树的单旋转问题(c语言实现)
最近在学《数据结构与算法分析》这本书,里面的AVL树的单旋转代码把我搞蒙了
如下

我自己刚学,在纸上模拟插入时破坏了AVL平衡特性时如何单旋转的情况
如下
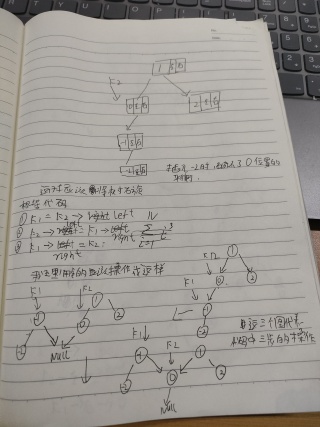
这样还是树的结构吗,请问具体错在哪里呢,希望有人指点一下具体代码的实现流程。
我建议你看看这一篇https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/Just-monika/solution-p3369
呀 今天刚好学这个平衡树
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int n = 1000019;
int root, tot;
struct node{
int size, rank, cnt, ls, rs, val;
}a[n];
int New(int val)
{
a[++tot].val = val;
a[tot].cnt = a[tot].size = 1;
a[tot].rank = rand();
a[tot].ls = a[tot].rs = 0;
return tot;
}
void push_up(int node)
{
a[node].size = a[a[node].ls].size + a[a[node].rs].size + a[node].cnt;
}
/*
mode:
0 左旋
1 右旋
*/
void rotate(int &id, int mode)
{
int tmp;
if (!mode){
tmp = a[id].rs;
a[id].rs = a[tmp].ls;
a[tmp].ls = id;
id = tmp;
push_up(a[id].ls);
}
else {
tmp = a[id].ls;
a[id].ls = a[tmp].rs;
a[tmp].rs = id;
id = tmp;
push_up(a[id].rs);
}
}
void insert(int &id, int val)
{
if (!id) {
id = New(val);
return;
}
if (val == a[id].val) {
a[id].cnt++;
push_up(id); // 这里千万不要忘记了, size代表的是以它为根的 树的大小 cnt: 只是说这个节点有多少个, 找这个错误几个小时 fuck...
return;
}
if (val < a[id].val) {
insert(a[id].ls, val);
if (a[id].rank < a[a[id].ls].rank)
rotate(id, 1);
}
else {
insert(a[id].rs, val);
if (a[id].rank < a[a[id].rs].rank)
rotate(id, 0);
}
push_up(id);
}
void del(int &id, int val)
{
if (!id) return;
if (val == a[id].val)
{
if (a[id].cnt > 1) {
a[id].cnt--;
push_up(id);
return;
}
else if(a[id].ls * a[id].rs == 0) {
id = a[id].ls + a[id].rs;
}
else if (a[a[id].ls].rank > a[a[id].rs].rank) {
rotate(id, 1);
del(a[id].rs, val); // id旋转到当前右子树 继续删, 直到成为叶子节点
}
else {
rotate (id, 0);
del(a[id].ls, val);
}
push_up(id);
}
if (val < a[id].val) del(a[id].ls, val);
else del(a[id].rs, val);
push_up(id);
}
int get_rank(int id, int val)
{
if (!id) return 0;
if (val == a[id].val) return a[a[id].ls].size + 1;
else if (val < a[id].val) return get_rank(a[id].ls, val);
else return a[a[id].ls].size + a[id].cnt + get_rank(a[id].rs, val);
}
int get_pos(int id, int pos)
{
if (!id) return 0;
if (pos <= a[a[id].ls].size) return get_pos(a[id].ls, pos);
else if (pos <= a[a[id].ls].size + a[id].cnt) return a[id].val;
else return get_pos(a[id].rs, pos - a[a[id].ls].size - a[id].cnt);
}
int get_pre(int id, int val)
{
int ans = 0;
while(id){
if (val > a[id].val) ans = a[id].val, id = a[id].rs;
else id = a[id].ls;
}
return ans;
}
int get_nex(int id, int val)
{
int ans = 0;
while(id) {
if (a[id].val > val) ans = a[id].val, id = a[id].ls;
else id = a[id].rs;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int q; scanf("%d", &q);
while(q--)
{
int op, x; scanf("%d%d", &op, &x);
if (op == 1) insert(root, x);
if (op == 2) del(root, x);
if (op == 3) printf("%d\n", get_rank(root, x));
if (op == 4) printf("%d\n", get_pos(root, x ));
if (op == 5) printf("%d\n", get_pre(root, x));
if (op == 6) printf("%d\n", get_nex(root, x));
}
return 0;
}
介绍一个 LL 的单旋, RR 的也是类似的,就是水平翻转一下。
1、LL
1)算法原理
LL,即往左子树的左子树插入一个结点。这种情况下,如果树出现了不平衡的情况,根结点的当前平衡因子一定是 +2。
如图所示,假设树 $T$ 的高度为 $h$,那么,左子树 $L$ 的高度为 $h-1$,$L$ 的左子树 $L_L$ 的高度为 $h-2$。$T_1$,$T_2$,$T_3$,$T_4$ 的树高均为 $h-3$。

对上述的树,进行一个右旋,如下:

得到结果如图所示:

这一步操作完成后,我们发现,$L$、$T$、$L_L$这三棵子树都已经平衡了,看不懂没有关系,让我们来看下详细的变换过程:

如图所示,总共发生了三个关系的变化:
1)结点 $T$ 和 $L$ 交换了父子关系,参见图中的 「 绿色箭头 」;
2)$T_3$ 的父结点从原先的 $L$ 变成了 $T$,参见图中的「 橙色箭头 」;
3)树的根结点,从原先的 $T$,变成了 $L$;
2)源码详解
PTreeNode RRotate(PTreeNode T) {
PTreeNode L = T->left; // (1)
T->left = L->right; // (2)
L->right = T; // (3)
AVLCalcHeight(T); // (4)
AVLCalcHeight(L); // (5)
return L; // (6)
}
- $(1)$ $L$ 作为 $T$ 的左孩子结点,缓存一下;
- $(2)$ 将 $L$ 的右子树作为 $T$ 的左子树,对应上文 「 橙色箭头 」 做的事情;
- $(3)$ 将 $T$ 作为 $L$ 的右子树,对应上文 「 绿色箭头 」 做的事情;
- $(4)$ $T$ 的左孩子结点产生变化,所以需要重新计算树高;
- $(5)$ $L$ 是 $T$ 的父结点,$T$ 的树高变了,$L$ 的树高自然也需要重新计算;
- $(6)$ 将原先的 $L$ 作为新的树根返回;