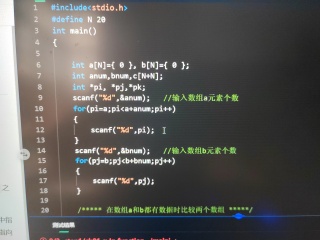
用指针实现两个有序数组合并一个有序数组
合并后数组从小到大
pi=a;
pj=b;
pk=c;
while (pi<a+anum&&pj<b+bnum)
{
if (*pi<*pj)
{
*pk=*pi;
pi++;
pk++;
}
else
{
*pk=*pj;
pj++;
pk++;
}
}
while (pi<a+anum)
{
*pk=*pi;
pi++;
pk++;
}
while (pj<b+bnum)
{
*pk=*pj;
pj++;
pk++;
}
这是一个用指针实现两个有序数组合并一个有序数组的 C 语言代码示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
void mergeArrays(int *a, int *b, int m, int n, int *c) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// Merge the two arrays until we reach the end of one of them
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (a[i] < b[j]) {
c[k] = a[i];
i++;
} else {
c[k] = b[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of the array that has elements left
while (i < m) {
c[k] = a[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j < n) {
c[k] = b[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
int main(void) {
int a[5] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int b[3] = {2, 4, 6};
int m = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
int n = sizeof(b) / sizeof(b[0]);
int *c = malloc((m + n) * sizeof(int));
mergeArrays(a, b, m, n, c);
for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++) {
printf("%d ", c[i]);
}
printf("\n");
free(c);
return 0;
}