#include <iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include<vector>
#include<chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace chrono;
void lcsLength(string x, string y, vector< vector<int>>& c, vector< vector<char>>& b)
{
int m = x.size();
int n = y.size();
/*c.push_back(m);
b.push_back(n);*/
c.resize(m + 10);
b.resize(m + 10);
for (int i = 0; i < c.size(); ++i)
c[i].resize(n + 3);
for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); ++i)
b[i].resize(n + 10);
for (size_t i = 0; i <= c.size() - 1; i++) {
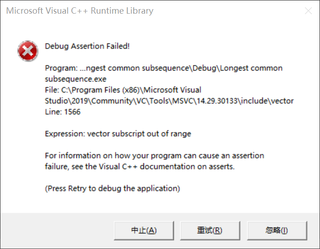
if (i >= c.size() || i < 0) {
cout << "vetcor下标越界" << endl; break;
}
c[i].resize(n + 10);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i <= b.size() - 1; i++) {
if (i >= b.size() || i < 0) {
cout << "vetcor下标越界" << endl; break;
}
b[i].resize(n + 10);
}
for (size_t i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (size_t j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]) {
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
b[i][j] = 'c';
}
else if (c[i - 1][j] >= c[i][j - 1]) {
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j];
b[i][j] = 'u';
}
else {
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1];
b[i][j] = 'l';
}
}
}
}
void print_lcs(vector< vector<char>>& b, string x, size_t i, size_t j)
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
return;
if (b[i][j] == 'c') {
print_lcs(b, x, i - 1, j - 1);
cout <<x[i - 1];
}
else if (b[i][j] == 'u')
print_lcs(b, x, i - 1, j);
else
print_lcs(b, x, i, j - 1);
}
string gengerString(int n,string str) {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //产生随机化种子
/*printf("生成%d个字符的字符串\n", n);*/
/*std::string str = "";*/
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int flag;
flag = rand() % 2; //随机使flag为1或0,为1就是大写,为0就是小写
if (flag == 1) //如果flag=1
str += rand() % ('Z' - 'A' + 1) + 'A'; //追加大写字母的ascii码
else
str += rand() % ('z' - 'a' + 1) + 'a'; //如果flag=0,追加为小写字母的ascii码
}
cout << str << endl; //将字符串输出
return str;
}
int main()
{
int len1,len2 ;/*= "ABCBDAB"*/
string x,y ;/*= "BDCABA"*/
cout << "请输入x的长度len1:" << endl;
cin >> len1;
gengerString(len1,x);
cout << "请输入y的长度len2:" << endl;
cin >> len2;
gengerString(len2,y);
vector< vector<int>> c;
vector< vector<char>> b;
auto t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
lcsLength(x, y, c, b);
print_lcs(b, x, len1, len2);
cout << endl;
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto d = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(t1 - t0);
cout << "time cost:" << d.count() << "ns" << endl;
cout << endl << "长度为:" << c[len1][len2] << endl;
}