JAVA学习上的疑问,多线程
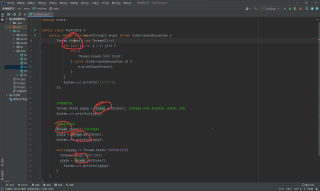
请问第一个thread和下面四个thread的区别是不是:下面四个thread是不是主线程里面执行的
对的,理解没问题
你好,上面的一个和下面的都是同一个实例对象thread,其中getState()方法会返回当前线程对象的状态,并且你的代码中,都是写在的main方法内部的。
可能你有很多理解会有问题,我用编译器的自动扫描给你做演示好了。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//1//");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
当我将它实例的对象名称修改为a时,接下来将会报错
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread a = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//1//");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
那由此我们也就知道了下面的四个只是调用了thread对象的getState()方法
你好,上面的一个和下面的都是同一个实例对象thread,其中getState()方法会返回当前线程对象的状态,并且你的代码中,都是写在的main方法内部的。
可能你有很多理解会有问题,我用编译器的自动扫描给你做演示好了。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//1//");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
当我将它实例的对象名称修改为a时,接下来将会报错
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread a = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//1//");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
那由此我们也就知道了下面的四个只是调用了thread对象的getState()方法