer_list, list); if (tmp == &timer_list_head) { break; } } list_add_to_behind(tmp->list.prev, &timer->list); } }
- 关于死循环的问题
你提到的第二个问题,如果 timer_list_head 链表中所有结点的 expire_jiffies 值都比 timer 的小,那么 while 循环就会进入死循环,因为双向循环链表的结尾指向了头结点。这个问题实际上是不存在的,因为在 while 循环中,tmp 指针会不断向后移动,直到 tmp 指向了 timer_list_head 结点时,while 循环才会结束。
你可能会认为如果 while 循环结束了,那么 tmp 指向的就是 timer_list_head,此时再执行 list_add_to_behind 函数时,不就会出现死循环的情况了吗?实际上,这个问题也不用担心。因为 list_add_to_behind 函数中,会将新节点插入到 entry 结点的后面。而 entry 结点就是 tmp 的前一个结点,它肯定不是 timer_list_head 结点,所以并不会出现死循环的情况。
希望我的回答能够帮到你。
对于第一个问题,因为这段代码在链表尾部添加了新节点,而不是按照expire_jiffies值从小到大排序插入新节点。如果要实现从小到大排序,应该从头结点开始遍历链表,找到第一个expire_jiffies值大于要插入节点的expire_jiffies值的节点,并将新节点插入到该节点之前。
对于第二个问题,可以在list_add_to_behind()函数中添加一个条件判断,如果链表为空,则直接将新节点插入到链表中。例如:
void list_add_to_behind(struct timer_list *list, struct timer_list *timer) {
if (list_is_empty(list)) {
list->next = timer;
timer->prev = list;
} else {
struct timer_list *node = list->next;
while (node != list && timer->expire_jiffies >= node->expire_jiffies) {
node = node->next;
}
timer->prev = node->prev;
timer->next = node;
node->prev->next = timer;
node->prev = timer;
}
}
对于第一个问题,你的理解是正确的,如果希望按照expire_jiffies的大小从小到大插入节点,则插入的节点应该在while循环内部。而现在的实现方式是在while循环之外,所以可能会导致前大后小的情况。
对于第二个问题,如果链表中所有节点的expire_jiffies值都比timer小,那么while循环中的判断条件将一直成立,但由于是双向循环链表,当temp移动到最后一个节点时,它的下一个节点是头结点,而头结点的expire_jiffies值应该是最小的,因此循环不会进入无限循环状态。
综上所述,红圈的部分的确存在第一个问题,如果希望节点按照expire_jiffies的大小从小到大插入,应该将插入操作放在while循环内部。至于第二个问题,可以放心使用。
第一个问题的解决方法:
在 while 循环内部插入新定时器节点前,需要先判断链表是否为空,如果为空,则直接插入到链表头部即可。
在 while 循环内部插入新定时器节点时,需要判断当前节点的 expire_jiffies 是否大于等于新定时器节点的 expire_jiffies,如果是,则插入到当前节点的前面;如果否,则继续向链表下一个节点移动,直到找到合适的位置插入新节点。如果链表已经遍历到最后一个节点仍然没有找到合适的位置,则说明新节点的 expire_jiffies 值大于链表中的所有节点,此时应该将新节点插入到链表的末尾。
void add_timer(struct timer_list * timer)
{
struct timer_list * tmp = container_of(list_next(&timer_list_head.list), struct timer_list, list);
if (list_is_empty(&timer_list_head.list))
{
list_add_to_behind(&timer_list_head.list, &timer->list);
return;
}
while (1)
{
if (tmp->expire_jiffies >= timer->expire_jiffies)
{
list_add_to_behind(tmp->list.prev, &timer->list);
break;
}
tmp = container_of(list_next(&tmp->list), struct timer_list, list);
if (tmp == container_of(&timer_list_head.list, struct timer_list, list))
{
list_add_to_behind(tmp->list.prev, &timer->list);
break;
}
}
}