数据结构邻接表问题C语言
根据输入的邻接表矩阵创建图的邻接表,然后进行遍历操历操作。
(1)输入图的邻接表矩阵数据
(2)创建图的邻接表并数出
(3)按照DFS遍历输出
(4)按照BFS遍历输出
要求输入:
顶点个数n
邻接矩阵nxn
顶点编号(DFS起点)
顶点编号(BFS起点)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 图的邻接表节点
struct Node {
int vertex;
Node* next;
};
// 创建图的邻接表
vector<Node*> createGraph(int n, int** matrix) {
vector<Node*> adjacencyList(n, nullptr);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Node* current = nullptr;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->vertex = j;
newNode->next = nullptr;
if (current == nullptr) {
adjacencyList[i] = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
}
}
}
return adjacencyList;
}
// DFS遍历
void DFS(vector<Node*>& adjacencyList, int start) {
vector<bool> visited(adjacencyList.size(), false);
stack<int> s;
s.push(start);
while (!s.empty()) {
int current = s.top();
s.pop();
if (!visited[current]) {
cout << current << " ";
visited[current] = true;
Node* temp = adjacencyList[current];
while (temp != nullptr) {
s.push(temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
}
// BFS遍历
void BFS(vector<Node*>& adjacencyList, int start) {
vector<bool> visited(adjacencyList.size(), false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!visited[current]) {
cout << current << " ";
visited[current] = true;
Node* temp = adjacencyList[current];
while (temp != nullptr) {
q.push(temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cout << "请输入顶点个数n:";
cin >> n;
int** matrix = new int*[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i] = new int[n];
cout << "请输入邻接矩阵第 " << i+1 << " 行的数据(以空格分隔):";
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> matrix[i][j];
}
}
int dfsStart, bfsStart;
cout << "请输入DFS起点的顶点编号:";
cin >> dfsStart;
cout << "请输入BFS起点的顶点编号:";
cin >> bfsStart;
vector<Node*> adjacencyList = createGraph(n, matrix);
cout << "DFS遍历结果为:";
DFS(adjacencyList, dfsStart);
cout << endl;
cout << "BFS遍历结果为:";
BFS(adjacencyList, bfsStart);
// 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
delete[] matrix[i];
}
delete[] matrix;
return 0;
}


- 这篇博客: 数据结构实验9_图的遍历(无向邻接矩阵图的构建、递归DFS、非递归DFS、非递归BFS)中的 数据结构实验9_图的遍历 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
- (1)实验目的
通过该实验,使学生掌握图的几种存储结构,理解图的深度优先和广度优先遍历算法的思想和实现办法, - (2)实验内容
实现教材算法7.2利用邻接矩阵构造无向图的算法,在此基础上进行深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历。 - (3)参考界面

(4)验收/测试用例
创建所示无向图
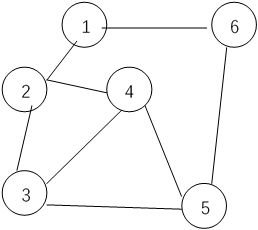
屏幕输出邻接矩阵
0 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 0
0 0 1 1 0 1
1 0 0 0 1 0深度优先遍历
屏幕输出: 1 2 3 4 5 6广度优先遍历
屏幕输出:1 2 6 3 4 5
- (1)实验目的