为什么下面的代码跑出的结果不对

#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float e(float x);
float x;
cout << "请输入x" << endl;
cin >> x;
float sinh;
sinh = (e(x) - e(-x)) / 2;
cout << sinh;
return 0;
}
float e(float x)
{
int fac(int x);
float s;
float m;
int n;
s = 1;
for (n = 1; n <= 1000; n++)
{
m = x / fac(n);
s = s + m;
x *= x;
}
return s;
}
int fac(int x)
{ int s = 1;
if (x == 0)
return s;
else
{
for (; x >= 1; x--)
s *= x;
return s;
}
}
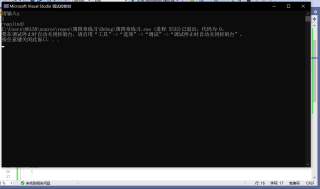
中间溢出了。int只能存下12的阶乘,double只能存下170的阶乘。换个算法吧。
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
double factorial(int n) {
double ret = 1;
bool int_fl = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ret *= i;
if (ret > std::numeric_limits<int>::max() && !int_fl) {
std::cout << "max factorial that int can store: " << i-1 << "\n";
int_fl = true;
}
if (ret > std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) {
std::cout << "max factorial that double can store: " << i-1 << "\n";
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
int imax = std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
std::cout << imax << '\n';
double dmax = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
std::cout << dmax << '\n';
std::cout << factorial(1000) << '\n';
return 0;
}
结果:
2147483647
1.79769e+308
max factorial that int can store: 12
max factorial that double can store: 170
inf
PS D:\src\cpp_back_to_basics> py -c 'import math; print(math.factorial(13)>2147483647)'
True
PS D:\src\cpp_back_to_basics> py -c 'import math; print(math.factorial(171)>1.79769e+308)'
True