C语言为什么输出出栈的字符串时会输出乱码如0xz,是因为没有正确分配内存吗?希望大佬们解答
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
struct LLNode
{
char ID[5];
struct LLNode *next;
};
struct LLNode * createNode(char val[5])
{
struct LLNode *temp;
temp=(struct LLNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct LLNode));
temp->next=NULL;
strcpy(temp->ID, val);
return temp;
};
void push(char* val, struct LLNode *head)
{
struct LLNode *temp;
temp = createNode(val);
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
}
char* pop(struct LLNode *head)
{
struct LLNode *temp;
char *val = (char *)malloc(5*sizeof(char));
strcpy(head->next->ID, val);
temp = head->next;
head->next = head->next->next;
free(temp);
return val;
}
char nothing(struct LLNode *head, struct LLNode *tail)
{
if(head->next == NULL)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char* value = (char *)malloc(5*sizeof(char));
struct LLNode *head = NULL;
struct LLNode *tail = NULL;
head = createNode("");
tail = createNode("");
head->next = tail;
printf("head->ID = %s\n", head->ID);
push ("C201", head);
printf("head->next->ID = %s\n",head->next->ID) ;
push ("C202", head);
printf("head->next->ID = %s\n",head->next->ID) ;
push ("C203", head);
printf("head->next->ID = %s\n",head->next->ID) ;
push ("C204", head);
printf("head->next->ID = %s\n",head->next->ID) ;
push ("C205", head);
printf("head->next->ID = %s\n",head->next->ID) ;
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
value = (char *)malloc(5*sizeof(char));
strcpy(value, pop(head));
printf("The value pop = %s\n", value);
printf("head->next->ID= %s\n",head->next->ID);
free(value);
}
if (nothing(head,tail))
printf("The stack is empty");
printf("Remaining IDs:");
struct LLNode *curr = head;
while (curr)
{
printf("%s ",curr->ID);
curr = curr->next;
}
return 0;
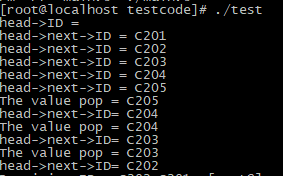
}输出:
char* pop(struct LLNode *head)
{
struct LLNode *temp;
char *val = (char *)malloc(5*sizeof(char));
//strcpy(head->next->ID, val);
strcpy( val,head->next->ID);
temp = head->next;
head->next = head->next->next;
free(temp);
return val;
}拷贝反了。
strcpy(head->next->ID,val);
改为
strcpy( val,head->next->ID);
试试
char* pop()函数中,定义了val,也申请了内存,但是整个函数一直没使用这个变量,只在最后return val,它里面是什么东西谁都不知道,在后面strcpy中,第二个参数是pop()函数的返回值,所以复制的内容谁也不知道是什么
您好,我是有问必答小助手,您的问题已经有小伙伴解答了,您看下是否解决,可以追评进行沟通哦~
如果有您比较满意的答案 / 帮您提供解决思路的答案,可以点击【采纳】按钮,给回答的小伙伴一些鼓励哦~~
ps:问答VIP仅需29元,即可享受5次/月 有问必答服务,了解详情>>>https://vip.csdn.net/askvip?utm_source=1146287632
