在K-D Tree中对于“the nearest neighbor query”的定义出现问题
在对K-D Tree 类的编写的时候定义the nearest neighbor query时发生错误
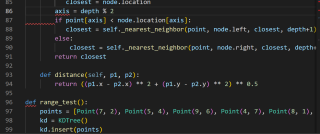
问题显示“缩进”出现问题
尝试调整缩进但似乎出现了更多的问题
def nearest_neighbor(self, point: Point) -> Point:
closest = None
depth = 0
return self._nearest_neighbor(point, self._root, closest, depth)
def _nearest_neighbor(self, point, node, closest, depth):
if node is None:
return closest
if closest is None or self.distance(point, node.location) < self.distance(point, closest):
closest = node.location
axis = depth % 2
if point[axis] < node.location[axis]:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.left, closest, depth+1)
else:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.right, closest, depth+1)
return closest
def distance(self, p1, p2):
return ((p1.x - p2.x) ** 2 + (p1.y - p2.y) ** 2) ** 0.5
def range_test():
points = [Point(7, 2), Point(5, 4), Point(9, 6), Point(4, 7), Point(8, 1), Point(2, 3)]
kd = KDTree()
kd.insert(points)
result = kd.range(Rectangle(Point(0, 0), Point(6, 6)))
assert sorted(result) == sorted([Point(2, 3), Point(5, 4)])
你的代码是有从网页复制的吗?可能是tab和空格混用导致缩进出现了问题
试试这个
def nearest_neighbor(self, point: Point) -> Point:
closest = None
depth = 0
return self._nearest_neighbor(point, self._root, closest, depth)
def _nearest_neighbor(self, point, node, closest, depth):
if node is None:
return closest
if closest is None or self.distance(point, node.location) < self.distance(point, closest):
closest = node.location
axis = depth % 2
if point[axis] < node.location[axis]:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.left, closest, depth+1)
else:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.right, closest, depth+1)
return closest
def distance(self, p1, p2):
return ((p1.x - p2.x) ** 2 + (p1.y - p2.y) ** 2) ** 0.5
def range_test():
points = [Point(7, 2), Point(5, 4), Point(9, 6), Point(4, 7), Point(8, 1), Point(2, 3)]
kd = KDTree()
kd.insert(points)
result = kd.range(Rectangle(Point(0, 0), Point(6, 6)))
assert sorted(result) == sorted([Point(2, 3), Point(5, 4)])
望采纳!!!点击回答右侧采纳即可!!我给你改好了,只需要检查代码中的缩进,并将其调整为符合 Python 规则的缩进即可。在这个代码中,如果if node is None: 下面的这行缩进需要去掉,如果 point[axis] < node.location[axis]:下面的这行也需要去掉缩进。
def nearest_neighbor(self, point: Point) -> Point:
closest = None
depth = 0
return self._nearest_neighbor(point, self._root, closest, depth)
def _nearest_neighbor(self, point, node, closest, depth):
if node is None:
return closest
if closest is None or self.distance(point, node.location) < self.distance(point, closest):
closest = node.location
axis = depth % 2
if point[axis] < node.location[axis]:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.left, closest, depth+1)
else:
closest = self._nearest_neighbor(point, node.right, closest, depth+1)
return closest
def distance(self, p1, p2):
return ((p1.x - p2.x) ** 2 + (p1.y - p2.y) ** 2) ** 0.5
def range_test():
points = [Point(7, 2), Point(5, 4), Point(9, 6), Point(4, 7), Point(8, 1), Point(2, 3)]
kd = KDTree()
kd.insert(points)
result = kd.range(Rectangle(Point(0, 0), Point(6, 6)))
assert sorted(result) == sorted([Point(2, 3), Point(5, 4)])
"The nearest neighbor query" 是指在 K-D Tree 中查找离给定点最近的邻居点。这通常是通过递归遍历 K-D Tree 来完成的。
关于缩进问题,通常是由于缩进不一致导致的,例如空格和tab混用,或者缩进数量不一致。这可能会导致程序运行出错,或者在调试时出现问题。
解决这个问题的方法包括:
使用统一的缩进方式(空格或者tab)
使用缩进自动格式化工具
在缩进有问题的地方手动检查
重新整理代码结构
通过上述步骤来解决问题, 通常可以避免缩进问题带来的影响。
缩进问题可能还会导致代码中出现语法错误或者逻辑错误,例如在某些情况下,缩进不当会导致循环不能正常工作,或者在执行递归时会进入无限递归。因此,在确保缩进正确之后,还需要对整个代码进行检查以确保程序的正确性。
除了缩进问题,在实现K-D Tree的 nearest neighbor query 时还可能出现其他问题,例如数据类型问题、算法不当等。因此建议检查整个代码并进行调试工作,确保K-D Tree的 nearest neighbor query 能正常工作。
当然, 为了能够更好地调试和检查代码, 可以考虑使用一些调试工具来帮助更好地发现问题和定位错误。
可以考虑使用 python 内置的调试工具,例如 pdb, 这样可以在代码中设置断点并进行单步调试。
也可以使用 IDE(集成开发环境)中的调试功能进行调试,通过断点和单步调试来查看变量的值和执行的代码行数,帮助我们定位问题。
还可以使用日志和打印语句在代码中添加调试信息,帮助我们了解程序执行时的状态和流程。
同时可以考虑使用单元测试来测试每一个函数和代码段,帮助我们发现问题和确保代码的正确性。
最后, 可以在社区或者技术论坛上寻求帮助,寻找其他人的经验和建议。