字符串首尾相接c++
描述
小明有两个字符串 S1 和 S2,小明想把 S1 接到 S2 后面。因为 S1 前面有一些字符和 S2 后面 的一些字母一样,所以小明在连接的时候就没必要重复了,比如 S1 为cdefgh,S2 为abcde, 那么cde这部分就是最长的重复部分,小明可以将这两个串连接为abcdefgh。现在,给你串 S1 和串 S2,请你帮小明找出最长重复部分的长度。
输入描述
共两行,每行一个字符串,由小写字母构成,第一行表示串 S1,第二行表示串 S2。
(1≤∣S1∣,∣S2∣≤50000)
输出描述
答案输出在一行,先输出重复的字符串,再输出其长度,中间以空格隔开。若该串为空,只需 输出 0。
用例输入
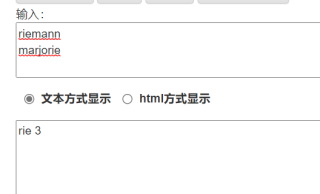
riemann
marjorie
用例输出
rie 3
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX_LEN 50007
// 以字符串 t 求 next 数组,n 为字符串长度
int* getNext(const char* t, int length) {
int* next = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (length + 1));
next[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= length; i++) {
int j = next[i - 1];
while(t[j + 1] != t[i] && j > 0) {
j = next[j];
}
if(t[j + 1] == t[i]) {
next[i] = j + 1;
} else {
next[i] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
// 拼接两个字符串
char* concat(const char* s1, const char* s2) {
int len1 = strlen(s1);
int len2 = strlen(s2);
char* s3 = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len1 + len2 + 2));
strncpy(s3 + 1, s1, len1);
strncpy(s3 + 1 + len1, s2, len2);
s3[1 + len1 + len2] = '\0';
return s3;
}
void print(const char * t, const int* next, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%c%c", t[i], i == n ? '\n' : '\t');
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d%c", next[i], i == n ? '\n' : '\t');
}
}
int main() {
char s1[MAX_LEN], s2[MAX_LEN];
scanf("%s%s", s1, s2);
char* s3 = concat(s1, s2);
int len3 = strlen(s3 + 1);
int* next3 = getNext(s3, len3);
// print(s3, next3, len3);
int ans = next3[len3];
if (ans > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < ans; i++) {
printf("%c", s1[i]);
}
printf(" ");
}
printf("%d", ans);
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX_LEN 50007
// 以字符串 t 求 next 数组,n 为字符串长度
int* getNext(const char* t, int length) {
int* next = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (length + 1));
next[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= length; i++) {
int j = next[i - 1];
while(t[j + 1] != t[i] && j > 0) {
j = next[j];
}
if(t[j + 1] == t[i]) {
next[i] = j + 1;
} else {
next[i] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
// 拼接两个字符串
char* concat(const char* s1, const char* s2) {
int len1 = strlen(s1);
int len2 = strlen(s2);
char* s3 = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len1 + len2 + 2));
strncpy(s3 + 1, s1, len1);
strncpy(s3 + 1 + len1, s2, len2);
s3[1 + len1 + len2] = '\0';
return s3;
}
void print(const char * t, const int* next, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%c%c", t[i], i == n ? '\n' : '\t');
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d%c", next[i], i == n ? '\n' : '\t');
}
}
int main() {
char s1[MAX_LEN], s2[MAX_LEN];
scanf("%s%s", s1, s2);
char* s3 = concat(s1, s2);
int len3 = strlen(s3 + 1);
int* next3 = getNext(s3, len3);
// print(s3, next3, len3);
int ans = next3[len3];
if (ans > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < ans; i++) {
printf("%c", s1[i]);
}
printf(" ");
}
printf("%d", ans);
}