猜数字游戏用python怎么解决
一.题目描述
实现一个经典"猜数字"游戏。
给定答案序列和用户猜的序列,统计有多少数字位置正确(A),有多少数字在两个序列都出现过但位置不对(B)。
输入包含多组数据。
每组输入第一行为序列长度n,第二行是答案序列,接下来是若干猜测序列。
猜测序列全0时该组数据结束。n=0时输入结束。
二.示例
样例输入:
4
1 3 5 5
1 1 2 3
4 3 3 5
6 5 5 1
6 1 3 5
1 3 5 5
0 0 0 0
10
1 2 2 2 4 5 6 6 6 9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5
1 2 1 3 1 5 1 6 1 9
1 2 2 5 5 5 6 6 6 7
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
样例输出:
(1,1)
(2,0)
(1,2)
(1,2)
(4,0)
(2,4)
(3,2)
(5,0)
(7,0)
解释:
输入:
第一行,数字表示答案是多少个数字组成的序列。第二行为答案序列。接下来每一行为猜测的序列。
输出:
接下来每一行括号内左边的数表示猜测序列中位置和值都猜对的个数(A),右边的数表示仅猜对值的个数(B)。
我的代码如下:
n = int(input())
l = []
while n != 0:
daan = [int(x) for x in input().split(' ')]
caice = [int(x) for x in input().split(' ')]
while any(caice):
a = 0
b = 0
for v in range(0, n): # 除第一次,剩下的不会进行比较
if daan[v] == caice[v]:
a += 1
for i in range(1, 10):
m = 0
n = 0
for j in range(0, n): # 完全没有进入此循环
if daan[j] == i:
m += 1
if caice[j] == i:
n += 1
if m < n:
b += m
else:
b += n
l.append([a, b - a])
caice = [int(x) for x in input().split(' ')]
n = int(input())
for i in l:
print('(%d,%d)' % (i[0], i[1]))
但我的结果:
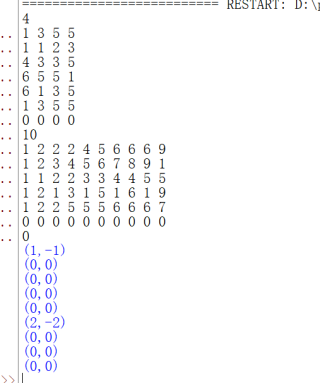
刚学python没多久,基本上是自己摸索,不太明白为什么会出现这样的问题,万分感谢各位解答
首先我们需要分析一下题意:
输入包含多组数据,每一组数据的第一行是序列的长度 n
第二行是答案序列
后面的行是猜测的序列,0 0 0 0 为猜测序列结束
n=0 时输入结束
那么我们可以使用循环语句实现对每一组数据的处理。
对于每一组数据,我们需要先读入 n 和答案序列,然后读入猜测序列,对每一个猜测序列,我们把与答案序列相同的数的个数统计出来,然后再统计与答案序列值相同但位置不同的数的个数。我们可以使用变量 A 和 B 分别记录猜测序列中位置和值都猜对的个数(A),仅猜对值的个数(B)。
在统计猜测序列与答案序列相同的数的个数时,我们可以使用 for 循环,枚举猜测序列的每一位,如果值相同,就将 A 的值加 1。
在统计猜测序列与答案序列值相同但位置不同的数的个数时,我们可以使用两个 for 循环,枚举猜测序列的每一位和答案序列的每一位,如果值相同且位置不同,就将 B 的值加 1。
下面是完整的代码:
while True:
# 读入 n
n = int(input())
if n == 0:
break
# 读入答案序列
ans = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 读入猜测序列
while True:
guess = list(map(int, input().split()))
if guess == [0] * n:
break
# 记录 A 和 B 的值
A = 0
B = 0
# 统计 A 的值
for i in range(n):
if ans[i] == guess[i]:
A += 1
# 统计 B 的值
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if ans[i] == guess[j] and i != j:
B += 1
# 输出结果
print(f'({A},{B})')
注意,在统计 B 的值时,我们需要判断 i 与 j 的位置是否相同,如果相同就不能统计。
上述代码可以通过示例数据进行测试。
另外,在统计 B 的值时,我们还可以使用一种不同的方法,即使用两个字典分别记录答案序列和猜测序列中每个数字的出现次数,然后遍历字典,对于答案序列和猜测序列中出现过的每个数字,取出答案序列字典中的值和猜测序列字典中的值的最小值,累加到 B 中。
下面是使用这种方法的代码:
while True:
# 读入 n
n = int(input())
if n == 0:
break
# 读入答案序列
ans = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 读入猜测序列
while True:
guess = list(map(int, input().split()))
if guess == [0] * n:
break
# 记录 A 和 B 的值
A = 0
B = 0
# 统计 A 的值
for i in range(n):
if ans[i] == guess[i]:
A += 1
# 统计 B 的值
ans_dict = {}
guess_dict = {}
for i in range(n):
if ans[i] not in ans_dict:
ans_dict[ans[i]] = 1
else:
ans_dict[ans[i]] += 1
if guess[i] not in guess_dict:
guess_dict[guess[i]] = 1
else:
guess_dict[guess[i]] += 1
for num in ans_dict:
if num in guess_dict:
B += min(ans_dict[num], guess_dict[num])
# 输出结果
print(f'({A},{B})')
同样,上述代码可以通过示例数据进行测试。
希望这个回答能帮到你!如果你还有其他问题,请随时追问。
完整实现代码如下,望采纳
def guess_number(answer, guess):
a = 0
b = 0
for i in range(len(answer)):
if answer[i] == guess[i]:
a += 1
elif guess[i] in answer:
b += 1
return (a, b)
while True:
n = int(input())
if n == 0:
break
answer = list(map(int, input().split()))
while True:
guess = list(map(int, input().split()))
if all(x == 0 for x in guess):
break
print(guess_number(answer, guess))