C++有关类的变量的定义(简单的)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
class Person
{
private:
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
public:
string name;
void say()
{
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
int set_age(int a)
{
age = a;
}
int get_age()
{
return age;
}
void add_money(double x)
{
money += x;
}
} person_a, person_b, persons[100];
int main()
{
Person c;
c.name = "yxc"; // 正确!访问公有变量
c.age = 18; // 错误!访问私有变量
c.set_age(18); // 正确!set_age()是共有成员变量
c.add_money(100);
c.say();
cout << c.get_age() << endl;
return 0;
}
就是看不懂
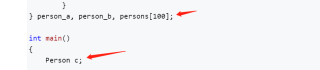
这两行,第二行我知道,就是创建一个实例对象,名字叫做c
那第一行后面的作用是什么?和这个的区别在哪?
创建类的时候就创建两个对象和一个数组,这个是全局对象
这个等价于:
class Person
{
//省略代码
};
Person person_a, person_b, persons[100]; //全局变量
int main()
{
Person c; //局部变量
//省略代码
}
class Person person_a, person_b, persons[100];
这样就好看了。作用域不同,一个是局部,一个是全局。