为什么输出不到想要的结果(C语言)

为什么输出不到想要的结果?
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define M 10
struct student
{
int num;
int score;
};
int fun(struct student *s,int low,int high,struct student *b);
int main()
{
int low,high;
int i,t;
struct student s[M];
struct student b[M];
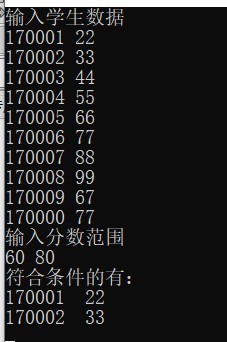
printf("输入学生数据\n");
for(i=0; i<M; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&s[i].num,&s[i].score);
}
printf("输入分数范围\n");
scanf("%d%d",&low,&high);
if ( high < low )
{
t=high;
high=low;
low=t;
}
fun(s,low,high,b);
printf("符合条件的有:\n");
do
{
printf("%d %d",b[i].num,b[i].score);
printf("\n");
i++;
}while(getchar()!='\0');
return 0;
}
int fun(struct student *s,int low,int high,struct student *b)
{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0; i<M; i++)
{
if(s[i].score>low && s[i].score<=high)
{
b[j].num=s[i].num;
b[j].score=s[i].score;
}
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define M 10
struct student
{
int num;
int score;
};
int fun(struct student *s, int low, int high, struct student *b);
int main()
{
int low, high;
int i, t;
struct student s[M];
struct student b[M];
printf("输入学生数据\n");
for (i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &s[i].num, &s[i].score);
}
printf("输入分数范围\n");
scanf("%d%d", &low, &high);
if (high < low)
{
t = high;
high = low;
low = t;
}
int count = fun(s, low, high, b);
printf("符合条件的有:\n");
i = 0;
do
{
printf("%d %d", b[i].num, b[i].score);
printf("\n");
i++;
count--;
} while (count > 0);
return 0;
}
int fun(struct student *s, int low, int high, struct student *b)
{
int i, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
if (s[i].score > low && s[i].score <= high)
{
b[j].num = s[i].num;
b[j].score = s[i].score;
j++;
}
}
return j;
}
逻辑问题
fun(s,low,high,b);
printf("符合条件的有:\n");
do
{
printf("%d %d",b[i].num,b[i].score);
printf("\n");
i++;
}while(getchar()!='\0');
这里i在循环前没有置零
int fun(struct student *s,int low,int high,struct student *b)
{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0; i<M; i++)
{
if(s[i].score>low && s[i].score<=high)
{
b[j].num=s[i].num;
b[j].score=s[i].score;
}
}
}
这里缺少j++,所以你一直在写b[0]