Java 带字母和数字的排序算法
按照作业的要求写出来的代码,但是总感觉过于麻烦了。因为规定是只能import java.io.*; 所以很多东西比如ArrayList都用不了。之前想用node写,但是最后给我自己绕晕了,就还是用了普通的array。有没有大神能帮忙看看哪里能精简一下?感谢
import java.io.*;
public class Sorter{
public static String InputFile;
public static String OutputFile;
private String[] list;
//constructor
public Sorter() {
list=new String[100];
}
//sort the numbers in ascending order, and return a string array
public String[] sortNumbs(double[] arr){
if(arr != null && arr.length > 1){
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
boolean flag = true;
for(int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1 ; j++){
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
double temp;
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag){
break;
}
}
}
//convert the ordered double array to string
String[] ascending=new String [arr.length];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
ascending[i]=String.valueOf(arr[i]);
}
return ascending;
}
//judge if the string is a natural number
public boolean isNumberic(String str) {
for(int i=str.length();--i>=0;) {
if(str.charAt(i)<48||str.charAt(i)>57)
return false;
}
return true;
}
//clear all empty elements in a double array
public static double[] replaceNull(double[] str){
int length=str.length;
//count the number of the 0 and calculate the length of the new array;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++) {
if(0==str[i]) {
length--;
}
}
double[] arr=new double[length];
int k=0,j=0;
while(k<str.length&&j<arr.length) {
if(0!=str[k]) {
arr[j]=str[k];
k++;
j++;
}
else if(0==str[k]) {
k++;
}
}
return arr;
}
//clear all empty elements in a string array
public static String[] replaceNull(String[] str){
int length=str.length;
//count the number of the null and calculate the length of the new array;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++) {
if(null==str[i]) {
length--;
}
}
String[] arr=new String[length];
int k=0,j=0;
while(k<str.length&&j<arr.length) {
if(null!=str[k]) {
arr[j]=str[k];
k++;
j++;
}
else if(null==str[k]) {
k++;
}
}
return arr;
}
//write the string in the output file
public static void WriteOutput(String out) {
try {
File file =new File(OutputFile);
//if the fill doesn't exist, create a new one
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
//append the new element in the file
FileWriter fileWritter = new FileWriter(file.getName(),true);
BufferedWriter bufferWritter = new BufferedWriter(fileWritter);
bufferWritter.write(out);
bufferWritter.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Sorter sort=new Sorter();
InputFile=args[0];
OutputFile=args[1];
//read the input file
File file=new File(InputFile);
FileReader filereader=new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(filereader);
double[] dou=new double[100];
try {
String line = reader.readLine();
int i=0;
//judge it's the end or not
while (line!= null) {
//if this is the blank line, throw an error
if(line.equals("")) {
WriteOutput("Input error.");
throw new Exception("Input error.");
}
//avoid 0 be cleared when the replaceNull used
if(line.equals("0")) {
dou[i]=0.1;
i++;
}
//convert all the natural numbers to the double
else if(sort.isNumberic(line)&&!line.equals("0")) {
dou[i]=Double.parseDouble(line);
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Do, use 0.5 to represent Do because 0<Do<1
else if(line.equals("Do")) {
dou[i]=0.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is &, use 3.6 to represent & because 3<@<&<4
else if(line.equals("&")) {
dou[i]=3.6;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is @, use 3.4 to represent @ because 3<@<&<4
else if(line.equals("@")) {
dou[i]=3.4;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Fa, use 15.5 to represent Fa because 15<Fa<16
else if(line.equals("Fa")) {
dou[i]=15.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is $, use 20.5 to represent $ because 20<$<21
else if(line.equals("$")) {
dou[i]=20.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Asymbolwithareallylongname, use 55.5 to represent Asymbolwithareallylongname
//because 55<Asymbolwithareallylongname<56
else if(line.equals("Asymbolwithareallylongname")) {
dou[i]=55.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Re, use 100.5 to represent Re because 100<Re<101
else if(line.equals("Re")) {
dou[i]=100.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is One, use 103.3 to represent One because 103<One<Two<Three<104
else if(line.equals("One")) {
dou[i]=103.3;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is OTwo, use 103.6 to represent Two because 103<One<Two<Three<104
else if(line.equals("Two")) {
dou[i]=103.6;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Three, use 103.9 to represent Three because 103<One<Two<Three<104
else if(line.equals("Three")) {
dou[i]=103.9;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is Mi, use 1000.5 to represent Mi because 1000<One<1001
else if(line.equals("Mi")) {
dou[i]=1000.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//if input is %, use 1005000.5 to represent One because 1005000<%<1005001
else if(line.equals("%")) {
dou[i]=1005000.5;
//System.out.println(dou[i]);
i++;
}
//other inputs will cause error
else {
WriteOutput("Input error.");
throw new Exception("Input error.");
}
line = reader.readLine();
}
//if there are 666s, change them to one @
int num6=0;
for(int k=0;k<dou.length;k++) {
if(dou[k]==666) {
if(num6==0) {
dou[k]=3.4;
num6++;
}
else {
dou[k]=0;
num6++;
}
}
}
dou=replaceNull(dou);
//sort the double array and convert them to string
String[] str=new String[dou.length];
str=sort.sortNumbs(dou);
//change all double numbers which is natural numbers originally back to the integer
for(int j=0;j<str.length;j++) {
for(int k=0;k<str[j].length()-1;k++) {
if(str[j].charAt(k)=='.'&&str[j].charAt(k+1)=='0') {
str[j]=str[j].substring(0,k);
}
}
}
//change all symbols back
for(int j=0;j<str.length;j++) {
if(str[j].equals("0.5")) {
str[j]="Do";
}
else if(str[j].equals("3.6")) {
str[j]="&";
}
else if(str[j].equals("3.4")) {
str[j]="@";
}
else if(str[j].equals("15.5")) {
str[j]="Fa";
}
else if(str[j].equals("20.5")) {
str[j]="$";
}
else if(str[j].equals("55.5")) {
str[j]="Asymbolwithareallylongname";
}
else if(str[j].equals("100.5")) {
str[j]="Re";
}
else if(str[j].equals("103.3")) {
str[j]="One";
}
else if(str[j].equals("103.6")) {
str[j]="Two";
}
else if(str[j].equals("103.9")) {
str[j]="Three";
}
else if(str[j].equals("1000.5")) {
str[j]="Mi";
}
else if(str[j].equals("1005000.5")) {
str[j]="%";
}
}
//if there is 666, the array will be ascending
if(num6>0) {
for(int k=0;k<str.length;k++) {
sort.list[k]=str[k];
}
}
//if there is no 666, the result list should be sorted in descending order;
else {
int reverse=str.length;
for(int k=0;k<str.length;k++) {
sort.list[reverse-1]=str[k];
reverse--;
}
}
sort.list=replaceNull(sort.list);
//if there is 0 originally, change it back because it was changed to 0.1 before
for(int j=0;j<sort.list.length;j++) {
if(sort.list[j].equals("0.1")) {
sort.list[j]="0";
}
}
for(int j=0;j<sort.list.length-1;j++) {
WriteOutput(sort.list[j]+"\n");
//System.out.println(sort.list[j]);
}
WriteOutput(sort.list[sort.list.length-1]);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//close the file
finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
没有了~~~
看不懂你这个题目,没有样例吗?或者你再给我描述一下把
建议题主把题目完整链接放出来。
精度要求不高的话,都转换成float就行了,然后自己写个简单的排序算法即可。计算数组长度后使用普通array就行。
这样写应该可以增加可阅读性
import java.io.*;
/* 使用自己写的排序方式和获取字符串方式可以不需要下面两个工具包 */
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("读取文件路径");
fw = new FileWriter("输出文件路径");
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
/*使用自己的方式得到数字和字母的对象*/
Stream<String> lines = br.lines();
Object[] strs = lines.toArray();
NumberAndWord[] naw = new NumberAndWord[strs.length];
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
naw[i] = new NumberAndWord(strs[i].toString());
}
/*使用自己的排序方式*/
Arrays.sort(naw, ((o1, o2) -> {
if (o1.getNumber() > o2.getNumber()) return 0;
return -1;
}));
for (NumberAndWord numberAndWord : naw) {
fw.write(numberAndWord.getWord() + "\n");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
br.close();
fr.close();
bw.close();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class NumberAndWord {
private String word;
private Double number;
public NumberAndWord (String word) {
this.word = word;
setNumber(word);
}
private void setNumber (String word) {
try {
this.number = new Double(word);
}catch (NumberFormatException e) {
switch (word) {
case "Do" :
this.number = 0.5;
return;
case "&" :
this.number = 3.6;
return;
case "@" :
this.number = 3.4;
return;
case "Fa" :
this.number = 15.5;
return;
case "$" :
this.number = 20.5;
return;
case "Asymbolwithareallylongname" :
this.number = 55.5;
return;
case "Re" :
this.number = 100.5;
return;
case "One" :
this.number = 103.3;
return;
case "Two" :
this.number = 103.6;
return;
case "Three" :
this.number = 103.9;
return;
case "Mi" :
this.number = 1000.5;
return;
case "%" :
this.number = 1005000.5;
return;
}
}
}
public String getWord() {
return word;
}
public Double getNumber() {
return number;
}
}
你可以试试换算成ascii码 然后再排序
太长,懒得看,既然只能import java.io.* 那手动的使用全类名不就OK了吗 `java.util.ArrayList arrayList = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
`
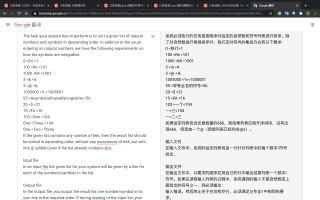
 大概就是要读取一个这样的文件,然后按照降序排好,输出
大概就是要读取一个这样的文件,然后按照降序排好,输出
刚才更新了一下我最后的代码,经过了几个testcase的测试,都成功了。但是实在是太长了,我自己都不想看T_T
我更新了一下代码。看了大家的评论之后换了一个思路,感觉好了很多。但还是有点麻烦,看看有没有什么更好的办法。当然这份代码我交作业已经完全够了。剩下的就是大家自由讨论讨论了。谢谢各位啦