关于List里迭代器Iterator的语法问题
在学习List的视频课程中,视频里说道ArrayList的搜索删除的几个写法。其中他说道用foreach语句删除的时候,是会出现ConcurrentModificationException异常,而且是无法解决。
下列为案例程序
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1号位置");
list.add("Java");
list.add("Java");
list.add("2号位置");
list.add("3号位置");
list.add("4号位置");
System.out.println(list);
下列foreach内容会报错,而且由于迭代器被隐藏了,然后就没法解决的
for (String s : list) {
if("Java".equals(s)){
list.remove(s);
}
}
然后我改了上述程序内容,把迭代器给弄出来,按道理来说应该是可以解决报错问题点,但是还是报错了,为什么呢?不是说只要应用迭代器的remove方法就不会有超出集合范围的风险吗?
for (String s : list) {
if("Java".equals(s)){
list.iterator().remove();
}
}

你使用要迭代器的方法不对,不是直接 list.iterator().remove(),而是循环迭代器再使用迭代器删除,修改如下:
Iterator<String> s = list.iterator();
while (s.hasNext()){
String v = s.next();
if(v.equals("Java")) {
s.remove();
}
}
list.iterator().remove()要配合迭代器自己的遍历方法去使用
你只要是在增强for循环的过程中修改list的长度,一定会报错
- 这篇博客: List在foreach循环的时候remove(ConcurrentModificationException)中的 (1)ArrayList的内部Iterator理解: 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
其实foreach语法糖在实际执行的时候是通过迭代器(Iterator)实现的, 主要用了上图的hasNext()和next() 看一下ArrayList的Iterator。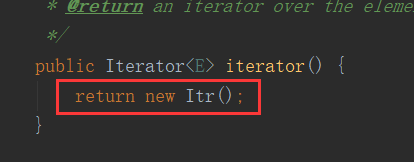
返回了内部类Itr
下面是itr 源码:/** * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr */ private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }先我们看一下它的几个成员变量:
cursor:表示下一个要访问的元素的索引,从next()和hasNext方法的具体实现都可以看出。 lastRet:表示上一个访问的元素的索引
lastRet:表示上一个访问的元素的索引
expectedModCount:表示对ArrayList修改次数的期望值,它的初始值为modCount。
modCount是AbstractList类中的一个成员变量:他代表着list被修改的次数初始值为0protected transient int modCount = 0;该值表示对List的修改次数,add()、remove()、addAll()、removeRange()
及clear()方法。这些方法每调用一次,modCount的值就加1。注:add()及
addAll()方法的modCount的值是在其中调用的ensureCapacity()方法中增
加的。- 以下回答由chatgpt基于相关博客总结生成:
很抱歉,根据您提供的参考资料和问题描述,我并没有发现任何明确的语法问题需要解决。段落0和段落1提供了关于使用List迭代器Iterator的示例代码,段落1还解释了为什么使用for循环时操作List会导致ConcurrentModificationException异常。如果您有特定的问题或需求,请提供更多信息,我会尽力提供帮助。