建立某链表的有关问题
建立一个链表,链表节点用于存储如下结构体:
struct Student
{ long num; //学号
char name[20]; //姓名
char sex; //性别
float score; //成绩
};
要求:使用函数和指针进行合理的编程,
建立链表
struct SLink
{ struct Student s;
struct SLink *next;
} *np;
,并设计如下函数:
1)createLink()生成一个空链表;
2)insertData(struct Student s)按学生学号由小到大的顺序,将s插入到链表合适的位置;
提示:使用np=(struct SLink *) malloc(sizeof(struct SLink)开辟内存以建立新节点。
3)deleteData(long num)删除学号为num的节点。
提示:使用free(np)释放被删除节点的内存;
4)printLink()顺序打印输出链表各节点的内容。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
long num; //学号
char name[20]; //姓名
char sex; //性别
float score; //成绩
};
struct SLink
{
struct Student s;
struct SLink* next;
} *np;
void createLink()
{
np = nullptr;
}
void insertData(struct Student s)
{
if (np == nullptr){
np = (struct SLink*)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
np->s = s;
np->next = nullptr;
return;
}
SLink* pPrevNode = nullptr;
SLink* pNode = np;
while (pNode) {
if (s.num <= pNode->s.num) {
if (pPrevNode == nullptr) {
np = (struct SLink*)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
np->s = s;
np->next = pNode;
}
else {
pPrevNode->next = (struct SLink*)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
pPrevNode->next->s = s;
pPrevNode->next->next = pNode;
}
break;
}
if (pNode->next == nullptr){
pNode->next = (struct SLink*)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
pNode->next->s = s;
pNode->next->next = nullptr;
break;
}
pPrevNode = pNode;
pNode = pNode->next;
}
}
void deleteData(long num)
{
SLink* pPrevNode = nullptr;
SLink* pNode = np;
while (pNode){
if (num == pNode->s.num){
if (pPrevNode == nullptr){
np = pNode->next;
}
else{
pPrevNode->next = pNode->next;
}
//SLink* pNext = pNode->next;
free(pNode);
break;
// pNode = pNext;
}
else{
pPrevNode = pNode;
pNode = pNode->next;
}
}
}
void printStudent(const Student& stud)
{
cout << stud.num << "\t" << stud.name << "\t" << (stud.sex ? "male" : "female") << "\t" << stud.score << endl;
}
void printLink()
{
cout << "num\t" << "name\t" << "sex\t" << "score" << endl;
SLink* pNode = np;
while (pNode) {
printStudent(pNode->s);
pNode = pNode->next;
}
}
int main(void)
{
createLink();
struct Student a {0, "a", true, 100};
struct Student b {10, "b", true, 90};
struct Student c {2, "c", true, 80};
struct Student d {3, "d", true, 100};
struct Student e {43, "e", true, 99};
struct Student f {5, "f", true, 60};
insertData(a);
insertData(b);
insertData(c);
insertData(d);
insertData(e);
insertData(f);
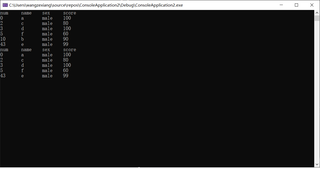
printLink();
deleteData(10);
printLink();
int i;
cin >> i;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
struct Student{
long num;
char name[20];
char sex;
float score;
};
typedef struct SLink
{
struct Student s;
struct SLink * next;
}*Np;
Np L = NULL;
void createLink(){
L = (Np)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
L->next = NULL;
}
void insertData(struct Student s){
Np p = L;
Np node = (Np)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
node->s = s;
node->next = NULL;
if (p->next == NULL)
p->next = node;
else{
while (p->next != NULL){
if (p->next->s.num > s.num){
Np node = (Np)malloc(sizeof(struct SLink));
node->s = s;
node->next = p->next;
p->next = node;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
if (p->next == NULL)
p->next = node;
}
}
void deleteData(long num){
Np p = L;
while (p->next != NULL){
if (p->next->s.num == num){
Np tmp = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void relaseData(){
Np p = L;
while (p->next != NULL){
Np tmp = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}
free(L);
L = NULL;
}
void printLink(){
Np p = L->next;
while (p != NULL){
cout << p->s.num << " " << p->s.name << " " << p->s.score << " " << p->s.sex << endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int main() {
createLink();
struct Student s = { 1, "sde", 1, 100 };
struct Student s1 = { 2, "weeu", 1, 10 };
struct Student s2 = { 5, "wsdfer", 2, 97 };
struct Student s3 = { 3, "weeu", 1, 10 };
insertData(s);
insertData(s1);
insertData(s2);
insertData(s3);
printLink();
deleteData(2);
printLink();
relaseData();
system("pause");
return 0;
}