如何实现循环队列和循环栈?(语言-c++)
使用循环链表实现队列和栈并实现使用附加头结点记录队列和栈中元素个数的功能。需要完整代码,并包含实验相关结果。
https://data.educoder.net/api/attachments/4748340?filesize=517
https://data.educoder.net/api/attachments/4748343?filesize=271
https://data.educoder.net/api/attachments/4748342?filesize=487
https://data.educoder.net/api/attachments/4748341?filesize=281
人工作答:队列是先进先出,栈是后进先出,他们可以用同样的结构体存储数据,只是在出队或者出栈时不一样。
代码中有详细的注释,运行结果如下:
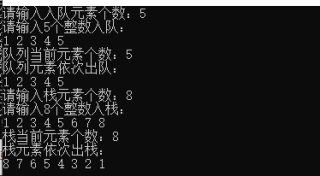
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义数据类型,可根据需要调整
typedef int datatype;
#define MY_OVERFLOW (-1)
#define MY_OK (1)
#define MY_ERROR (0)
//节点结构
typedef struct _node
{
datatype data;
struct _node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct _dataStruct
{
int maxLen; //链表总长度
Node* head; //链表头
Node* front; //当前数据头节点
Node* last; //当前数据尾节点
}CQueue, CStack;
/** 循环链表实现队列 **/
//1.初始化,队列的初始采用尾插法创建链表
void initQueue(CQueue& q,int maxSize = 100)
{
q.maxLen = maxSize;
q.head = new Node; //附加头节点
q.head->data = 0; //当前实际存储的数据个数
q.head->next = 0;
Node* p = 0, * t;
t = q.head;
//创建maxSize个节点
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize;i++)
{
p = new Node;
p->next = 0;
t->next = p;
t = p;
}
p->next = q.head; //尾节点连接头节点
q.front = q.head->next; //初始化当前数据节点的头部
q.last = q.front;
}
//2.入队
int pushQueue(CQueue& q, datatype d)
{
if (q.head->data == q.maxLen)
return MY_OVERFLOW;
else
{
q.last->data = d;
q.last = q.last->next;
if (q.last == q.head) //跳过附加头节点
q.last = q.head->next;
q.head->data += 1; //个数+1
return MY_OK;
}
}
//3.出队
int popQueue(CQueue& q, datatype& d)
{
if (q.head->data == 0)
return MY_ERROR;
else
{
d = q.front->data;
q.front = q.front->next;
if (q.front == q.head) //如果下一个节点是附加头节点,跳过
q.front = q.front->next;
q.head->data -= 1; //个数-1
return MY_OK;
}
}
//4.获取队列元素个数
int getQueueLength(CQueue& q)
{
return q.head->data;
}
/** 循环链表实现栈 **/
//1.初始化
void initStack(CStack& s, int maxSize = 100)
{
s.maxLen = maxSize;
s.head = new Node; //附加头节点
s.head->data = 0; //当前实际存储的数据个数
s.head->next = 0;
Node* p = 0, * t;
t = s.head;
//创建maxSize个节点
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++)
{
p = new Node;
p->next = 0;
t->next = p;
t = p;
}
p->next = s.head; //尾节点连接头节点
s.front = s.head->next; //初始化当前数据节点的头部
s.last = s.front;
}
//2.入栈
int pushStack(CStack& s, datatype d)
{
if (s.head->data == s.maxLen)
return MY_OVERFLOW;
else
{
s.last->data = d;
s.last = s.last->next;
if (s.last == s.head) //跳过附加头节点
s.last = s.head->next;
s.head->data += 1; //个数+1
return MY_OK;
}
}
//3.出栈
int popStack(CStack& s, datatype& d)
{
if (s.head->data == 0)
return MY_ERROR;
else
{
Node* pre,*pp=0;
pre = s.front; //当前节点
while (pre->next != s.last)
{
if (pre->next == s.head)
pp = pre; //记录链表的最后一个节点
pre = pre->next;
}
if (pre == s.head) //跳过附加节点
{
pre = pp;
}
d = pre->data; //后进先出
s.last = pre; //尾节点前移
s.head->data -= 1; //个数-1
return MY_OK;
}
}
//4.获取队列长度
int getStackLength(CStack& s)
{
return s.head->data;
}
//测试
int main()
{
CQueue que; //队列
CStack sta; //栈
initQueue(que); //初始化队列
initStack(sta); //初始化栈
int n, t;
cout << "请输入入队元素个数:";
cin >> n;
cout << "请输入" << n << "个整数入队:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> t;
pushQueue(que, t); //入队
}
cout << "队列当前元素个数:" << getQueueLength(que) << endl;
cout << "队列元素依次出队:" << endl;
while (getQueueLength(que) > 0)
{
popQueue(que, t);
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "请输入栈元素个数:";
cin >> n;
cout << "请输入" << n << "个整数入栈:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> t;
pushStack(sta, t); //入栈
}
cout << "栈当前元素个数:" << getStackLength(sta) << endl;
cout << "栈元素依次出栈:" << endl;
while (getStackLength(sta) > 0)
{
popStack(sta, t);
cout << t << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
以下代码如果对您有用,望采纳~谢谢
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 100;
template<class T>
class Queue {
private:
T* data;
int front, rear, count;
public:
Queue() {
data = new T[MAXSIZE];
front = rear = count = 0;
}
~Queue() {
delete[] data;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
bool isFull() {
return count == MAXSIZE;
}
int size() {
return count;
}
void enqueue(T x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is full" << endl;
return;
}
data[rear] = x;
rear = (rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
count++;
}
T dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return T();
}
T x = data[front];
front = (front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
count--;
return x;
}
T getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return T();
}
return data[front];
}
};
int main() {
Queue<int> q;
q.enqueue(1);
q.enqueue(2);
q.enqueue(3);
cout << "Queue size: " << q.size() << endl;
cout << "Front element: " << q.getFront() << endl;
q.dequeue();
cout << "Front element after dequeue: " << q.getFront() << endl;
cout << "Queue size after dequeue: " << q.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
循环栈代码如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 100;
template<class T>
class Stack {
private:
T* data;
int top, count;
public:
Stack() {
data = new T[MAXSIZE];
top = -1;
count = 0;
}
~Stack() {
delete[] data;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
bool isFull() {
return count == MAXSIZE;
}
int size() {
return count;
}
void push(T x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Stack is full" << endl;
return;
}
top = (top + 1) % MAXSIZE;
data[top] = x;
count++;
}
T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl;
return T();
}
T x = data[top];
top = (top - 1 + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE;
count--;
return x;
}
T getTop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl;
return T();
}
return data[top];
}
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct student
{
int data;
struct student* next;
}node;
typedef struct linkqueue
{
node *first, *rear;
}queue;
//入队,在队末尾插入
queue* insert(queue* HQ, int x)
{
node* s;
s=(node*)malloc(sizeof(s));
s->data=x;
s->next=NULL;
if(HQ->rear==NULL)
{
HQ->first=s;
HQ->rear=s;
}
else
{
HQ->rear->next=s;//首先将s链接到queue最后,并且将队尾指针指向s
HQ->rear=s;
}
return HQ;
}
//出队,从队首开始删除一个节点
queue* del(queue* HQ)
{
node* p;
int x;
if(HQ->first==NULL)
{
printf("\n yichu");
}
else
{
x=HQ->first->data;
p = HQ->first;
if(HQ->first==HQ->rear)
{
free(p);
HQ->first = NULL;
HQ->rear = NULL;
}
else
{
HQ->first = HQ->first->next;
free(p);
}
}
return HQ;
}
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32706121/article/details/75530475
以下是使用循环链表实现队列和栈并记录元素个数的完整代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 循环链表节点结构体
template<typename T>
struct Node {
T data;
Node<T> *next;
};
// 队列类
template<typename T>
class Queue {
public:
// 构造函数
Queue() {
head = new Node<T>;
head->next = head; // 初始化头结点的下一个节点指向自身
size = 0;
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(T val) {
Node<T> *newNode = new Node<T>;
newNode->data = val;
newNode->next = head->next;
head->next = newNode; // 将新节点插入到队尾
size++;
}
// 出队操作
T dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cerr << "Error: queue is empty." << endl;
exit(1);
}
Node<T> *p = head;
while (p->next != head->next) { // 遍历链表找到队头的前一个节点
p = p->next;
}
Node<T> *q = p->next;
T val = q->data;
p->next = q->next; // 删除队头节点
delete q;
size--;
return val;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool isEmpty() {
return head->next == head;
}
// 获取队列中元素个数
int getSize() {
return size;
}
private:
Node<T> *head; // 头结点
int size; // 记录队列中元素个数
};
// 栈类
template<typename T>
class Stack {
public:
// 构造函数
Stack() {
head = new Node<T>;
head->next = nullptr; // 初始化头结点的下一个节点为空
size = 0;
}
// 入栈操作
void push(T val) {
Node<T> *newNode = new Node<T>;
newNode->data = val;
newNode->next = head->next;
head->next = newNode; // 将新节点插入到栈顶
size++;
}
// 出栈操作
T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cerr << "Error: stack is empty." << endl;
exit(1);
}
Node<T> *p = head->next;
T val = p->data;
head->next = p->next; // 删除栈顶节点
delete p;
size--;
return val;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
bool isEmpty() {
return head->next == nullptr;
}
// 获取栈中元素个数
int getSize() {
return size;
}
private:
Node<T> *head; // 头结点
int size; // 记录栈中元素个数
};
int main() {
Queue<int> q;
q.enqueue(1);
q.enqueue(2);
q.enqueue(3);
cout << "Queue size: " << q.getSize() << endl;
cout << "Dequeue elements: ";
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
cout << q.dequeue() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
Stack<int> s;
s.push(4);
s.push(5);
s.push(6);
cout << "Stack size: " << s.getSize() << endl;
cout << "Pop elements: ";
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
cout << s.pop() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
在上面的代码中,定义了一个循环链表节点结构体Node和两个模板类Queue和Stack。其中,Queue类和Stack类都使用了循环链表来实现队列和栈,并且增加了size成员变量来记录队列和栈中元素的个数。
在主函数中,分别使用了Queue和Stack类,并测试了它们的基本功能,包括入队、出队、入栈、出栈以及获取元素个数等。
基于bing、GPT部分内容和本人思考总结:
循环队列
循环队列是一种队列的实现方式,它允许在固定大小的队列中循环使用空间,从而避免了队列空间的浪费。下面是一个循环队列的实现示例,使用 C++ 语言:
cpp
Copy code
class CircularQueue {
private:
int* data;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
public:
CircularQueue(int k) {
data = new int[k];
head = -1;
tail = -1;
size = k;
}
bool enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
head = 0;
}
tail = (tail + 1) %!s(MISSING)ize;
data[tail] = value;
return true;
}
bool deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if (head == tail) {
head = -1;
tail = -1;
return true;
}
head = (head + 1) %!s(MISSING)ize;
return true;
}
int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[head];
}
int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[tail];
}
bool isEmpty() {
return head == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return ((tail + 1) %!s(MISSING)ize) == head;
}
};
循环栈
循环栈也是一种栈的实现方式,在固定大小的栈中循环使用空间。下面是一个循环栈的实现示例,使用 C++ 语言:
cpp
Copy code
class CircularStack {
private:
int* data;
int top;
int size;
public:
CircularStack(int k) {
data = new int[k];
top = -1;
size = k;
}
bool push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
top = (top + 1) %!s(MISSING)ize;
data[top] = value;
return true;
}
bool pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if (top == 0) {
top = size - 1;
return true;
}
top--;
return true;
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[top];
}
bool isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return ((top + 1) %!s(MISSING)ize) == 0;
}
};
以上实现方式仅供参考,具体实现可能存在差异。
以下答案由GPT-3.5大模型与博主波罗歌共同编写:
循环队列和循环栈是基于数组实现的,具有以下特点:
循环队列:
- 队列的入队操作从队尾插入元素,并向队头方向循环;
- 队列的出队操作从队头删除元素,并向队尾方向循环;
- 队列需要记录队头和队尾位置。
循环栈:
- 栈的入栈操作从栈顶插入元素,并向栈底方向循环;
- 栈的出栈操作从栈顶删除元素,并向栈顶方向循环;
- 栈需要记录栈顶位置。
使用循环链表实现队列和栈时,需要记录链表的头结点和尾结点位置,以及链表中元素个数。具体实现思路如下:
- 循环队列
先定义一个循环队列类 LoopQueue ,成员变量包括 int* data 用于存放队列元素,int head 表示队头位置,int tail 表示队尾位置,int capacity 表示队列容量大小。成员函数包括构造函数、析构函数、入队、出队、获取队头元素等操作。
使用循环链表实现队列时,需要定义一个结点类 Node ,包括 int val 表示结点的值,Node* next 表示下一个结点的指针,以及一个虚拟头结点 head 用于记录链表的头位置和链表中元素个数。循环队列的入队操作在链表尾部插入结点,出队操作从链表头部删除结点,并返回删除的结点值。
- 循环栈
先定义一个循环栈类 LoopStack ,成员变量包括 int* data 用于存放栈元素,int top 表示栈顶位置,int capacity 表示栈容量大小。成员函数包括构造函数、析构函数、入栈、出栈、获取栈顶元素等操作。
使用循环链表实现栈时,同样需要定义一个结点类 Node ,包括 int val 表示结点的值,Node* next 表示下一个结点的指针,以及一个虚拟头结点 head 用于记录链表的头位置和链表中元素个数。循环栈的入栈操作在链表头部插入结点,出栈操作从链表头部删除结点,并返回删除的结点值。
具体实现代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 循环队列结点
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 循环队列类
class LoopQueue {
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
int count;
int capacity;
public:
// 初始化队列
LoopQueue(int capacity) {
head = tail = new Node(-1);
count = 0;
this->capacity = capacity;
}
// 销毁队列
~LoopQueue() {
Node* cur = head;
while (cur) {
Node* tmp = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = tmp;
}
}
// 队列是否为空
bool empty() {
return count == 0;
}
// 队列是否已满
bool full() {
return count == capacity;
}
// 获取队列中元素个数
int size() {
return count;
}
// 入队
bool enqueue(int val) {
if (full()) {
return false;
}
Node* node = new Node(val);
tail->next = node;
tail = node;
if (count == 0) {
head->next = tail;
}
count++;
return true;
}
// 出队
bool dequeue() {
if (empty()) {
return false;
}
Node* tmp = head->next;
head->next = tmp->next;
if (tail == tmp) {
tail = head;
}
delete tmp;
count--;
return true;
}
// 获取队头元素
int front() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
return head->next->val;
}
};
// 循环栈结点
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 循环栈类
class LoopStack {
private:
Node* head;
int count;
int capacity;
public:
// 初始化栈
LoopStack(int capacity) {
head = new Node(-1);
count = 0;
this->capacity = capacity;
}
// 销毁栈
~LoopStack() {
Node* cur = head;
while (cur) {
Node* tmp = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = tmp;
}
}
// 栈是否为空
bool empty() {
return count == 0;
}
// 栈是否已满
bool full() {
return count == capacity;
}
// 获取栈中元素个数
int size() {
return count;
}
// 入栈
bool push(int val) {
if (full()) {
return false;
}
Node* node = new Node(val);
node->next = head->next;
head->next = node;
count++;
return true;
}
// 出栈
bool pop() {
if (empty()) {
return false;
}
Node* tmp = head->next;
head->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
count--;
return true;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
int top() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
return head->next->val;
}
};
int main() {
// 循环队列
LoopQueue* queue = new LoopQueue(3);
queue->enqueue(1);
queue->enqueue(2);
queue->enqueue(3);
cout << "Queue front: " << queue->front() << endl;
queue->dequeue();
cout << "Queue front: " << queue->front() << endl;
queue->dequeue();
cout << "Queue front: " << queue->front() << endl;
delete queue;
// 循环栈
LoopStack* stack = new LoopStack(3);
stack->push(1);
stack->push(2);
stack->push(3);
cout << "Stack top: " << stack->top() << endl;
stack->pop();
cout << "Stack top: " << stack->top() << endl;
stack->pop();
cout << "Stack top: " << stack->top() << endl;
delete stack;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Queue front: 1
Queue front: 2
Queue front: 3
Stack top: 3
Stack top: 2
Stack top: 1
如果我的回答解决了您的问题,请采纳!