Condition实现类中注入bean
烦请各位帮忙看看如何解决
背景描述
最近写了个springboot的后台,通过yaml配置了一些环境信息,写入到一个自建的实体。初衷是想通过一键式配置实现生产环境和测试环境中对RabbitMQ监听的切换,但是在bean的注入过程中出现了问题。
原思路:自定义condition接口的实现类,在实现类中注入yaml关联的配置类,根据配置信息确定实现类返回的boolean,最后利用@Conditional注解中的参数(即上文描述的boolean)控制RabbitMQ的监听类是否生效。
问题相关代码
版本实体类
/**
* 版本实体
*/
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="ecc-plus")
public class ECP_PLUS {
private String version;//版本号
private String pubtime;//发布时间
private String publisher;//发布人
private String comments;//发布说明
private String rsHadNotReadPre;//redis 消息未读键前缀
private Boolean pubVersion;//是否是正式版本
private String msgDbName;//消息数据库名称
}
自定义配置
#yaml配置
ecc-plus:
version: 1.2.0.RELEASE
pubtime: 2022-07-07
publisher: wayne
comments: 修复了一些已知的bug。
rs-had-not-read-pre: usr-hadRead- #消息未读键前缀
pub-version: true #是否是发布版本
msg-db-name: terminal2022
自定义Condition实现类
/**
* 生产环境
* 控制动态加载监听Mq监听Bean的注入
*/
@Component
public class MsgMqProdCondition implements Condition {
@Autowired
private ECP_PLUS ecp_plus;
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
boolean flag = false;
//flag = ecp_plus.getPubVersion()==true? true:false;
return flag;
}
}
MQ监听
/**
* RabbitMQ监听-开发
*/
@Component
@Lazy(false)
@Conditional(MsgMqProdCondition.class)
public class RabbitMqListener {
/**
* 监听异步处理消息标签请求
* @param msg
* @param channel
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = MsgRabbitMqConfig.TAG_QUEUE_NAME)//正式环境
public void listenTagMQ_PROD(Message msg,Channel channel){
String jsonStr = new String(msg.getBody());
JSONObject msgJson = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
String code = msgJson.getString("CODE");
MSG_TAG_SCAT tag =msgJson.getObject("tags",MSG_TAG_SCAT.class);
if (tag!=null){
msgService.asynDueMsgTag(code,tag);
}
}
}
运行结果及报错内容
在启动过程中,condition实现类自动注入的实体类是null
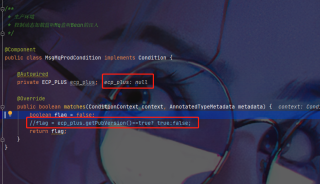
按照我之前的写法这里就会报空指针,目测问题应该是出在bean的生命周期上,想请教各位,这种场景应该如何让配置实体先加载呢?
原因分析
原因在于我的思路过于僵化了,原本的思路一心只想自己将装配好的ECP_PLUS注入到Condition中,而忽略了Condition接口中关键方法matches的参数ConditionContext,其实通过它就可以直接拿yml的值,下面是源码(可自行跳过)。
关键源码
ConditionContext部分源码
/**
* Context information for use by {@link Condition} implementations.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 4.0
*/
public interface ConditionContext {
/**
* Return the {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} that will hold the bean definition
* should the condition match.
* @throws IllegalStateException if no registry is available (which is unusual:
* only the case with a plain {@link ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider})
*/
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
/**
* Return the {@link ConfigurableListableBeanFactory} that will hold the bean
* definition should the condition match, or {@code null} if the bean factory is
* not available (or not downcastable to {@code ConfigurableListableBeanFactory}).
*/
@Nullable
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory();
/**
* Return the {@link Environment} for which the current application is running.
*/
Environment getEnvironment();
/**
* Return the {@link ResourceLoader} currently being used.
*/
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
/**
* Return the {@link ClassLoader} that should be used to load additional classes
* (only {@code null} if even the system ClassLoader isn't accessible).
* @see org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#forName(String, ClassLoader)
*/
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
ConditionContext接口中的getEnvironment()方法引起了我的注意,我们继续看这个方法的返回值;
/**
* Interface representing the environment in which the current application is running.
* Models two key aspects of the application environment: <em>profiles</em> and
* <em>properties</em>. Methods related to property access are exposed via the
* {@link PropertyResolver} superinterface.
*
* <p>A <em>profile</em> is a named, logical group of bean definitions to be registered
* with the container only if the given profile is <em>active</em>. Beans may be assigned
* to a profile whether defined in XML or via annotations; see the spring-beans 3.1 schema
* or the {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile @Profile} annotation for
* syntax details. The role of the {@code Environment} object with relation to profiles is
* in determining which profiles (if any) are currently {@linkplain #getActiveProfiles
* active}, and which profiles (if any) should be {@linkplain #getDefaultProfiles active
* by default}.
*
* <p><em>Properties</em> play an important role in almost all applications, and may
* originate from a variety of sources: properties files, JVM system properties, system
* environment variables, JNDI, servlet context parameters, ad-hoc Properties objects,
* Maps, and so on. The role of the {@code Environment} object with relation to properties
* is to provide the user with a convenient service interface for configuring property
* sources and resolving properties from them.
*
* <p>Beans managed within an {@code ApplicationContext} may register to be {@link
* org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware EnvironmentAware} or {@code @Inject} the
* {@code Environment} in order to query profile state or resolve properties directly.
*
* <p>In most cases, however, application-level beans should not need to interact with the
* {@code Environment} directly but instead may have to have {@code ${...}} property
* values replaced by a property placeholder configurer such as
* {@link org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
* PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer}, which itself is {@code EnvironmentAware} and
* as of Spring 3.1 is registered by default when using
* {@code <context:property-placeholder/>}.
*
* <p>Configuration of the {@code Environment} object must be done through the
* {@code ConfigurableEnvironment} interface, returned from all
* {@code AbstractApplicationContext} subclass {@code getEnvironment()} methods. See
* {@link ConfigurableEnvironment} Javadoc for usage examples demonstrating manipulation
* of property sources prior to application context {@code refresh()}.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see PropertyResolver
* @see EnvironmentCapable
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see AbstractEnvironment
* @see StandardEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#setEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#createEnvironment
*/
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* Return the set of profiles explicitly made active for this environment. Profiles
* are used for creating logical groupings of bean definitions to be registered
* conditionally, for example based on deployment environment. Profiles can be
* activated by setting {@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
* "spring.profiles.active"} as a system property or by calling
* {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)}.
* <p>If no profiles have explicitly been specified as active, then any
* {@linkplain #getDefaultProfiles() default profiles} will automatically be activated.
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* Return the set of profiles to be active by default when no active profiles have
* been set explicitly.
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/**
* Return whether one or more of the given profiles is active or, in the case of no
* explicit active profiles, whether one or more of the given profiles is included in
* the set of default profiles. If a profile begins with '!' the logic is inverted,
* i.e. the method will return {@code true} if the given profile is <em>not</em> active.
* For example, {@code env.acceptsProfiles("p1", "!p2")} will return {@code true} if
* profile 'p1' is active or 'p2' is not active.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if called with zero arguments
* or if any profile is {@code null}, empty, or whitespace only
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
* @see #acceptsProfiles(Profiles)
* @deprecated as of 5.1 in favor of {@link #acceptsProfiles(Profiles)}
*/
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* Return whether the {@linkplain #getActiveProfiles() active profiles}
* match the given {@link Profiles} predicate.
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
可以看到Environment这个接口描述了大量的关于环境配置的信息,这里我们梳理一下这些接口的实现关系。
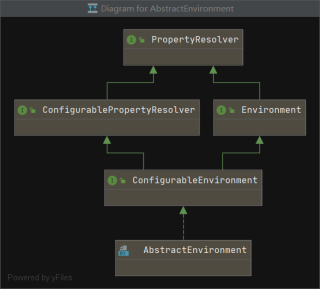
底层接口PropertyResolver源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.core.env;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Interface for resolving properties against any underlying source.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see Environment
* @see PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
*/
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* Return whether the given property key is available for resolution,
* i.e. if the value for the given key is not {@code null}.
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @see #getProperty(String, String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
*/
@Nullable
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or
* {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
@Nullable
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key (never {@code null}).
* @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, converted to the given
* targetType (never {@code null}).
* @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value are ignored and passed through unchanged.
* @param text the String to resolve
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown.
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* or if any placeholders are unresolvable
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
破案的关键就是这个getProperty(String key)
通过ConditionContext直接获取yml中的配置
直接调用
public class MsgMqProdCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
boolean flag = false;
String property = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("ecc-plus.pub-version");
if (property.equals("true")){
flag=true;
}
return flag;
}
}
如有谬误,欢迎各位批评指正,感激不尽。
是自动注入失败,跟先后无关
bean加载先后问题
在你的MsgMqProdCondition 类加一个注解
@ConditionalOnClass(ECP_PLUS.class)