关于strcpy,strcat,开辟空间问题(求大佬指点)
#pragma warning (disable:4996)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
protected:
char* str;
public:
String();
String(const char* content);
String(const String& cstr);
~String();
void set(const char* content);
int length() const;
void print() const;
String& operator=(const String& cstr);
String& operator=(const char* cstr);
char& operator[](int index);
operator char* ();
friend String operator+(const String& cstr1, const String& cstr2);
friend String operator+(const String& cstr1, const char* cstr2);
friend String operator+(const char* cstr1, const String& cstr2);
friend String& operator++(String& cstr);
friend String operator++(String& cstr, int);
};
String::String()
{
str = 0;
}
String::String(const char* content)
{
int len = strlen(content);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, content);
}
String::String(const String& cstr)
{
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr.str);
}
String::~String()
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
}
void String::set(const char* content)
{
int len = strlen(content);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, content);
}
int String::length() const
{
int len = strlen(str);
return len;
}
void String::print() const
{
cout << "字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
String& String::operator=(const String& cstr)
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr.str);
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* cstr)
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
int len = strlen(cstr);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr);
return *this;
}
char& String::operator[](int index)
{
return str[index];
}
String::operator char* ()
{
return str;
}
String operator+(const String& cstr1, const String& cstr2)
{
String cp1;
int len = strlen(cstr1.str) + strlen(cstr1.str);
cp1.str = new char[len+1];
strcpy(cp1.str, cstr1.str);
strcat(cp1.str, cstr2.str);
return cp1;
}
String operator+(const String& cstr1, const char* cstr2)
{
String cp2;
int len = strlen(cstr1.str) + strlen(cstr2);
cp2.str = new char[len+1 ];
strcpy(cp2.str, cstr1.str);
strcat(cp2.str, cstr2);
return cp2;
}
String operator+(const char* cstr1, const String& cstr2)
{
String cp3;
int len = strlen(cstr1) + strlen(cstr2.str);
cp3.str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(cp3.str, cstr1);
strcat(cp3.str, cstr2.str);//先复制用strcpy,将\0复制最后面,然后strcat的内容将\0覆盖最后结尾加了一个\0.(理论感觉可以,但实际操作却有的成功,有的失败了)
return cp3;
}
String& operator++(String& cstr)
{
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (cstr.str[i] >= 'a' && cstr.str[i] <= 'z')
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i] - 32;
else
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i];
}
return cstr;
}
String operator++(String& cstr, int)
{
String cp4(cstr.str);
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (cstr.str[i] >= 'a' && cstr.str[i] <= 'z')
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i] - 32;
else
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i];
}
return cp4;
}
int main()
{
char* nstr;
char zemb[7] = "hdjj";
nstr = zemb;
String temp1("Sgd");
String temp2("bhd");//把这里改成“gdhfjkvb”则无法运行成功
String temp7, temp8;
temp7 = temp1;
temp8 = nstr;
temp7.print();
temp8.print();
String temp3 = temp1 + temp2;
temp3.print();
String temp4;
temp4 = temp1 + nstr;
temp4.print();
String temp5;
temp5 = nstr + temp1;
temp5.print();
++temp1;
temp1.print();
String temp6;
temp6 = temp2++;
temp6.print();
return 0;
}
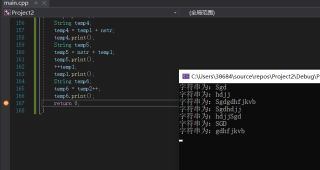
改完就对了。
strcpy好用,不过我经常用memcpy
可以看一下strcpy 和 strcat是怎么操作内存的。
strcpy函数:
原型声明:extern char *strcpy(char* dest, const char *src);
头文件:#include
功能:把从src地址开始且含有NULL结束符的字符串复制到以dest开始的地址空间
说明:src和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳src的字符串。
返回指向dest的指针。
2. strcat函数:
原型:
extern char *strcat(char *dest,char *src)
头文件:
#include <string.h>
在C++中,则存在于<cstring>头文件中。
功能:
把src所指字符串添加到dest结尾处(覆盖dest结尾处的'\0')并添加'\0'。
说明:
src和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳src的字符串。
返回指向dest的指针。
是不是由于gdhfjkvb导致数组越界了。
cp3.str的字符长度必须超过2个字符串相加的总长度。

这里写错了
String operator+(const String& cstr1, const String& cstr2)
{
String cp1;
int len = strlen(cstr1.str) + strlen(cstr2.str);
cp1.str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(cp1.str, cstr1.str);
strcat(cp1.str, cstr2.str);
return cp1;
}strlen(cstr2.str);
#pragma warning (disable:4996)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
protected:
char* str;
public:
String();
String(const char* content);
String(const String& cstr);
~String();
void set(const char* content);
int length() const;
void print() const;
String& operator=(const String& cstr);
String& operator=(const char* cstr);
char& operator[](int index);
operator char* ();
friend String operator+(const String& cstr1, const String& cstr2);
friend String operator+(const String& cstr1, const char* cstr2);
friend String operator+(const char* cstr1, const String& cstr2);
friend String& operator++(String& cstr);
friend String operator++(String& cstr, int);
};
String::String()
{
str = 0;
}
String::String(const char* content)
{
int len = strlen(content);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, content);
}
String::String(const String& cstr)
{
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr.str);
}
String::~String()
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
}
void String::set(const char* content)
{
int len = strlen(content);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, content);
}
int String::length() const
{
int len = strlen(str);
return len;
}
void String::print() const
{
cout << "字符串为:" << str << endl;
}
String& String::operator=(const String& cstr)
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr.str);
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* cstr)
{
if (str != 0)
delete[]str;
int len = strlen(cstr);
str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(str, cstr);
return *this;
}
char& String::operator[](int index)
{
return str[index];
}
String::operator char* ()
{
return str;
}
String operator+(const String& cstr1, const String& cstr2)
{
String cp1;
int len = strlen(cstr1.str) + strlen(cstr2.str);
cp1.str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(cp1.str, cstr1.str);
strcat(cp1.str, cstr2.str);
return cp1;
}
String operator+(const String& cstr1, const char* cstr2)
{
String cp2;
int len = strlen(cstr1.str) + strlen(cstr2);
cp2.str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(cp2.str, cstr1.str);
strcat(cp2.str, cstr2);
return cp2;
}
String operator+(const char* cstr1, const String& cstr2)
{
String cp3;
int len = strlen(cstr1) + strlen(cstr2.str);
cp3.str = new char[len + 1];
strcpy(cp3.str, cstr1);
strcat(cp3.str, cstr2.str);//先复制用strcpy,将\0复制最后面,然后strcat的内容将\0覆盖最后结尾加了一个\0.(理论感觉可以,但实际操作却有的成功,有的失败了)
return cp3;
}
String& operator++(String& cstr)
{
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (cstr.str[i] >= 'a' && cstr.str[i] <= 'z')
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i] - 32;
else
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i];
}
return cstr;
}
String operator++(String& cstr, int)
{
String cp4(cstr.str);
int len = strlen(cstr.str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (cstr.str[i] >= 'a' && cstr.str[i] <= 'z')
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i] - 32;
else
cstr.str[i] = cstr.str[i];
}
return cp4;
}
int main()
{
char* nstr;
char zemb[7] = "hdjj";
nstr = zemb;
String temp1("Sgd");
String temp2("gdhfjkvb");//把这里改成“gdhfjkvb”则无法运行成功
String temp7, temp8;
temp7 = temp1;
temp8 = nstr;
temp7.print();
temp8.print();
String temp3 = temp1 + temp2;
temp3.print();
String temp4;
temp4 = temp1 + nstr;
temp4.print();
String temp5;
temp5 = nstr + temp1;
temp5.print();
++temp1;
temp1.print();
String temp6;
temp6 = temp2++;
temp6.print();
return 0;
}
是的,有些错误
C和C++完整教程:https://blog.csdn.net/it_xiangqiang/category_10581430.html
您好,我是有问必答小助手,您的问题已经有小伙伴解答了,您看下是否解决,可以追评进行沟通哦~
如果有您比较满意的答案 / 帮您提供解决思路的答案,可以点击【采纳】按钮,给回答的小伙伴一些鼓励哦~~
ps:问答VIP仅需29元,即可享受5次/月 有问必答服务,了解详情>>>https://vip.csdn.net/askvip?utm_source=1146287632
非常感谢您使用有问必答服务,为了后续更快速的帮您解决问题,现诚邀您参与有问必答体验反馈。您的建议将会运用到我们的产品优化中,希望能得到您的支持与协助!
速戳参与调研>>>https://t.csdnimg.cn/Kf0y