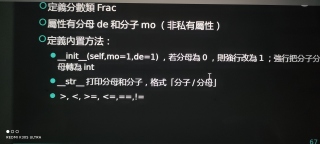
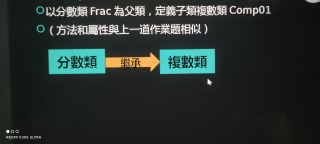
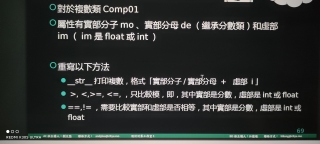
一道定义题,定义分数类Frac
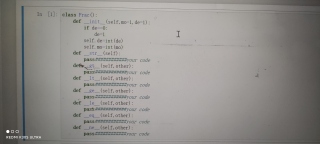
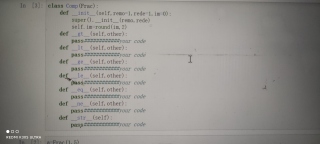
class Frac():
def __init__(self,mo=1,de=1):
if de == 0:
de = 1
self.de = int(de)
self.mo = int(mo)
def __str__(self):
return "[{}/{}]".format(self.mo,self.de)
def __gt__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError("> 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de > (other.mo / other.de)
def __lt__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError("< 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de < (other.mo / other.de)
def __ge__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError(">= 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de >= (other.mo / other.de)
def __le__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError("<= 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de <= (other.mo / other.de)
def __eq__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError("== 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de == (other.mo / other.de)
def __ne__(self,other):
if not isinstance(other,Frac):
raise TypeError("!= 的运算对象必须是Frac")
return self.mo / self.de != (other.mo / other.de)
f1 = Frac(1,2)
f2 = Frac(3,1)
print(f1,f2)
print(f1 > f2)
print(f1 < f2)
print(f1 >= f2)
print(f1 <= f2)
print(f1 == f2)
print(f1 != f2)
结果:
