数据结构图的基本操作(DFS,BFS算法实现)
图的基本操作
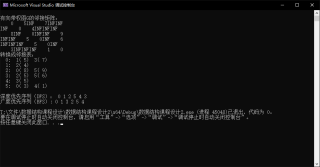
如图,如何在此代码基础上两种存储类型(邻接表,邻接矩阵)实现_DFS,BFS的、递归,非递归算法_!!
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define INF 32767
typedef int InfoType;
#define MAXV 100
//领接矩阵类型的定义
typedef struct
{
int no;
InfoType info;
}VertexType;
//图的定义
typedef struct
{
int edges[MAXV][MAXV];
int n, e;
VertexType vex[MAXV];
}MGraph;
//领接表类型的定义
typedef struct ANode
{
int adjvex;
struct ANode* nextarc;
InfoType info;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct Vnode
{
int data;
int count;
ArcNode* firstarc;
}VNode;
typedef VNode AdjList[MAXV];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjlist;
int n, e;
}ALGraph;
int visited[MAXV];
//将领接矩阵g转换成邻接表G
void MatToList(MGraph g, ALGraph*& G)
{
int i, j, n = g.n;
ArcNode* p;
G = (ALGraph*)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
G->adjlist[i].firstarc = NULL;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
for (j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (g.edges[i][j] > 0 && g.edges[i][j] < INF)
{
p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex = j;
p->info = g.edges[i][j];
p->nextarc = G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
G->adjlist[i].firstarc = p;
}
G->adjlist[i].count = 0;
}
G->n = n;
G->e = g.e;
}
//输出邻接矩阵
void DisMat(MGraph g)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < g.n; j++)
if (g.edges[i][j] >= 0 && g.edges[i][j] < INF)
printf("%5d", g.edges[i][j]);
else printf("%s", "INF");
printf("\n");
}
}
//输出邻接表
void DisAdj(ALGraph* G)
{
int i;
ArcNode* p;
for (i = 0; i < G->n; i++)
{
p = G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
printf("%3d:", i);
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%3d(%2d)", p->adjvex, p->info);
p = p->nextarc;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//深度优先遍历算法DFS
void ShenduDFS(ALGraph* G, int v)
{
ArcNode* p;
visited[v] = 1;
printf("%2d", v);
p = G->adjlist[v].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (visited[p->adjvex] == 0)
{
ShenduDFS(G, p->adjvex);
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
//广度优先遍历算法BFS
void GuangduBFS(ALGraph* G, int v)
{
ArcNode* p;
int queue[MAXV], front = 0, rear = 0;
int visited[MAXV];
int w, i;
for (i = 0; i < G->n; i++)visited[i] = 0;
printf("%2d", v);
visited[v] = 1;
rear = (rear + 1) % MAXV;
queue[rear] = v;
while (front != rear)
{
front = (front + 1) % MAXV;
w = queue[front];
p = G->adjlist[w].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (visited[p->adjvex] == 0)
{
printf("%2d", p->adjvex);
visited[p->adjvex] = 1;
rear = (rear + 1) % MAXV;
queue[rear] = p->adjvex;
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int i, j, u = 0, v = 0, d = -4;
bool flag = false;
MGraph g;
ALGraph* G;
int A[MAXV][6] = {
{0,5,INF,7,INF,INF },
{INF,0,4,INF,INF,INF},
{8,INF,0,INF,INF,9},
{INF,INF,5,0,INF,6},
{INF,INF,INF,5,0,INF},
{3,INF,INF,INF,1,0} };
g.n = 6; g.e = 10;
for (i = 0; i < g.n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < g.n; j++)
g.edges[i][j] = A[i][j];
printf("\n");
printf("有向带权图G的邻接矩阵:\n");
DisMat(g);
G = (ALGraph*)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph));
printf("转换成邻接表:\n");
MatToList(g, G);
DisAdj(G);
printf("\n");
printf("深度优先序列(DFS):");
ShenduDFS(G, 0);
printf("\n");
printf("广度优先序列(BFS):");
GuangduBFS(G, 0);
}

非递归前序遍历:
void preorder(bitree *t)//前序遍历的非递归算法
{
bitree *temp = t;//定义一个树节点,用它来遍历
while(temp != NULL || s.top != 0)
{
while(temp != NULL)//先遍历左孩子,并输出。
{
printf("%4d",temp->data);
push(temp);
temp = temp->lchild;
}
if(s.top != 0)//当左孩子遍历完后,取栈顶,找右孩子。此时循环还没有结束,再遍历它的左孩子,直至孩子全部遍历结束。
{
temp = pop();
temp = temp->rchild;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
非递归中序遍历:
void inorder(bitree *t)//中序遍历的非递归算法
{
bitree *temp = t;
while(temp != NULL||s.top != 0)
{
while(temp != NULL)//先把左孩子入栈,所有左孩子入栈结束
{
push(temp);
temp = temp->lchild;
}
if(s.top != 0)//左孩子入栈结束,取栈顶,输出栈顶元素,遍历右孩子
{
temp = pop();
printf("%4d",temp->data);
temp = temp->rchild;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
非递归后序遍历:
void laorder(bitree *root)//后序遍历的非递归算法
{
bitree *temp = root;
while(temp!=NULL||s.top!=0)
{
while(temp!= NULL)
{
temp->cishu=1; // 当前节点首次被访问
push(temp);
temp=temp->lchild;
}
if(s.top!=0)
{
temp=pop( );
if(temp->cishu == 1) // 第一次出现在栈顶
{
temp->cishu++;
push(temp);
temp=temp->rchild;
}
else
if(temp->cishu==2)//第二次输出并制空,防止陷入死循环
{
printf("%4d",temp->data);
temp=NULL;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
参考连接1:
《二叉树的非递归遍历(前序中序后序非递归C语言)》 https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_43009982/article/details/83343229?utm_source=app&app_version=5.0.1&code=app_1562916241&uLinkId=usr1mkqgl919blen
参考链接2:
《【数据结构】--- 二叉树的递归遍历和非递归遍历【C语言实现】》, 一起来围观吧 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40587575/article/details/107410498?utm_source=app&app_version=5.0.1&code=app_1562916241&uLinkId=usr1mkqgl919blen
我用python写过非递归的遍历,你可以参考一下
http://t.csdn.cn/k1hxa
- 你可以参考下这个问题的回答, 看看是否对你有帮助, 链接: https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7630373
三种非递归遍历二叉树的方法_禹哥。。。的博客-CSDN博客_非递归遍历二叉树
可以参考一下https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66120913/article/details/124515135
二叉树结点数据结构:
typedef char datatype;
typedef struct node{
datatype data;
struct node *lchild,*rchild;
}bintnode;
typedef bintnode *bintree;
bintree root;
定义一个顺序栈及其操作:
typedef struct stack{
bintree data[100];
int tag[100];
int top;
}seqstack;
void push(seqstack* s,bintree t){
s->data[s->top]=t;
s->top++;
}
bintree pop(seqstack* s){
if(s->top!=0){
s->top--;
return s->data[s->top];
}
else return NULL;
}
前序遍历的非递归实现:
void preorder1(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top=0;
while(t||s.top!=0){
if(t){
printf("%c",t->data);
push(&s,t);
t=t->lchild;
}
else{
t=pop(&s);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
中序遍历的非递归实现:
void inorder1(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top=0;
while(t||s.top!=0){
if(t){
push(&s,t);
t=t->lchild;
}
else{
t=pop(&s);
printf("%c",t->data);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
后序遍历的非递归实现:
void postorder1(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top=0;
while(t||s.top!=0){
if(t){
s.data[s.top]=t;
s.tag[s.top]=0;
s.top++;
t=t->child;
}
else{
if(s.tag[s.top-1]==1){ //左右都遍历完
s.top--;
t=s.data[s.top];
printf("%c",t->data);
t=NULL;
}
else{ //只遍历了左,接下来遍历右边
t=s.data[s.top-1];
s.tag[s.top-1]=1;
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
}