Scanner同时读取数字和字符串时的问题
详见代码:
public static void test(){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
////////读取整数/////////
int a=0,b=0;
if (scanner.hasNextLine()) //会在这里挂起程序 相当与while(true) 直到键盘输入回车
{
a=scanner.nextInt();
b=scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(a+" "+b);
/*//////读取double////////*/
double c=0,d=0;
if (scanner.hasNextDouble()){
c=scanner.nextDouble();
d=scanner.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println(c+" "+d);
//////////////读取字符数组 空格分开/////////////////////////
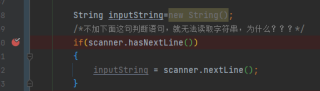
String inputString=new String();
/*不加下面这句判断语句,就无法读取字符串,为什么???*/
if(scanner.hasNextLine())
{
scanner.nextLine();
}
inputString=scanner.nextLine();
String[] strings=inputString.split(" ");
char[] chars=new char[strings.length];
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
chars[i]=strings[i].charAt(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]+" ");
}
}
通过debug可以很容易发现问题,在图中的位置加上端点
在调试时强制进入就能看到下边的结果
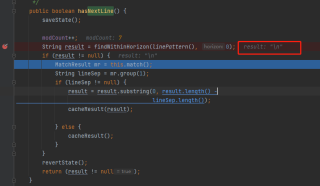
由此我们就可以知道,其实不是无法读到,而是读到了‘\n’也就是换行这个不可见字符
scanner.hasNextLine(),他要知道是否有换行,然后根据换行符改变状态值然后继续读取下一行,如果不执行这段代码,程序自己也不知道还有没有后续的行
前面用hasNextLine(),那么后面要用 nextLine() 来处理输入;
后面用 nextInt() 方法的话,那么前面要使用 hasNext()方法去判断
这其实就是判断是否有下一行输入,如果不加,没法判断是否有下一行,就获取不到字符串。
你把这句代码提到最前面,他也是能直接获取到字符串的