STM32串口通信无法接收数据
问题遇到的现象和发生背景
我想使用STM32开发板编程与OpenMV模块进行串口通信,代码编译没有问题OpenMV也能够正常发送数据出来,当时好像STM32开发板没有办法正常接收OpenMV接收到的数据
针脚设置:

遇到的现象和发生背景
STM32开发板没有正常接收到数据
代码
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2023 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
#include "usart.h"
#include "gpio.h"
#include "stdio.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
#ifdef __GNUC__ //串口重定向
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1 , (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
/* USER CODE END PFP */
void SystemClock_Config(void);
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
while (1)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin ( GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_SET ) ;
HAL_GPIO_WritePin ( GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_SET ) ;
HAL_GPIO_WritePin ( GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_SET ) ;
HAL_GPIO_WritePin ( GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_SET ) ;
}
}
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSI_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLMUL = RCC_PLL_MUL16;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
int theta_err,rho_err;
void Optical_Flow_Receive_Prepare(uint8_t data)
{
/* 局部静态变量:接收缓存 */
static uint8_t RxBuffer[10];
/* 数据长度 *//* 数据数组下标 */
static uint8_t _data_cnt = 0;
/* 接收状态 */
static uint8_t state = 0;
/* 帧头1 */
if(state==0&&data== 0x2C )
{
state=1;
}
/* 帧头2 */
else if(state==1&&data== 0x12 )
{
state=2;
_data_cnt = 0;
}
/* 接收数据租 */
else if(state==2)
{
RxBuffer[++_data_cnt]=data;
if(_data_cnt>=8)
{
state = 0;
Data_Processing(RxBuffer,_data_cnt);
}
}
/* 若有错误重新等待接收帧头 */
else
state = 0;
}
void Data_Processing(uint8_t *data_buf,uint8_t num)
{
int theta_org,rho_org;
/* 读取偏移角度原始数据 */
theta_org = (int)(*(data_buf+1)<<0) | (int)(*(data_buf+2)<<8) | (int)(*(data_buf+3)<<16) | (int)(*(data_buf+4)<<24) ;
theta_err = theta_org;
/* 读取偏移尺寸原始数据 */
rho_org = (int)(*(data_buf+5)<<0) | (int)(*(data_buf+6)<<8) | (int)(*(data_buf+7)<<16) | (int)(*(data_buf+8)<<24) ;
rho_err = rho_org;
}
运行结果及详细报错内容
对应的A56针脚没有电压反应
我的解答思路
是不是针脚设置有问题还是说是代码的编译有问题
怎么样才能够正常的接收数据呢
- 帮你找了个相似的问题, 你可以看下: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7620210
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: 超详细OpenMV与STM32单片机通信 (有完整版源码)中的 6.学习补充 (代码看不懂的时候可以来看一下) 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
补充1:static关键字(静态变量)的使用
static 修饰全局函数和全局变量,只能在本源文件使用。举个例子,比如用以下语句
static u8 RxBuffer[10]定义了一个名为RxBuffer的静态数组,数组元素类型为unsigned char型。在包含Rxbuffer的源文件中,Rxbuffer相当于一个全局变量,任意地方修改RxBuffer的值,RxBuffer都会随之改变。而且包含RxBuffer的函数在多次运行后RxBuffer的值会一直保存(除非重新赋值)。在C语言学习中,利用static关键字求阶乘是一个很好的例子:#include“stdio.h” long fun(int n); void main() { int i,n; printf("input the value of n:"); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { printf("%d! = %1d\n",i,fun(i)); } } >long fun(int n) { static long p=1; p=p*n; return p; }效果为依次输出n!(n=1,2,3…n)
这个例子中,第一次p的值为1,第二次p的值变成了p x n=1 x 2=2,这个值会一直保存,如果p没有定义为静态类型,那么在第一次运算过后p的值会重新被赋值为1,这就是auto型(不声明默认为auto型)与static型的最大区别。总结:static关键字定义的变量是全局变量,在static所包含的函数多次运行时,该变量不会被多次初始化,只会初始化一次。
补充2:extern关键字(外部变量)的使用
程序的编译单位是源程序文件,一个源文件可以包含一个或若干个函数。在函数内定义的变量是局部变量,而在函数之外定义的变量则称为外部变量,外部变量也就是我们所讲的全局变量。它的存储方式为静态存储,其生存周期为整个程序的生存周期。全局变量可以为本文件中的其他函数所共用,它的有效范围为从定义变量的位置开始到本源文件结束。
如果整个工程由多个源文件组成,在一个源文件中想引用另外一个源文件中已经定义的外部变量,同样只需在引用变量的文件中用 extern 关键字加以声明即可。下面就来看一个多文件的示例:/****max.c****/ #include <stdio.h> /*外部变量声明*/ extern int g_X ; extern int g_Y ; int max() { return (g_X > g_Y ? g_X : g_Y); } /***main.c****/ #include <stdio.h> /*定义两个全局变量*/ int g_X=10; int g_Y=20; int max(); int main(void) { int result; result = max(); printf("the max value is %d\n",result); return 0; } 运行结果为: the max value is 20对于多个文件的工程,都可以采用上面这种方法来操作。对于模块化的程序文件,可在其文件中预先留好外部变量的接口,也就是只采用 extern 声明变量,而不定义变量,max.c 文件中的 g_X 与 g_Y 就是如此操作的。比如想要在主函数中调用usart.c中的变量x,usart.c中有着这样的定义:
static u8 x=0在usart.h中可以这样写:extern u8 x在main.c中包含usart.h头文件,这样在编译的时候就会在main.c中调用x外部变量。总结:extern关键字是外部变量,静态类型的全局变量,可以在源文件中调用其他文件中的变量,在多文件工程中配合头文件使用。
补充3:MicroPython一些库函数的解释
1.ustruct.pack函数:
import ustruct,在ustruct中data = ustruct.pack("<bbhhhhb", #格式为俩个字符俩个短整型(2字节) 0x2C, #帧头1 0x12, #帧头2 int(cx), # up sample by 4 #数据1 int(cy), # up sample by 4 #数据2 int(cw), # up sample by 4 #数据1 int(ch), # up sample by 4 #数据2 0x5B)""bbhhhhb"简单来说就是要发送数据的声明,bbhhhhb共七个,代表发送七个数据,对照下面的表,可以知道七个数据按时序发送为unsigner char、unsigned char、short、short、short、short、unsigned char。0x2c为数据帧的帧头,即检测到数据流的开始,但是一个帧头可能会出现偶然性,因此设置两个帧头0x2c与0x12以便在中断中检测是否检测到了帧头以便存放有用数据。0x5b为帧尾,即数据帧结束的标志。
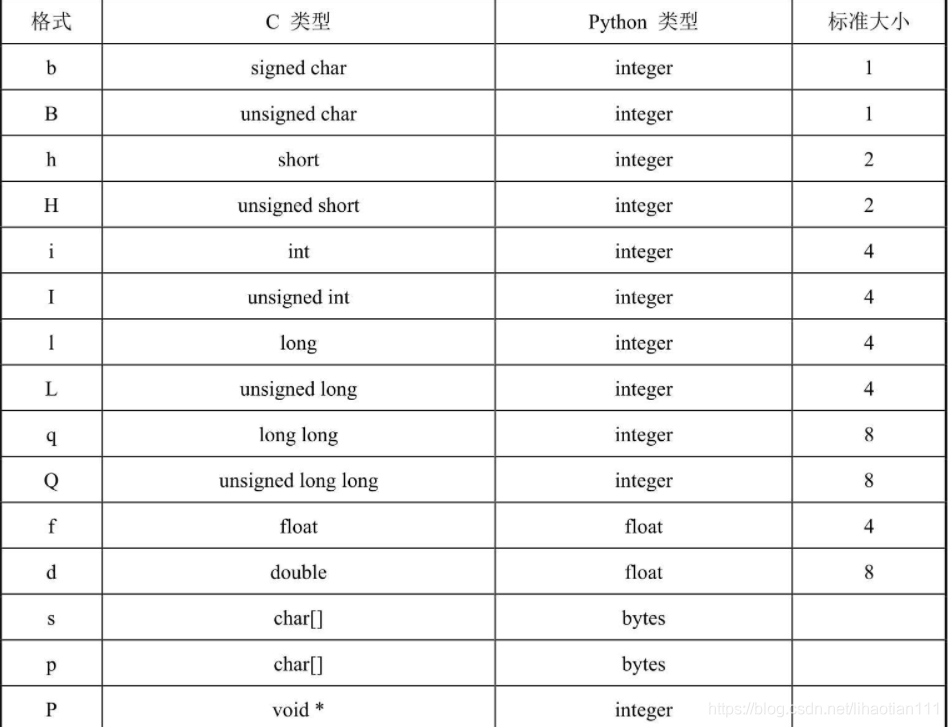
2.bytearray([ , , , ])函数:
用于把十六进制数据以字节形式存放到字节数组中,以便以数据帧的形式发送出去进行通信。FH = bytearray([0x2C,0x12,cx,cy,cw,ch,0x5B]) uart,write(FH)