该怎么才能优化这个代码,运行超时了😭
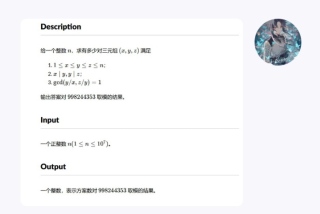
#include
long long gcd(long long a, long long b)
{
if (a % b == 0)
return b;
else
return (gcd(b, a % b));
}
long long test(long long n)
{
long long count = 0;
long long x, y, z;
for (x = 1; x <= n; x++)
{
for (y = x; y <= n; y += x)
{
for (z = y; z <= n; z += y)
{
if (y % x == 0 && z % y == 0)
{
if (gcd(y / x, z / y) == 1)
{
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
return count % 998244353;
}
int main()
{
long long n;
scanf("%lld", &n);
printf("%lld", test(n));
return 0;
}
参考这个吧
/*
思路:暴力判断
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
map<int,int>m;
cin>>n;
int f[n];
int index=0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int v;
cin>>v;
if(m[v]==0)
f[index++]=v;
else
m[v]=1;
}
sort(f,f+index);
int ans=0;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
for(int j = i+1; j < index; j++) {
for(int z = j+1; z < index; z++) {
if((__gcd(f[i],f[j])==1&&__gcd(f[i],f[z])==1&&__gcd(f[j],f[z])==1)||(__gcd(f[i],f[j])!=1&&__gcd(f[i],f[z])!=1&&__gcd(f[j],f[z])!=1))
ans++;
}
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
这个函数认为a > b了,但实际可能出现 a < b的情况,应该添加一下判断。
long long gcd(long long a, long long b)
{
if (a % b == 0)
return b;
else
return (gcd(b, a % b));
}