如何自定义map模板排序
我先定义了一个Stu类:
class Stu {
private:
string name;
int id;
string sex;
int type;
float mathscore;
float engscore;
float cppscore;
public:
Stu()=default;
Stu(string n,int i,string s,float math,float eng,float cpp):name(n),id(i),sex(s),mathscore(math),engscore(eng),cppscore(cpp){};
~Stu();
主程序中定义了map<int,Stu>Stu_map;
默认是按id排序,如何实现按mathscore(数学成绩)排序并输出?
map默认是使用key排序的,因为mathScore是value中的值,需要借助vector和sort函数来实现对map的排序。
调用add函数,在map中添加数据及排序后的运行结果:
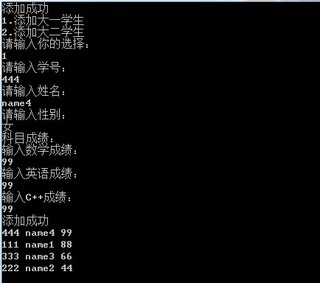
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Stu
{
private:
string name;
int id;
string sex;
int type;
float mathscore;
float engscore;
float cppscore;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(string n,int i,string s,float math,float eng,float cpp):name(n),id(i),sex(s),mathscore(math),engscore(eng),cppscore(cpp){}
~Stu(){}
//暂时写这几个
string getname(){return name;}
int get_id(){return id;};
float getmathscore() const {return mathscore;} //不要漏了这里的const 否则cmp函数会报错
int get_type(){return type;}
void set_type(int t){type = t;}
void change_id(int d){id = d;}
void change_name(char* nn){name = nn;}
void change_sex(char* sx){sex = sx;}
void set_mathscore(float f){mathscore = f;}
void set_engscore(float f){engscore = f;}
void set_cppscore(float f){cppscore = f;}
};
map<int,Stu>Stu_map; //声明全局变量,因为add函数中没有参数,所以把这个作为全局变量
bool cmp(const pair<int,Stu> p1,const pair<int,Stu> p2)//要用常数,不然编译错误
{
return p1.second.getmathscore() > p2.second.getmathscore();
}
istream &operator>>(istream &is,Stu &stu)
{
char temp[50];
double te;
is.getline(temp,50);
cout<<"请输入学号:"<<endl;
is.getline(temp,50);
stu.change_id(atoi(temp));
cout<<"请输入姓名:"<<endl;
is.getline(temp,20);
stu.change_name(temp);
cout<<"请输入性别:"<<endl;
is.getline(temp,10);
if(!strcmp(temp,"男")||!strcmp(temp,"女"))
{
stu.change_sex(temp);
} else
{
cout<<"性别输入错误 Σ( ° △ °|||)︴"<<endl;
}
cout<<"科目成绩:"<<endl;
cout<<"输入数学成绩:"<<endl;
cin>>te;
stu.set_mathscore(te);
cout<<"输入英语成绩:"<<endl;
cin>>te;
stu.set_engscore(te);
cout<<"输入C++成绩:"<<endl;
cin>>te;
stu.set_cppscore(te);
return is;
}
void add_stu()
{
int choice=0;
Stu stu;
cout<<"1.添加大一学生"<<endl;
cout<<"2.添加大二学生"<<endl;
cout<<"请输入你的选择:"<<endl;
cin>>choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
{
cin >> stu;
stu.set_type(1);
Stu_map.insert(map<int, Stu>::value_type(stu.get_id(), stu));
cout<<"添加成功"<<endl;
break;
}
case 2:
{
cin >> stu;
stu.set_type(2);
Stu_map.insert(map<int, Stu>::value_type(stu.get_id(), stu));
cout<<"添加成功"<<endl;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
int main()
{
//调用函数添加4个数据
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
add_stu();
map<int,Stu>::iterator it = Stu_map.begin();
vector< pair<int,Stu> > arr;
for (; it != Stu_map.end(); it++)
{
arr.push_back(make_pair(it->first,it->second) );
}
//排序
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),cmp);
//输出
vector< pair<int,Stu> >::iterator is = arr.begin();
for (; is != arr.end(); is++)
{
cout << is->first << " " << is->second.getname() << " " << is->second.getmathscore()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
再用map<float, Stu>中间变量保存一份,然后输出?
你没有定义type变量, 这里就没考虑了。有用请采纳
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Stu {
private:
string name;
int id;
string sex;
int type;
float mathscore;
float engscore;
float cppscore;
public:
Stu() = default;
Stu(string n, int i, string s, float math, float eng, float cpp) :name(n), id(i), sex(s), mathscore(math), engscore(eng), cppscore(cpp) {};
~Stu() {};
float getMathScore () const;
void showInfo();
};
float Stu::getMathScore() const{
return mathscore;
}
void Stu::showInfo() {
cout << "name: " << name << " ";
cout << "id: " << id << " ";
cout << "sex: " << sex << " ";
cout << "mathscore: " << mathscore << " ";
cout << "engscore: " << engscore << " ";
cout << "cppscore: " << cppscore << " ";
cout << endl;
}
/*
* 对自定义字典排序: 比较函数
* 对字典中的Value排序: map默认不可对Value排序, 因此得转换成Vecotr进行排序
*/
// 比较函数
bool cmp(const pair<int, Stu>& a, const pair<int, Stu>& b) {
return a.second.getMathScore() > b.second.getMathScore();
}
void sortMap(map<int, Stu>& Stu_map) {
vector<pair<int, Stu>> sortAsMathScore(Stu_map.begin(), Stu_map.end());
sort(sortAsMathScore.begin(), sortAsMathScore.end(), cmp);//用sort排序
for (vector<pair<int, Stu>>::iterator it = sortAsMathScore.begin(); it != sortAsMathScore.end(); it++) {
it->second.showInfo();
}
}
int main() {
// 你自己定义的没有用到type参数
Stu stu1 = Stu("小红", 1, "女",90.0f, 92.5f, 85.0f);
Stu stu2 = Stu("小明", 2, "男", 94.0f, 92.5f, 85.0f);
Stu stu3 = Stu("小军", 3, "男", 85.0f, 92.5f, 85.0f);
map<int, Stu> Stu_map;
Stu_map.insert(make_pair(1, stu1));
Stu_map.insert(make_pair(2, stu2));
Stu_map.insert(make_pair(3, stu3));
sortMap(Stu_map);
}
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class B {
int n;
public:
B(int t = 0) :n(t) {}
friend bool operator<(const B& lh, const B& rh);
};
bool operator<(const B& lh, const B& rh) {
return lh.n < rh.n;
}
int main()
{
map<B,string> m;
m.insert(make_pair(B(3), "hello"));
m.insert(make_pair(B(1), "foo"));
}
给你一个简单例子,参考一下
mark一下