这段代码是什么意思啊,希望讲解一下
@GetMapping("/toWebScenicSpotListPage")
public ModelAndView toWebScenicSpotListPage(ModelAndView modelAndView,
Integer type, Long page, Long limit,
ScenicSpot scenicSpot) {
List<ScenicType> scenicTypeList = scenicTypeService.getListData();
条件分页查询列表数据
- 这有个类似的问题, 你可以参考下: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7513467
- 你也可以参考下这篇文章:调整微服务代码结构的一些常见技术
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: 弹性动画的实现中的 指示器弹性滑动,效果如下 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:

首先,黄色的指示器是一个imageview,我们通过改变它的leftMargin值,即属性动画来达到滑动的效果,要用属性动画给view设置动画的时候,要求view必须具有set和get,但是这有一个问题,imageview的leftMargin属性并没有提供get方法和set方法,因此我们要写一个包装类为其添加这两个方法public class ViewWrapper { private View mTarget; //这里的params必须是传入控件的父布局的params!! // 当然也可以直接在构造函数中传入params, 这样会保险点 , // 不过params需要有下面的mParams.leftMargin 。。等对应方法!! private RelativeLayout.LayoutParams mParams ; public ViewWrapper(View target) { mTarget = target; mParams = (RelativeLayout.LayoutParams) mTarget.getLayoutParams(); } public int getLeftMargin() { return mParams.leftMargin; } public void setLeftMargin(int margin) { mParams.setMargins(margin,0,0,0); mTarget.requestLayout(); } }如上所示,我们提供了getLeftMargin和setLeftMargin方法;
接着在我们点击指示器对应的tab时,调用setMarginAnimation方法,传入LeftMargin的起始值和结束值。setMarginAnimation方法中我们使用了上文提到的工具类private void setMarginAnimation(int startValue,int endValue){ spring = new PrincipleSpring(300, 20); spring.setListener(new PrincipleSpring.PrincipleSpringListener() { @Override public void onPrincipleSpringStart(float value) { Log.d(TAG, "onPrincipleSpringStart: value = " + value); } @Override public void onPrincipleSpringStop(float value) { Log.d(TAG, "onPrincipleSpringStop: value = " + value); } @Override public void onPrincipleSpringUpdate(float value) { Log.d(TAG, "onPrincipleSpringUpdate: value = " + value); int currentValue = (int) value; new ViewWrapper(iv_tab_line).setLeftMargin(currentValue); } }); spring.start(startValue, endValue); }rebound实现的弹性动画执行时间是跟传入的摩擦力和拉力有关。如果摩檫力为0,则动画会一直执行下去,摩擦力越大,动画执行时间越少。
rebound的效果是模拟弹簧振子的阻尼振动,根据牛顿运动定律,可以用如下微分方程表示: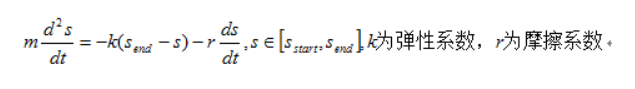
- 您还可以看一下 孙玖祥老师的图解数据结构与算法课程中的 背包问题代码实现小节, 巩固相关知识点