学生的姓名长度排序,姓名长度相同时比较学生姓名,姓名相同时,比较学生年龄。
package javaapplication83;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class JavaApplication83 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("Tom",18);
Student s2=new Student("Jerry",19);
Student s3=new Student("Jack",18);
Student s4=new Student("Rose",17);
Student s5=new Student("Rose",20);
Course c1=new Course("C",48);
Course c2=new Course("JAVA",64);
Course c3=new Course("C++",48);
Course c4=new Course("Python",64);
Teacher t1=new Teacher("老王",38,"通信技术");
Teacher t2=new Teacher("老张",52,"通信技术");
Teacher t3=new Teacher("老李",48,"通信技术");
HashMap map =new HashMap(){
public int compare(Student s1,Student s2){
int num =s1.name.length()-s2.name.length();
int num2=(num==0)?(s1.name.compareTo(s2.name)):num;
int num3 =((num2==0)?(s1.age-s2.age):num2);
return num3;
}
};
map.put(s1,c1);
map.put(s2,c2);
map.put(s3,c3);
map.put(s4,c4);
map.put(s5,c4);
Set ks=map.keySet();
Iterator it =ks.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object key=it.next();
Object value=map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"-->"+value);
}
package javaapplication83;
public class Course {
public String name;
public int credit;
public Course(){}
public Course(String name, int credit){
super();
this.credit=credit;
this.name=name;
}
public int compareTo(Object o){
Course c1=(Course)o;
if(this.name.charAt(0)==c1.name.charAt(0)){
return 1;
}
else if(this.name.charAt(0)==c1.name.charAt(0)){
return this.credit-c1.credit;
}
else{
return -1;
}
}
public String toString(){
return this.name+":"+credit+"学分";
}
}
package javaapplication83;
public class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(){}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(){
this.name=name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public Student(String name, int age){
super();
this.age=age;
this.name=name;
}
public int compare(Object obj){
Student stu=(Student)obj;
if(this.age-stu.age>0){
return 1;
}
if(this.age-stu.age==0){
return this.name.compareTo(stu.name);
}
return -1;
}
public String toString(){
return this.name+":"+age+"岁";
}
}
package javaapplication83;
public class Teacher {
public String name;
public int age;
public String major;
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(){
this.name=name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public Teacher(){}
public Teacher(String name, int age,String major){
super();
this.age=age;
this.name=name;
this.major=major;
}
public String toString(){
return this.name+":"+age+":岁"+major;
}
}
你的代码就差一步
package javaapplication83;
import java.util.*;
public class JavaApplication83 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("Tom", 18);
Student s2 = new Student("Jerry", 19);
Student s3 = new Student("Jack", 18);
Student s4 = new Student("Rose", 17);
Student s5 = new Student("Rose", 20);
Course c1 = new Course("C", 48);
Course c2 = new Course("JAVA", 64);
Course c3 = new Course("C++", 48);
Course c4 = new Course("Python", 64);
Teacher t1 = new Teacher("老王", 38, "通信技术");
Teacher t2 = new Teacher("老张", 52, "通信技术");
Teacher t3 = new Teacher("老李", 48, "通信技术");
TreeMap<Student, Course> map = new TreeMap<Student, Course>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num =s1.name.length()-s2.name.length();
int num2=(num==0)?(s1.name.compareTo(s2.name)):num;
int num3 =((num2==0)?(s1.age-s2.age):num2);
return num3;
}
});
map.put(s1, c1);
map.put(s2, c2);
map.put(s3, c3);
map.put(s4, c4);
map.put(s5, c4);
Set ks = map.keySet();
Iterator it = ks.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object key = it.next();
Object value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "-->" + value);
}
}
}
红色框起来的地方该改成我这样就行了
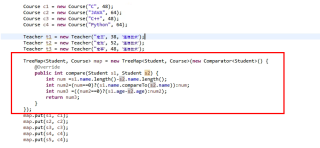
结果:
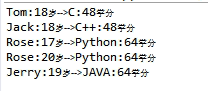
整理一下格式吧
- 关于该问题,我找了一篇非常好的博客,你可以看看是否有帮助,链接:输入学生的个数,姓名,成绩,然后按照学生的成绩的降序来打印学生的姓名
参考代码:
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* <p>
* Title Test
* </p>
* <p>
* Description //TODO
* </p>
*
* @Author X
* @Date 2022-10-17 20:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Tom").age(18).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Tom").age(16).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Jerry").age(19).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Jack").age(18).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Rose").age(17).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("Rose").age(20).build());
//studentList.sort(new NameLengthComparator());
//studentList.sort(new NameComparator());
//studentList.sort(new AgeComparator());
studentList.forEach(System.out::println);
Map<String, List<Student>> groupMap = studentList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName));
System.out.println("分组:" + groupMap);
groupMap.entrySet().stream().sorted((s1, s2) -> {
try {
s1.getValue().sort(new AgeComparator());
s2.getValue().sort(new AgeComparator());
return s1.getKey().length() - (s2.getKey().length());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}).collect(Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal,
LinkedHashMap::new
));
System.out.println("排序后:" + groupMap);
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
static class Student {
String name;
int age;
}
static class NameLengthComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getName().length() - (s2.getName().length());
}
}
static class NameComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
}
}
static class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
}
}
}
结果集:
Test.Student(name=Tom, age=18)
Test.Student(name=Tom, age=16)
Test.Student(name=Jerry, age=19)
Test.Student(name=Jack, age=18)
Test.Student(name=Rose, age=17)
Test.Student(name=Rose, age=20)
分组:{Tom=[Test.Student(name=Tom, age=18), Test.Student(name=Tom, age=16)], Rose=[Test.Student(name=Rose, age=17), Test.Student(name=Rose, age=20)], Jack=[Test.Student(name=Jack, age=18)], Jerry=[Test.Student(name=Jerry, age=19)]}
排序后:{Tom=[Test.Student(name=Tom, age=16), Test.Student(name=Tom, age=18)], Rose=[Test.Student(name=Rose, age=17), Test.Student(name=Rose, age=20)], Jack=[Test.Student(name=Jack, age=18)], Jerry=[Test.Student(name=Jerry, age=19)]}