这个判断左右括号输入是否正确的程序哪里错了
比如【】正确,【{】}错误
每次无论输入啥都是输出“bye”是为啥。
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Node;
typedef struct Node *Stack;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
bool IsEmpty(Stack);
void Push(Stack S,char value);
void Pop(Stack S);
int Top(Stack S);
Stack CreateStack(); //“格式化”一个栈
void MakeEmpty(Stack S);
struct Node
{
char ch;
PtrToNode next;
};
#include "Stack-link.h"
bool IsEmpty(Stack S){
return S->next == NULL;
}
void Push(Stack S,char value){
PtrToNode new_cell;
new_cell = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (IsEmpty(S))
{
S->next = new_cell;
new_cell->next = NULL;
new_cell->ch = value;
}
else
{
new_cell->next = S->next;
S->next = new_cell;
new_cell->ch = value;
}
}
void Pop(Stack S){
PtrToNode temp;
if (IsEmpty(S))
printf("Empty stack!!!");
else
{
temp = S->next;
S->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
int Top(Stack S){
if (!IsEmpty(S))
return S->next->ch;
printf("Empty stack!!!");
return 0;
}
Stack CreateStack(){
Stack S;
S=malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
S->ch = 'h';
if (S == NULL)
printf("Out of space!!!");
else
S->next = NULL;
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
} //初始化一个栈
void MakeEmpty(Stack S){
if (S == NULL)
printf("You must creat a stack first!");
else
{
while (!IsEmpty(S))
{
Pop(S);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ch;
bool judge = true;
Stack s = CreateStack();
fputs("Please enter the test line:",stdout);
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(')
Push(s,ch);
else
{
switch (ch)
{
case '}':
if (Top(s) != '{') judge = false;
break;
case ']':
if (Top(s) != '(') judge = false;
break;
case ')':
if (Top(s) != '(') judge = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (judge != false) Pop(s);
}
if (judge == false) fputs("false!",stdout); break;
}
fputs("bye!",stdout);
return 0;
}
先上结果:
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Node;
typedef struct Node *Stack;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
bool IsEmpty(Stack);
void Push(Stack S,char value);
void Pop(Stack S);
int Top(Stack S);
Stack CreateStack(); //“格式化”一个栈
void MakeEmpty(Stack S);
struct Node
{
char ch;
PtrToNode next;
};
bool IsEmpty(Stack S){
return S->next == NULL;
}
void Push(Stack S,char value){
PtrToNode new_cell;
new_cell = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (IsEmpty(S))
{
S->next = new_cell;
new_cell->next = NULL;
new_cell->ch = value;
}
else
{
new_cell->next = S->next;
S->next = new_cell;
new_cell->ch = value;
}
}
void Pop(Stack S){
PtrToNode temp;
if (IsEmpty(S))
printf("Empty stack!!!");
else
{
temp = S->next;
S->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
int Top(Stack S){
if (!IsEmpty(S))
return S->next->ch;
return 0;
}
Stack CreateStack(){
Stack S;
S=(Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
S->ch = 'h';
if (S == NULL)
printf("Out of space!!!");
else
S->next = NULL;
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
} //初始化一个栈
void MakeEmpty(Stack S){
if (S == NULL)
printf("You must creat a stack first!");
else
{
while (!IsEmpty(S))
{
Pop(S);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int ch;
bool judge = true;
Stack s = CreateStack();
fputs("Please enter the test line:",stdout);
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF && ch != '\n')
{
if (ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(')
Push(s,ch);
else
{
switch (ch)
{
case '}':
if (Top(s) != '{') judge = false;
break;
case ']':
if (Top(s) != '[') judge = false;
break;
case ')':
if (Top(s) != '(') judge = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (judge != false)
{
Pop(s);
fputs("Yes! ",stdout);
}
}
if (judge == false)
{
fputs("false! ",stdout);
while (!IsEmpty(s))
{
Pop(s);
}
judge = true;
}
}
fputs("\nbye!",stdout);
return 0;
}
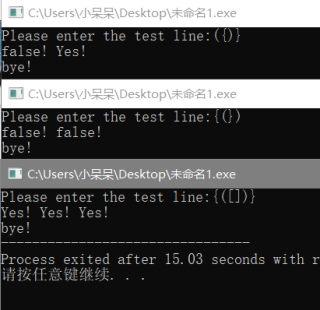
首先 fputs 我没用过我看你用的这我就用你的这改了一下,你这个代码只输出bye是因为你的循环直接就跳出来了,你看你这一行 if (judge == false) fputs("false!",stdout); break; 你这个代码执行一遍就直接break了,后面就没法跑,所以就直接bye了,这是一个逻辑问题所以建议以后还是 if 后面的语句都写到大括号里,不然就容易犯这种错误,这也直接导致我看了半天没看出来是这问题,哈哈哈,以后小心点哦
还有一个就是主函数里面的ch变量最好是int类型的,你想想(ch = getchar()) != EOF这句话里EOF等于-1,那char类型哪里来的-1,所以要改成int类型,这里牵扯到一个字符集的问题,就不细说了,这种方法你再输入的时候是停不下来的需要你手动输入EOF,windows下输入方法是ctrl+z输入,当然你要不想专门输入一个EOF你可以像我一样加个条件
还有一个就是在你的createstack函数里面,我发现你这么写了,我有点没搞懂
S=(Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
S->ch = 'h';
if (S == NULL)
你看你先给s分配空间,然后又给s->赋值,那只有分配好了才能赋值么,所以我觉得你的s==null应该写到赋值的前面去
以上就是我个人观点,如果你还有什么问题可以私信我
截图发一下
fputs("bye!",stdout);
这个条件始终成立,所以会输出bye,然后根据判断条件及常识,符号嵌套要成对出现,能[{}],不能({)},希望对你有帮助
}