Python数字排序问题
Python 输入一个正整数,将该数各位上的数字重新排列,给出比原来数大的最小数和比原来数小的最大数
例:输入2651392641
输出
比原来数大的最小数2651394126
比原来数小的最大数2651392614
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
pass
def sort_max(self, num: int) -> int:
"""
:param num:
:return:
"""
num_count = Counter(str(num))
while True:
num += 1
buffer_json = Counter(str(num))
if buffer_json == num_count:
return num
def sort_min(self, num: int) -> int:
"""
:param num:
:return:
"""
num_count = Counter(str(num))
while True:
num -= 1
buffer_json = Counter(str(num))
if buffer_json == num_count:
return num
if __name__ == '__main__':
st = 2651392641
U = Solution()
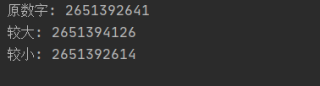
print("原数字:", st)
the_max = U.sort_max(st)
print("较大:", the_max)
the_min = U.sort_min(st)
print("较小:", the_min)
对每个数字计数,然后将原来的数字递加,或者递减,第一个满足数字哈希表相等的就是最接近的极值,我的这个做法技术含量不大.........你可以直接提取每一位数字,我用的字符串转换
好像看懂了,研究一下,逻辑最简单的方式就是原数字递增递减,然后判断数值包含的数字与原数字是否相同,但是这个计算量较大,先给个计算量小但是逻辑比较复杂的方式
def minmax(a):
lst = [n for n in str(a)]
lst.reverse()
index = 0
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i]<lst[i+1]:
continue
else:
index = i+1
break
index1 = 0
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i]<lst[index]:
continue
else:
index1 = i
break
t = lst[index]
lst[index]= lst[index1]
lst[index1] = t
pre = lst[0:index]
pre.sort()
pre.reverse()
lst[0:index] = pre
lst.reverse()
return ''.join(lst)
def maxmin(a):
lst = [n for n in str(a)]
lst.reverse()
index = 0
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i]>lst[i+1]:
continue
else:
index = i+1
break
index1 = 0
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i]>lst[index]:
continue
else:
index1 = i
break
t = lst[index]
lst[index]= lst[index1]
lst[index1] = t
pre = lst[0:index]
pre.sort()
lst[0:index] = pre
lst.reverse()
return ''.join(lst)
a = 2651392641
print(minmax(a))
print(maxmin(a))
给个思路:
先将个位数和十位数对调,如果对调后的数字比原来的小,那这个数字就是比原来小的最大数;如果比原来的大,那么这个数字就是比原来大的最小数;如果相等就忽略,进行下一步。
再讲个位数字与百位数对调,进行同上的比较。
依次类推。
个位数依次与前面的数对调完还没有找到两个结果,就用百位数字与它前面的数字依次对调继续对比。
直到两个结果都找到
如果个位数对调完还没有找到两个结果,再用百位数与前面的数字对比,依次类推
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/359911f567ac0a16fe03069b.html