Java怎么实现队列头部删除元素尾部插入元素啊?可以用两个栈,但是全部的实现代码我不会写,希望能够帮我解答一下
import java.util.Stack;
public class Demo08 {
static Stack<Object> A=new Stack<>();
static Stack<Object> B = new Stack<>();
public Demo08(){
}
public void add(int value){
A.push(value);
}
public int delete(){
while(!A.empty()){
B.push(A.pop());
}
int result = B.empty() ? -1 : B.pop();
while(!B.empty()){
A.push(B.pop());
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A.push("one");
A.push("two");
A.push("three");
B.push(3);
A.add(4);
System.out.println(A);
System.out.println(B);
}
}
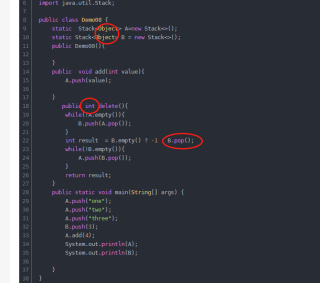
类型不对
我觉得应该用LinkedList呀
private static void testList() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<100000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++) {
list.remove(0);
}
System.out.println("用时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis()-start) + "毫秒");
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}