使用了synchronized,为啥还有线程安全问题?
使用了synchronized,为啥还有线程安全问题?
public class Run9 {
static int count = 5;
static class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread(String name) {
this.setName(name);
}
@Override
synchronized public void run() {
super.run();
{
count --;
System.out.println("由 " + this.getName() + "计算,count = " + count);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread[] arr = new MyThread[5];
String[] name = {"A","B","C","D","E"};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = new MyThread(name[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i].start();
}
}
}
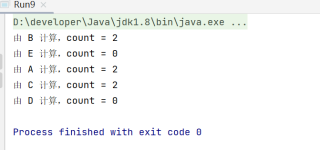
synchronized 用于非 static 方法时,会把锁加在对象实例上,而不是类对象上。你在 main() 中实际创建了 5 个不同的 MyThread 对象实例,因此他们之间没有锁竞争关系。
public class Run9 {
static int count = 5;
static class MyThread extends Thread {
public MyThread(String name) {
this.setName(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Run9.class) {
count--;
System.out.println("由 " + this.getName() + "计算,count = " + count);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread[] arr = new MyThread[5];
String[] name = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = new MyThread(name[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i].start();
}
}
}
count是静态变量,实例共享的,所以线程间操作会有影响
推荐使用AtomicInteger,java自带的线程安全类。
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(5);
count.incrementAndGet();