C++申请类对象数组内存大小的问题
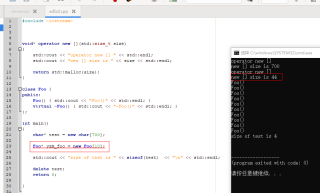
如图,为啥申请了44字节的内存,而不是40字节。
类对象4字节,申请了10个,不应该是40字节吗?
附代码
#include <iostream>
void* operator new [](std::size_t size)
{
std::cout << "operator new [] " << std::endl;
std::cout << "new [] size is " << size << std::endl;
return std::malloc(size);
}
class Foo {
public:
Foo() { std::cout << "Foo()" << std::endl; }
virtual ~Foo() { std::cout << "~Foo()" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
char* test = new char[700];
Foo* yzm_foo = new Foo[10];
std::cout << "size of test is " << sizeof(test) << "\n" << std::endl;
delete test;
return 0;
}
还有一个虚函数指针4字节。虚函数内部类似指针实现,不同类对象指向不同的实现。
虚函数指针也会占用空间
如果是空的类(类内没有数据成员,成员函数不占用内存)占用1字节,也就是如果你去掉的话,这里就变成一个字节了。
有虚函数的占用4字节(X86机器,也就是32位机,你目前就是),也就是一个指针的大小,并且无论有多少个虚函数都是占用4字节。
相应的,如果是64位机器,则变更为8个字节
- 这个问题的回答你可以参考下: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7418188
- 这篇博客也不错, 你可以看下(c++)从键盘输入任意20个整型数,统计其中的负数个数并求所有正数的平均值。 保留两位小数
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: C++函数模板特化,类模板特化中的 2. 类模板的特化:与函数模板类似,当类模板内需要对某些类型进行特别处理时,使用类模板的特化。 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或跳转源博客中阅读:
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include"tt.h" // general version template<class T> class Compare { public: static bool IsEqual(const T& lh, const T& rh) { std::cout << "in the general class..." << std::endl; return lh == rh; } }; // specialize for float template<> class Compare<float> { public: static bool IsEqual(const float& lh, const float& rh) { std::cout << "in the float special class..." << std::endl; return std::abs(lh - rh) < 10e-3; } }; // specialize for double template<> class Compare<double> { public: static bool IsEqual(const double& lh, const double& rh) { std::cout << "in the double special class..." << std::endl; return std::abs(lh - rh) < 10e-6; } }; int main(void) { Compare<int> comp1; std::cout << comp1.IsEqual(3, 4) << std::endl; std::cout << comp1.IsEqual(3, 3) << std::endl; Compare<float> comp2; std::cout << comp2.IsEqual(3.14, 4.14) << std::endl; std::cout << comp2.IsEqual(3, 3) << std::endl; Compare<double> comp3; std::cout << comp3.IsEqual(3.14159, 4.14159) << std::endl; std::cout << comp3.IsEqual(3.14159, 3.14159) << std::endl; std::cout << hh<string>()("11") << std::endl; system("pause"); return 0; }其中tt.h如下:
#include<string> using std::string; template<typename key> class hh { public: size_t operator()(const key& k) const { size_t hashVal = 0; key tmp = k; while (tmp > 0) { hashVal = 37 * hashVal + tmp % 10; tmp /= 10; } return hashVal; } }; template<> class hh<string> { public: size_t operator()(const string& key) { size_t hashVal = 0; std::cout << key << std::endl; for (char ch : key) { std::cout << "hasVal: " << hashVal << std::endl; hashVal = 37 * hashVal + ch; } return hashVal; } };- 您还可以看一下 夏曹俊老师的C++ 设计模式原理与实战大全-架构师需备课程课程中的 完成控制器、模型、视图的抽象工厂模式创建小节, 巩固相关知识点