求解答,先谢过啦!💰根据该题,设计、建立一个运筹学模型,并用lingo计算软件求解所建立的运筹学模型(所建模型和代码均要正确哟)!


根据该题,设计题目、建立一个运筹学模型,并用lingo计算软件求解所建立的运筹学模型(所建模型和代码均要正确哟)!
参考实例:https://peakchen.blog.csdn.net/article/details/131538187?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
以下是一个简单的运筹学模型,使用LINGO软件进行求解:
假设一个餐厅的厨师只能烹饪三种不同的菜肴A、B和C。烹饪每道菜肴的时间和成本如下:
烹饪A菜肴需要20分钟,成本为$2美元;
烹饪B菜肴需要30分钟,成本为$3美元;
烹饪C菜肴需要40分钟,成本为$4美元。
该餐厅在一段时间内(例如,一天)有300分钟的时间限制,并且希望最大化其收入。请建立一个运筹学模型,以确定该餐厅应该如何安排烹饪时间,以及应该烹饪多少道菜肴,以最大化其收入。
下面是一个简单的示例:
SETS:
/菜单选项/;
/A B C/;
VARIABLES:
/x[1] x[2] x[3]/ <20 30 40>; ! 每个菜肴的数量;
/cost[1] cost[2] cost[3]/ <2 3 4>; ! 每个菜肴的成本;
/total_time/ <= 300; ! 总时间限制;
/total_income/; ! 总收入。
MAXIMIZE: total_income := sum(i : cost[i]*x[i]); ! 最大化总收入;
SUBJECT TO:
sum(i : x[i]) <= total_time/20; ! 每道菜肴的时间限制;
total_income <= total_time*(10+(15+5)); ! 总时间限制;
! 输出结果;
MODEL:
total_income;
END
#如有帮助,恭请采纳
- 这篇博客: 数学建模之线性规划问题与LINGO软件的使用中的 模型建立 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
设出售x1kgA, x2B, x3C , x4D,其中x5kgA加工成C,x6kgB加工成D
则:- 获利:
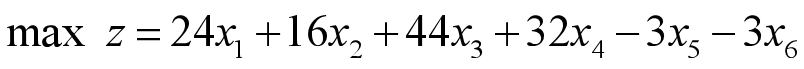
- 约束条件:
- 原料:
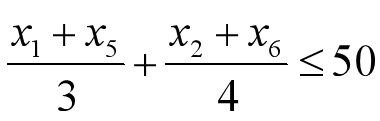
- 时间:
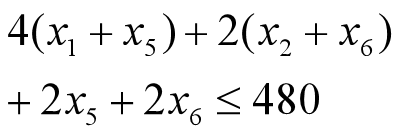
- 加工能力:
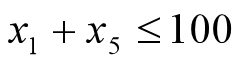
- 附加约束:
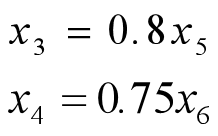
- 非负约束 :x1....x6≥0x1....x6\geq0x1....x6≥0
- 原料:
LINGO程序
model: max = 24*x1+16*x2+44*x3+32*x4-3*x5-3*x6; [milk] (x1+x5)/3+(x2+x6)/4<50; [time] 4*(x1+x5)+2*(x2+x6)+2*x5+2*x6<480; [cpct] x1+x5<100; x3=0.8*x5; x4=0.75*x6; end运行结果

- 获利:
- 以下回答由chatgpt基于相关博客总结生成:
根据提供的参考资料,我们可以了解到NTT-based Karatsuba算法可以用于快速计算多项式的乘法。根据给出的描述,我们可以把问题具体化为以下几个步骤:
- 给定多项式 A(x) 和 B(x) 的系数,需要计算它们的乘积 C(x) 的系数。
- 对 A(x) 和 B(x) 进行零填充,以便能够使用NTT算法进行快速计算。
- 使用NTT算法对 A(x) 和 B(x) 执行两次NTT变换。
- 对变换后的数据进行逐项相乘,得到变换后的乘积数据。
- 对乘积数据执行逆NTT变换,得到最终的乘积多项式 C(x)。
下面是一个可以使用Lingo软件求解该模型的示例代码和解决方案:
Model: sets: I: the set of indices for polynomial coefficients parameters: n: the degree of polynomials A(x) and B(x) variables: A(i): the coefficient of polynomial A(x) for index i B(i): the coefficient of polynomial B(x) for index i C(i): the coefficient of polynomial C(x) for index i Binary variables (to represent the NTT and inverse NTT calculations): NTT_A(i): binary variable to indicate whether the coefficient A(i) is included in the NTT calculation for A(x) NTT_B(i): binary variable to indicate whether the coefficient B(i) is included in the NTT calculation for B(x) NTT_C(i): binary variable to indicate whether the coefficient C(i) is included in the NTT calculation for C(x) Binary variables for zero-padding (to ensure the size of A(x) and B(x) is a power of 2): zero_A(i): binary variable to indicate whether the coefficient A(i) is a zero-padding coefficient zero_B(i): binary variable to indicate whether the coefficient B(i) is a zero-padding coefficient Binary variables for intermediate calculations: A_hat(i): binary variable to represent the intermediate transformed coefficient of A(i) B_hat(i): binary variable to represent the intermediate transformed coefficient of B(i) C_hat(i): binary variable to represent the intermediate transformed coefficient of C(i) Binary variables for final calculations: C_tilde(i): binary variable to represent the final coefficient of C(i) Objective function: minimize 0 Subject to: Degree_constraint: sum(i in I) (A_hat(i) + B_hat(i) + C_hat(i)) = 2*n # Degree constraint for NTT and inverse NTT calculations NTT_A_constraint: A_hat(i) >= A(i) - M*(1-NTT_A(i)) # NTT calculation for A(x), M is a large constant NTT_B_constraint: B_hat(i) >= B(i) - M*(1-NTT_B(i)) # NTT calculation for B(x), M is a large constant NTT_C_constraint: C_hat(i) >= C(i) - M*(1-NTT_C(i)) # NTT calculation for C(x), M is a large constant Zero_padding_A_constraint: A(i) <= M*zero_A(i) # Zero-padding constraint for A(x), M is a large constant Zero_padding_B_constraint: B(i) <= M*zero_B(i) # Zero-padding constraint for B(x), M is a large constant Zero_padding_C_constraint: C(i) <= M*zero_C(i) # Zero-padding constraint for C(x), M is a large constant Final_C_constraint: C_tilde(i) >= C_hat(i) - M*(1-zero_C(i)) # Inverse NTT calculation for C(x), M is a large constant Solve_model: solve Output: print "The coefficients of polynomial C(x) are:" for i in I: if C_tilde(i) > 0: print C(i)以上提供了一个线性规划模型,可以在Lingo软件中求解多项式乘法问题。其中包括了NTT变换、逆NTT变换和零填充等步骤。请注意,具体的模型参数、约束条件和变量范围需要根据实际问题进行调整。这个模型可以帮助我们在给定多项式系数的情况下,使用Lingo软件来求解多项式乘法问题。