java面对对象初级
设计一个类,用来表示点,其中包含计算两点之间距离的方法,
该怎么操作呀,没有思路。/头秃
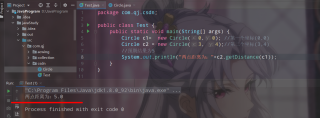
public class Circle {
public double x; //x坐标
public double y; //y坐标
public Circle(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
//计算两点距离的方法
public double getDistance(Circle c){
double distance=0;
double rdistance = (c.x - this.x) * (c.x - this.x) + (c.y - this.y) * (c.y - this.y);//距离平方和
return Math.sqrt(rdistance);
}
}
你这个问题的代码的设计思路:找到两个点在坐标中的x轴之间的距离以及y轴之间的距离,两个点当中,其中一个点的x轴和另外一个点的y轴的交点就可以类似的看做原点,然后就能用所求的x轴之间的距离和y轴之间的距离利用勾股定理求斜边的方式求出两个点的距离了。
下面的代码是我之前做过的一个,坐标轴中该点到原点的距离。
①先创建一个类体现两个点的在坐标中x轴和y轴的位置;并画出相对应的坐标图形
②创建一个方法计算这个点到原点的位置
public class XY {
int xlength;
int ylength;
int dis;
public XY() {
}
public XY(int xlength, int ylength,int dis) {
this.xlength = xlength;
this.ylength = ylength;
this.dis = dis;
}
public int getXlength() {
return xlength;
}
public void setXlength(int xlength) {
this.xlength = xlength;
}
public int getYlength() {
return ylength;
}
public void setYlength(int ylength) {
this.ylength = ylength;
}
public int getDis() {
return dis;
}
public void setDis(int dis) {
this.dis = dis;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("坐标如下:");
// 原点
System.out.print("0 ");
// x轴
for(int i = 0;i < xlength;i++){
System.out.print("—— ");
}
System.out.print(">X");
System.out.println();
// Y轴
for (int j = 0; j < ylength; j++) {
System.out.println("|");
System.out.println("");
}
System.out.println("Y");
}
public String distance(){
if (xlength == 0 && ylength != 0) {
dis = ylength;
}else if (xlength != 0 && ylength == 0) {
dis = xlength;
}else if (xlength != 0 && ylength != 0) {
dis = (int)(Math.sqrt(xlength * xlength + ylength * ylength ));
}else {
dis = 0;
}
// return getDis();
return "该点在坐标中为:" + "(" + xlength + "," + ylength + ")," +"距离原点为:" + dis;
}
}
③再测试创建的类中的方法
public class TestXY {
public static void main(String[] args) {
XY xy = new XY();
xy.setXlength(3);
xy.setYlength(4);
xy.show();
System.out.println(xy.distance());
}
}
面向对象设计思想早已不是什么新鲜事物,在Java实际项目中也是主流的编程思想。