C语言结构体和指针的问题。
最近学到操作系统的PV操作,想着自己写代码实现简单的PV操作,遇见了问题。
整个代码为
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct process{ //进程结构体
long pid;
long uid;
struct process *next;
};
typedef struct semaphore{ //记录型信号量
int value;
struct process *L;
} semaphore;
void PrintBlockQueue(semaphore S){ //输出阻塞队列
struct process *p = S.L;
if(p==NULL){
printf("NULL\n");
}else{
while(p!=NULL){
printf("%d-> ",p->pid);
p=p->next;
}
printf("Null\n");
}
}
void block(struct process *L,struct process P){
printf("\n%d 进程加入阻塞队列\n",P.pid);
if(L==NULL){
L=(struct process *) malloc(sizeof(struct process));
L->pid = P.pid;
L->uid = P.uid;
L->next = NULL;
printf("%d,%d\n",L->pid,L->uid);
}else{
struct process *p = L,*q;
while (p->next != NULL){
p = p->next;
}
q = (struct process *) malloc(sizeof (struct process));
q->pid = P.pid;
q->uid = P.uid;
q->next = NULL;
p->next = q;
}
}
void wakeup(struct process *L){
}
void wait(semaphore &S,struct process p){
S.value--;
if(S.value<0){
block(S.L,p);
}
printf("此时共享资源数量为: %d,此时阻塞队列:",S.value);
PrintBlockQueue(S);
}
void signal(semaphore &S){
S.value++;
if(S.value <= 0){
}
}
main(){
semaphore S;
S.value =2; //系统资源
S.L = NULL;
struct process p1,p2,p3,p4; //4个进程
p1.pid = 202201; p1.uid =1001;
p2.pid = 202202; p2.uid =1002;
p3.pid = 202203; p3.uid =1003;
p4.pid = 202204; p4.uid =1004;
wait(S,p1);
wait(S,p2);
wait(S,p3);
// wait(S,p4);
printf("%d\n",S.L->pid);
}
简单说明,用的C语言语法,但文件后缀是cpp的,因为在函数中用到 void wait(semaphore &S) 里面的&,这是cpp的语法吧,可以把函数里面的数值带回来。
运行结果及报错内容
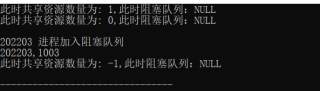
问题:在block()函数中已经把阻塞的进程插入到struct process *L;里面去了,为什么在主函数中输出S.L->pid还是为空呢?

是cpp里面的&这个符号不能带回结构体里面的指针吗?
关键就在这个声明:
void block(struct process *L,struct process P)
函数执行完称之后,L指向的内容可以改变,但是L本身不能改变。
如果要改变L,修改为指针的引用即可:
void block(struct process *&L,struct process P)
你这里所涉及到的问题,很经典的。
这里涉及几个知识点,函数的按值传递,按地址传递,按引用传递,按指针传递。
以及,如果在函数内部申请一个内存,如何把这个函数内部(有作用域)的指针让外部能识别到呢?
我只是简单的修改,一种方法而已,或者说你原来的方法,只是因为函数内部的L申请内存,没搞对。这个细节你可以百度,需要你思考
你说的函数按引用传参,没错,应该可行,
但是c语言同样,你可以用指针,用地址传参实现(这里我只是习惯了,就按这种,你的引用应该可以)
除此之外,注意你对s.L的初始化,这个传参也要注意,在函数内部申请内存并初始化,要传递给外部,怎样实现呢? (可以用返回值的方案,可以传参类似我这样)
代码我只是简单提供一种思路,就是这些知识点,你可以思考一下,具体代码逻辑以及细节,我也不曾关注。
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct process { //进程结构体
long pid;
long uid;
struct process* next;
};
typedef struct semaphore { //记录型信号量
int value;
struct process* L;
} semaphore;
void PrintBlockQueue(semaphore S) { //输出阻塞队列
struct process* p = S.L;
if (p == NULL) {
printf("NULL\n");
}
else {
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d-> ", p->pid);
p = p->next;
}
printf("Null\n");
}
}
void block(struct process** L, struct process P) {
printf("\n%d 进程加入阻塞队列\n", P.pid);
if (*L == NULL) {
(*L) = (struct process*)malloc(sizeof(struct process));
(*L)->pid = P.pid;
(*L)->uid = P.uid;
(*L)->next = NULL;
printf("%d,%d\n", (*L)->pid, (*L)->uid);
}
else {
struct process* p = *L, * q;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
q = (struct process*)malloc(sizeof(struct process));
q->pid = P.pid;
q->uid = P.uid;
q->next = NULL;
p->next = q;
}
}
void wakeup(struct process* L) {
}
void wait(semaphore* S, struct process p) {
S->value--;
if (S->value < 0) {
block(&(S->L), p);
}
printf("此时共享资源数量为: %d,此时阻塞队列:", S->value);
PrintBlockQueue(*S);
}
void signal(semaphore& S) {
S.value++;
if (S.value <= 0) {
}
}
int main() {
semaphore S;
S.value = 2; //系统资源
S.L = NULL;
struct process p1, p2, p3, p4; //4个进程
p1.pid = 202201; p1.uid = 1001;
p2.pid = 202202; p2.uid = 1002;
p3.pid = 202203; p3.uid = 1003;
p4.pid = 202204; p4.uid = 1004;
wait(&S, p1);
wait(&S, p2);
wait(&S, p3);
// wait(S,p4);
if (S.L != NULL)
{
printf("test :%d\n", S.L->pid);
}
else
{
printf("S.L is null \n");
}
return 0;
}