java sclipse程序设计
- 某高中的入学考试包含三门科目:语文,数学、英语。各科满分均为150分。
入学录取条件:
(1) 单科考试成绩需大于等于单科总分的60%且总分分数需大于等于300分,可录取;
(2) 若某一门分数大于等于95%,可以按特长生身份,录取。
学生类包含姓名、总分、三科成绩等成员变量及对应的getXX()和setXX()方法;定义接口JudgeInterface,其中抽象方法名为judge,其实现类为JudgeImplement,主要功能判断学生是否被录取;运行类Test,主要功能为录入学生信息、调用判断学生是否录取的方法、打印被录取的学生信息等。
要求: - 使用集合(或列表)保存学生对象;
- 指定考生数量,录入考生的信息及成绩;
- 输出所有考生姓名;
- 筛选录取学生,并对打印其全部信息。
示例代码如下:
学生类:
public class Student {
/**
* 满分
*/
public static final Double MAX = 150d;
/**
* 学生姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 语文成绩
*/
private Double chinese;
/**
* 数学成绩
*/
private Double math;
/**
* 英语成绩
*/
private Double english;
/**
* 总成绩
*/
private Double total;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(Double chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public Double getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(Double math) {
this.math = math;
}
public Double getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(Double english) {
this.english = english;
}
public Double getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(Double total) {
this.total = total;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MessageFormat.format("姓名:{0},语文成绩:{1},数学成绩:{2},英语成绩:{3},总成绩:{4}", name, chinese, math, english, total);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Student student = (Student) o;
return Objects.equals(name, student.name) && Objects.equals(chinese, student.chinese) && Objects.equals(math, student.math) && Objects.equals(english, student.english) && Objects.equals(total, student.total);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, chinese, math, english, total);
}
}
接口 JudgeInterface:
public interface JudgeInterface {
/**
* 学生能否被录取
* @param student
* @return
*/
boolean judge(Student student);
}
实现类 JudgeImplement:
public class JudgeImplement implements JudgeInterface {
@Override
public boolean judge(Student student) {
double percent60 = Student.MAX * 0.6;
double percent95 = Student.MAX * 0.95;
if (student.getChinese() >= percent60
&& student.getMath() >= percent60
&& student.getEnglish() >= percent60
&& (student.getChinese() + student.getMath() + student.getEnglish() >= 300)) {
// 单科考试成绩需大于等于单科总分的60%且总分分数需大于等于300分,可录取;
return true;
} else if (student.getChinese() >= percent95 || student.getMath() >= percent95 || student.getEnglish() >= percent95) {
// 若某一门分数大于等于95%,可以按特长生身份,录取。
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
运行类 Test:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请指定考生数量:");
int count = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入学生信息及成绩:");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.printf("录入第%d个学生信息及成绩:\n", i + 1);
Student student = new Student();
System.out.print("\t学生姓名:");
student.setName(scanner.next());
System.out.print("\t语文成绩:");
student.setChinese(scanner.nextDouble());
System.out.print("\t数学成绩:");
student.setMath(scanner.nextDouble());
System.out.print("\t英语成绩:");
student.setEnglish(scanner.nextDouble());
student.setTotal(student.getChinese() + student.getMath() + student.getEnglish());
students.add(student);
}
System.out.printf("所有考生姓名:%s\n", students.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("\t")));
System.out.println("录取学生:");
JudgeInterface judgeInterface = new JudgeImplement();
students.stream().filter(judgeInterface::judge).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
运行结果:
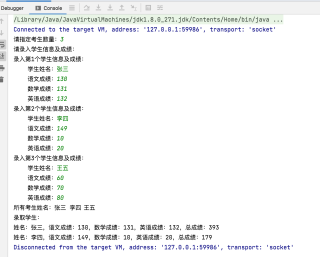
如有帮助,请采纳。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name;
int chinese, math, english;
System.out.println("请输入学生数量:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(
"请输入第" +
(i + 1) +
"个学生信息,包括 姓名 语文 数学 英语四项,以空格隔开:"
);
name = sc.next();
chinese = sc.nextInt();
math = sc.nextInt();
english = sc.nextInt();
Student s = new Student(name, chinese, math, english);
s.setTotal(chinese + math + english);
list.add(s);
}
sc.close();
System.out.println("所有考生姓名:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName());
}
System.out.println("所有录取考生有:");
JudgeImplement j = new JudgeImplement();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Student s = list.get(i);
if (j.judge(s)) {
System.out.println(
s.getName() +
" " +
s.getChinese() +
" " +
s.getMath() +
" " +
s.getEnglish() +
" " +
s.getTotal()
);
}
}
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private int total;
private int chinese;
private int math;
private int english;
public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) {
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(int total) {
this.total = total;
}
public int getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english) {
this.english = english;
}
}
public class JudgeImplement implements JudgeInterface{
@Override
public boolean judge(Student s) {
if(s.getChinese() >= 90 && s.getMath() >= 90 && s.getEnglish() >= 90 && s.getTotal() >= 300){
return true;
}else if(s.getChinese() >= 142.5 || s.getMath() >= 142.5 || s.getEnglish() >= 142.5){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
public interface JudgeInterface {
public boolean judge(Student s);
}
这个考察面向对象基础,先尝试自己写。