C语言简单的文件写入和读取
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct
{
int id;
char name[20];
float score;
}STUDENT;
void main()
{
//写入
/STUDENT s={1001,"zhangsan",80};
FILEp=fopen("d:\student.txt","wt");
fprintf(p,"id=%d name=%s score=%f",s.id,s.name,s.score);
fclose(p);/
//读取
STUDENT s;
FILEp=fopen("d:\student.txt","rt");
fscanf(p,"id=%d name=%s score=%f",&s.id,&s.name,&s.score);
fclose(p);
}
在注释中已经将数据输入到记事本中了

那么我现在要读取并将其显示出来,为什么显示不出来,怎么改正呢?谢谢
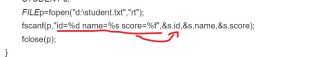
这里fscanf将p中读取到的数据,格式化之后写入右侧的变量中。引号中间是格式化的方式,不能添加其他字符。
另外 , s.name 表示的本身就是地址,不需要在取地址了
fscanf(p,"%d %s %f",&s.id,s.name,&s.score);
fscanf读取后要打印