进程的同步与互斥,解决进程的同步与互斥问题
/***************************************************************/
/* PROGRAM NAME: PRODUCER_CONSUMER */
/* This program simulates two processes, producer which */
/* continues to produce message and put it into a buffer */
/* [implemented by PIPE], and consumer which continues to get */
/* message from the buffer and use it. */
/* The program also demonstrates the synchronism between */
/* processes and uses of PIPE. */
/***************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#define PIPESIZE 8
#define PRODUCER 0
#define CONSUMER 1
#define RUN 0 /* statu of process */
#define WAIT 1 /* statu of process */
#define READY 2 /* statu of process */
#define NORMAL 0
#define SLEEP 1
#define AWAKE 2
#include <stdio.h>
struct pcb { char *name;
int statu;
int time; }; /* times of execution */
struct pipetype { char type;
int writeptr;
int readptr;
struct pcb *pointp; /* write wait point */
struct pcb *pointc; }; /* read wait point */
int pipe[PIPESIZE];
struct pipetype pipetb;
struct pcb process[2];
main()
{ int output,ret,i;
char in[2];
int runp(),runc(),prn();
pipetb.type = 'c'; pipetb.writeptr = 0; pipetb.readptr = 0;
pipetb.pointp = pipetb.pointc = NULL;
process[PRODUCER].name = "Producer\0";
process[CONSUMER].name = "Consumer\0";
process[PRODUCER].statu = process[CONSUMER].statu = READY;
process[PRODUCER].time = process[CONSUMER].time = 0;
output = 0;
printf("Now starting the program!\n");
printf("Press 'p' to run PRODUCER, press 'c' to run CONSUMER.\n");
printf("Press 'e' to exit from the program.\n");
for(i=0;i<1000;i++) { in[0]='N';
while(in[0]=='N') { scanf("%s",in);
if(in[0]!='e'&&in[0]!='p'&&in[0]!='c') in[0]='N';}
if(in[0]=='e') { printf("Program completed!\n"); exit(0); }
if(in[0]=='p'&&process[PRODUCER].statu==READY) {
output = (output+1)% 100 ;
if((ret=runp(output,process,pipe,&pipetb,PRODUCER))==SLEEP)
pipetb.pointp = &process[PRODUCER];
if(ret==AWAKE) {
(pipetb.pointc)->statu=READY; pipetb.pointc=NULL;
runc(process,pipe,&pipetb,CONSUMER); }
}
if(in[0]=='c'&&process[CONSUMER].statu==READY) {
if((ret=runc(process,pipe,&pipetb,CONSUMER))==SLEEP)
pipetb.pointc = &process[CONSUMER];
if(ret==AWAKE) {
(pipetb.pointp)->statu=READY; pipetb.pointp=NULL;
runp(output,process,pipe,&pipetb,PRODUCER); }
}
if(in[0]=='p'&&process[PRODUCER].statu==WAIT)
printf("PRODUCER is waiting, can't be scheduled.\n");
if(in[0]=='c'&&process[CONSUMER].statu==WAIT)
printf("CONSUMER is waiting, can't be scheduled.\n");
prn(process,pipe,pipetb); in[0]='N'; }
}
runp(out,p,pipe,tb,t) /* run producer */
int out,pipe[],t;
struct pcb p[];
struct pipetype *tb;
{ p[t].statu = RUN; printf("run PRODUCER. product %d ",out);
if(tb->writeptr>=PIPESIZE) { p[t].statu=WAIT; return(SLEEP); }
pipe[tb->writeptr]=out; tb->writeptr++; p[t].time++;
p[t].statu=READY; if((tb->pointc)!=NULL) return(AWAKE);
return(NORMAL);
}
runc(p,pipe,tb,t) /* run consumer */
int pipe[],t;
struct pcb p[];
struct pipetype *tb;
{ int c;
p[t].statu = RUN; printf("run CONSUMER. ");
if(tb->readptr>=tb->writeptr) { p[t].statu=WAIT; return(SLEEP); }
c = pipe[tb->readptr]; tb->readptr++;
printf(" use %d ",c);
if(tb->readptr>=tb->writeptr) tb->readptr=tb->writeptr=0;
p[t].time++; p[t].statu=READY;
//if(tb->pointp!=NULL)
if((tb->readptr)==0&&(tb->pointp)!=NULL) return(AWAKE);
return(NORMAL);
}
prn(p,pipe,tb)
int pipe[];
struct pipetype tb;
struct pcb p[];
{ int i;
printf("\n "); for(i=0;i<PIPESIZE;i++) printf("------ ");
printf("\n |");
for(i=0;i<PIPESIZE;i++)
if((i>=tb.readptr)&&(i<tb.writeptr)) printf(" %2d |",pipe[i]);
else printf(" |");
printf("\n "); for(i=0;i<PIPESIZE;i++) printf("------ ");
printf("\nwriteptr = %d, readptr = %d, ",tb.writeptr,tb.readptr);
if(p[PRODUCER].statu==WAIT) printf("PRODUCER wait ");
else printf("PRODUCER ready ");
if(p[CONSUMER].statu==WAIT) printf("CONSUMER wait ");
else printf("CONSUMER ready ");
printf("\n");
}
用高级语言模拟生产者消费者问题的实现(缓冲区容量为8),但是该程序存在缺陷,不能循环利用缓冲区,当出现如下图所示的情况时,表示有两个空闲的缓冲区,但运行程序时生产者却不能放置产品,请修改程序以得到正确的运行结果


你好想问一下这个代码哪里错了呢?谢谢不知道你这个问题是否已经解决, 如果还没有解决的话:
- 你可以参考下这个问题的回答, 看看是否对你有帮助, 链接: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7709728
- 你也可以参考下这篇文章:7.15 写函数输入职工姓名和工号,排序,以及使用折半查找法根据工号查找姓名
- 除此之外, 这篇博客: 猜数(含代码)计算机自动随机生成一个数,用户通过输入数字来猜数,来与随机数进行匹配并显示正确与否中的 猜数(含代码)计算机自动随机生成一个数,用户通过输入数字来猜数,来与随机数进行匹配并显示正确与否 部分也许能够解决你的问题, 你可以仔细阅读以下内容或者直接跳转源博客中阅读:
本人实际经验仅供参考
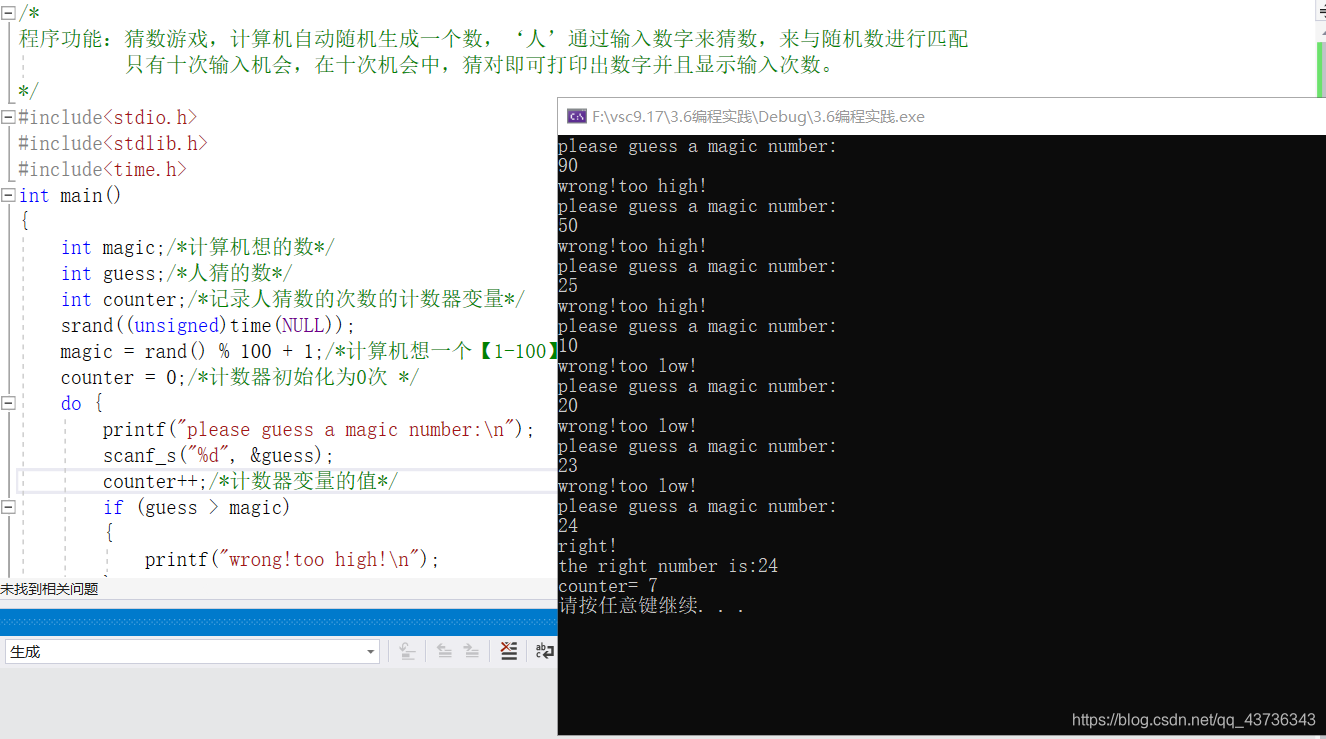
以下是程序的运行结果以下为程序代码
/*
程序功能:猜数游戏,计算机自动随机生成一个数,‘人’通过输入数字来猜数,来与随机数进行匹配
只有十次输入机会,在十次机会中,猜对即可打印出数字并且显示输入次数。
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
int magic;/计算机想的数/
int guess;/人猜的数/
int counter;/记录人猜数的次数的计数器变量/
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
magic = rand() % 100 + 1;/*计算机想一个【1-100】之间的数,即为magic */
counter = 0;/*计数器初始化为0次 */
do {
printf(“please guess a magic number:\n”);
scanf_s("%d", &guess);
counter++;/计数器变量的值/
if (guess > magic)
{
printf(“wrong!too high!\n”);
}
else if (guess < magic)
{
printf(“wrong!too low!\n”);
}
else
{
printf(“right!\n”);
printf(“the right number is:%d\n”, magic);
}
}while (guess != magic && counter<10);
printf(“counter= %d\n”, counter);
system(“pause”);
return 0;
} - 您还可以看一下 刘城龙老师的教你快速查找电脑中的文件课程中的 快速按文件内容查找文件的方法小节, 巩固相关知识点
如果你已经解决了该问题, 非常希望你能够分享一下解决方案, 写成博客, 将相关链接放在评论区, 以帮助更多的人 ^-^