C语言,字符串的输入输出printf
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void GetReal(char* R);
void GetString(char S[100]);
int main()
{
char R[100];
char S[100];
GetReal(R);
GetString(S);
printf("please input a number:\n");
printf("please input a string:\n");
printf("%s\n", R);
printf("%s\n", S);
return 0;
}
void GetReal(char* R)
{
scanf_s("%s", R,100);
}
void GetString(char S[100])
{
gets_s(S,100);
}
gets();如何使用,输入不了字符串
你一开始初始化好,就可以不在控制台中显示;
但是如果未初始化,需要通过输入来进行赋值,而输入需要在控制台上。
希望对题主有所帮助,可以的话,帮忙点个采纳!
你自己在控制台输入,肯定会显示出来你的输入
并且如果你想获取一行字符串,可以修改一下:
void GetString(char ar[100])
{
gets(arr); //gets函数可以将空格读入
printf("%s", ar);
}
printf("\b"); 可以退一格
可以加入清屏函数system("cls");,就是输入后清除显示再输出,这个函数是在Windows系统下的,可能需要加入include<windows.h>。希望采纳。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define N 80
void ignore_leading_whitespaces()
{
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if (isspace(ch))
continue;
ungetc(ch, stdin);
break;
}
}
int GetReal(double *num)
{
ignore_leading_whitespaces();
if (feof(stdin))
return 0;
printf("please input a number:\n");
return scanf("%lf", num) == 1;
}
int GetString(char *str, int n)
{
ignore_leading_whitespaces();
if (feof(stdin))
return 0;
printf("please input a string:\n");
if (!fgets(str, n, stdin))
return 0;
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (str[len - 1] == '\n')
str[len - 1] = '\0';
return 1;
}
#define N 80
int main()
{
double num;
char str[N];
int ok1 = GetReal(&num);
int ok2 = GetString(str, N);
if (ok1)
printf("%lg\n", num);
if (ok2)
printf("%s\n", str);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -Wall main.c
$ cat test1.txt # test1.txt is an empty file
$ ./a.out < test1.txt # no output for empty input
$ cat test1.txt
9.56
hello world
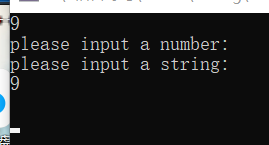
$ cat test1.txt | ./a.out
please input a number:
please input a string:
9.56
hello world